Saran Division and Its Districts
Saran Division is one of the administrative divisions of Bihar, known for its historical significance, fertile agricultural land, and cultural heritage. It is located in the northwestern part of the state, and the division derives its name from the ancient Saran region, which is mentioned in various historical and mythological texts. The division’s administrative center is located in Chhapra. As of 2005, the division is made up of the districts of Saran (also known as Chhapra District), Siwan, and Gopalganj. This division is the only one in Bihar where every district shares a border with Uttar Pradesh.
In ancient times, Modern Saran Division was part of KOSALA country. Saran Division’s history is inextricably linked to Kosala’s history, which included areas beyond the Saran Division’s current boundaries. The kingdom of Kosala was bordered by Nepal on the north, Gandak on the east, the river Sarpika (sai) in the south, and Panchala on the west. Modern day Faizabad, Gonda, Basti, Gorkhapur, Deoria, and Saran in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar made up the Kosala.
According to the district’s historical background as given in the ‘Ain-E-Akbari’, Saran is one of the six Sarkars (Revenue Divisions) that make up the province of Bihar. There were eight Sarkars, including Saran and Champaran, when Diwani was granted to the East India Company in 1765. Later on, these two were merged to create the single unit known as Saran. When the Commissioner’s Divisions were established in 1829, Saran (along with Champaran) was incorporated into the Patna Division. When Champaran was established as a distinct district in 1866, it was split off from Champaran and when the Tirhut Division was established in 1908, Saran became a part of it.
Overview of Districts
At this point, the district was divided into three subdivisions: Saran District, Siwan District, and Gopalganj District. Each of the former Saran district’s subdivisions became a separate district and a part of the Saran Division in 1981.
The origin of the name SARAN has been the subject of several theories. According to General Cunningham, Saran was formerly known as SARAN, or asylum, which was the name of a stupa (Pillar) constructed by Emperor Ashoka. On the other hand, according to a different theory, the district’s name, SARAN, is derived from SARANGA-ARANAYA, or the deer forest, which was well-known in prehistoric times for its vast tracts of forest and deer. Perhaps the earliest reliable historical record or fact about this district dates back to 898 A.D., when it was suggested that a copper plate issued during King Mahendra Paldeva’s reign had been supplied by the village of Dighwara Dubauli in Saran.
Hathwa Raj was a Bhumihar zamindari in Bihar’s Saran Division. It had 1,365 villages, over 391,000 residents, and generated nearly a million rupees in rental income annually.
Saran District
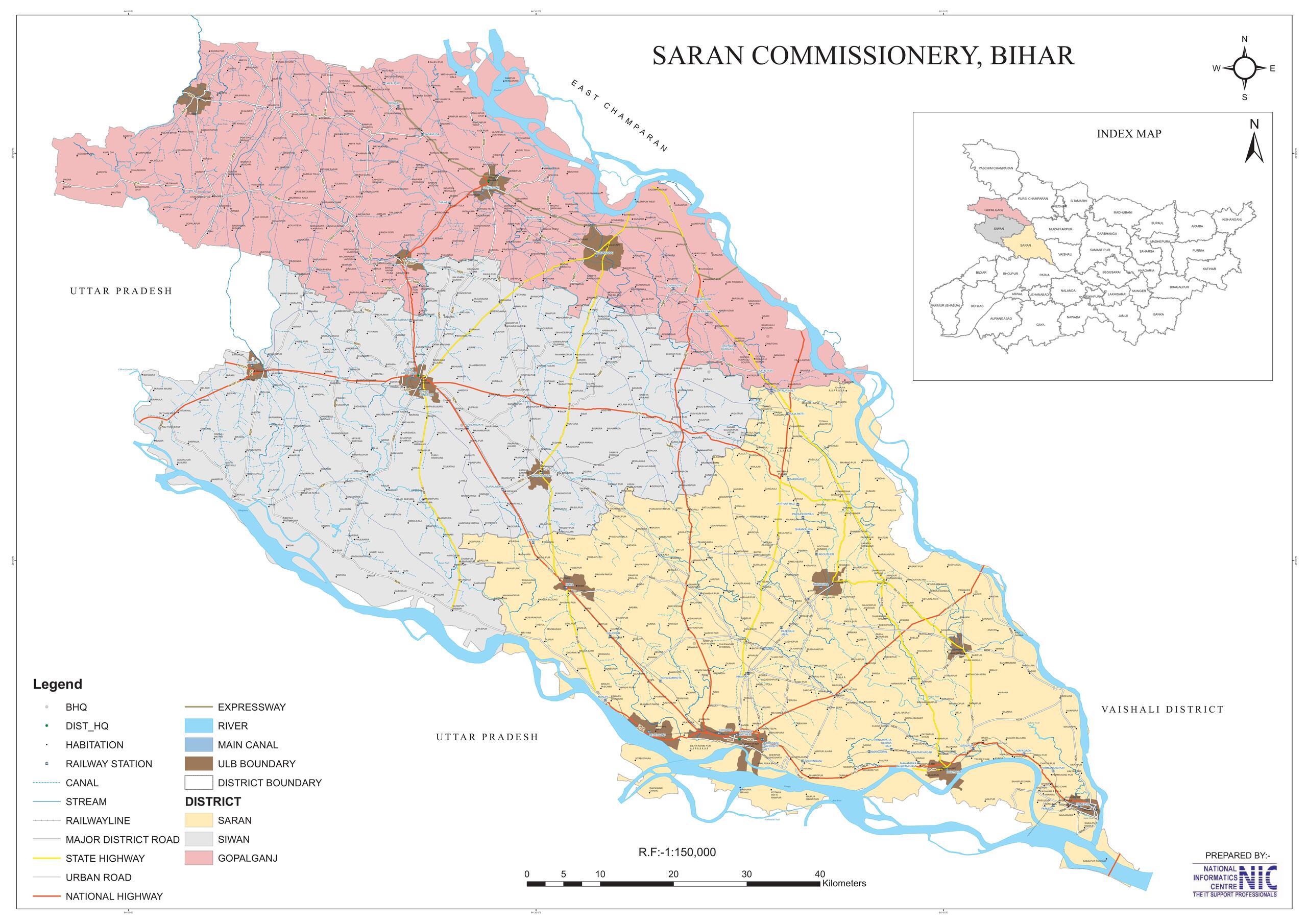
Spanning an area of 2,641 square kilometers (1,020 square miles), Saran district is located in the southern part of North Bihar, lies between 25°36′ to 26°13′ North latitude and 84°24′ to 85°15′ East longitude. The Ganges forms the district’s southern boundary, with Patna district and Bhojpur district beyond it. In addition, to the north of Saran are the Siwan district and Gopalganj district. The Gandak divides the Muzaffarpur district and Vaishali district in the east. Meanwhile, to the west of Saran are the Ballia district of Uttar Pradesh, with the Ghaghra serving as a natural boundary between the two districts. The district’s administrative headquarters is located at Chhapra town.
Siwan District
Spanning an area of 2,219 square kilometers (857 square miles), Siwan lies at 25.58º to 26.23º North latitude and 84.10º to 84.47º East longitude, and shares borders with Saran district to the East, Gopalganj district to the North, and two districts of Uttar Pradesh, Deoria and Balia, to the west and south, respectively. The district’s administrative headquarters is located at Siwan town. Originally, Siwan was a part of Saran District, which was formerly a part of Kosala Kingdom. In 1972, the area was officially recognized as a distinct district.
Gopalganj District
Spanning an area of 2,033 square kilometers (785 square miles), Gopalganj is an administrative district in the northwestern part of Bihar state, lies between 83.54°E to 85.56°E longitude and 26.12°N to 26.39°N latitude, and shares borders with West Champaran district to the North, Siwan district to the South, East Champaran district and River Gandak to the East, Muzaffarpur district and Saran district to the Southeast, Deoria district of Uttar Pradesh to the West, and Kushinagar district of Uttar Pradesh to the Northwest. The district administrative headquarters is located at Gopalganj town.
Key Facts About Saran Division
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Established: 1908
- Area: 6,893 km2 (2,661 sq mi)
- Coordinates: 25.7848°N 84.7274°E
- Division Headquarters: Chhapra
- Divisional Commissioner: Narmdeshwar Lal
- Number of Districts: 3 (Saran, Siwan, Gopalganj)
- Subdivisions: 7 (Sadar, Marhaura, Sonepur, Siwan Sadar, Maharajganj, Gopalganj, Hathua)
- Number of Blocks/Circles: 52
- Gopalganj – Baikunthpur, Barauli, Gopalganj, Kuchaikote, Manjha, Thawe, Sidhwaliya, Bhorey, Hathua, Kateya, Panchdewari, Phulwariya, Uchkagaon and Vijayipur.
- Siwan – Siwan, Mairwa, Darauli, Guthani, Hussainganj, Andar, Raghunathpur, Siswan, Barharia, Pachrukhi, Maharajganj, Duraondha, Goreakothi, Basantpur, Bhagwanpur and Lakri Nabiganj.
- Saran – Amnour, Baniyapur, Chhapra, Dariyapur, Dighwara, Ekma, Garkha, Ishupur, Jalalpur, Lahladpur, Maker, Manjhi, Marhaura, Mashrakh, Nagra, Panapur, Parsa, Revelganj, Sonpur and Taraiya.
- Gram Panchyat: 837
- Villages: 4903 (approx)
- Population (2011): 9,819,311
- Rivers: Burhi Gandak, Gandaki, Ganges
- Geography:
- Bounded by rivers like Ganga, Gandak, and Ghaghara, making the land fertile.
- Located in western Bihar, with good connectivity to the rest of the state.
- Transports:
- NH-727, NH-531, NH-331, NH-722
- Digha–Sonpur Bridge
- Barauni–Gorakhpur lines
- Raxaul and Jainagar lines
- Arrah–Chhapra Bridge
- Lok Sabha constituencies: 4 (Gopalganj, Maharajganj, Saran, Siwan)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 24
- Ekma, Manjhi, Baniapur, Taraiya, Marhaura, Chapra, Garkha, Amnour, Parsa, Sonpur
- Siwan, Jiradei, Darauli, Raghunathpur, Daraundha, Barharia, Goriyakothi, Maharajganj
- Baikunthpur, Barauli, Gopalganj, Kuchaikote, Bhore, Hathua
- Community development blocks: Sonpur, Dariapur, Kuchaikote, Ziradei
- Official Website: sarandivision.bih.nic.in
Districts of Saran Division: An Overview
Saran Division comprises three districts:
1. Saran (Chhapra) District:
- Area: 2,641 km2 (1,020 sq mi)
- Population (2011): 3,951,862
- Literacy Rate: 68.57%
- District Headquarters: Chhapra
- Gram Panchayats: 310
- Villages: 1807
- No. of Blocks: 20
- Police Station: 30
- No. of Subdivision: 3 (Sadar, Marhaura, Sonpur)
- Municipal corporation: 1 (Chhapra)
- Nagar Panchayats: 7 (Dighwara, Manjhi, Mashrakh, Rivilganj, Sonpur, Parsa Bazar, Ekma, Kopa, Marhaura)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 10
- Ekma, Manjhi, Baniapur, Taraiya, Marhaura, Chapra, Garkha, Amnour, Parsa, Sonpur
- Lok Sabha constituency: 2 (Saran, Maharajganj)
- Key Features:
- Known for the Sonepur Cattle Fair, one of Asia’s largest animal fairs.
- Important cultural heritage, with links to ancient Indian history.
- Tourist attractions include Aami Mandir and the Dhorh Ashram.
- The district is a key producer of rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
- Significance: Central to the division, with cultural and economic importance.
- Official Website: saran.nic.in
2. Siwan District:
- Area: 2,219 km2 (857 sq mi)
- Population (2011): 3,330,465
- Literacy Rate: 72.00%
- District Headquarters: Siwan town.
- Gram Panchayats: 293
- Villages: 1530
- No. of Subdivision: 2 (Maharajganj, Siwan Sadar)
- No. of Blocks: 19
- Police Station: 28
- Nagar Parishad: 1 (Siwan)
- Nagar Panchayats: 8 (Maharajganj, Mairwa, Andar, Barharia, Basantpur, Gopalpur, Guthani, Hasanpura
- Lok Sabha constituency: 2 (Siwan, Maharajganj)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 8
- Siwan, Jiradei, Darauli, Raghunathpur, Daraundha, Barharia, Goriyakothi, Maharajganj
- Key Features:
- Birthplace of Dr. Rajendra Prasad, India’s first President.
- Historically known for its contributions to the Indian independence movement.
- A primarily agrarian economy producing paddy, maize, and pulses.
- Significance: A district of historical and political importance in Bihar.
- Official Website: siwan.nic.in
3. Gopalganj District:
- Area: 2,033 km2 (785 sq mi)
- Population (2011): 2,562,012
- Literacy Rate: 65.47%
- District Headquarters: Gopalganj town
- Gram Panchayats: 234
- Villages: 1566
- No. of Subdivision: 2 (Hathua, Gopalganj)
- No. of Blocks: 14
- Police Station: 22
- Nagar Parishad: 1 (Gopalganj)
- Nagar Panchayat: 3 (Barauli, Kateya, Mirganj)
- Lok Sabha constituency: 1 (Gopalganj)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 6
- Baikunthpur, Barauli, Gopalganj, Kuchaikote, Bhore, Hathua
- Key Features:
- Fertile agricultural land, producing sugarcane, paddy, and wheat.
- Known for its lush greenery and proximity to rivers.
- Cultural importance due to temples and traditional festivals.
- Significance: A district with an agricultural backbone and cultural richness.
- Official Website: gopalganj.nic.in
Each district contributes uniquely to the division’s economic, cultural, and political landscape.
Geographical Overview
- Location: Saran Division is located in the northwestern part of Bihar and is bordered by the Ganga and Ghaghara rivers, which define its geography and economy.
- Rivers:
- The Ganga River forms its southern boundary and plays a crucial role in agriculture, transportation, and livelihood.
- The Ghaghara River flows along its western side, merging with the Ganga and influencing the division’s floodplain ecology.
- Topography: The division is characterized by alluvial plains, making it one of the most fertile regions in Bihar.
- Climate: The division experiences a humid subtropical climate with hot summers, monsoon rains, and cool winters.
Historical Significance
- Ancient History: The Saran region has been a prominent part of Indian history since ancient times. It was part of the Kosala Kingdom during the Vedic period and later integrated into the Magadha Empire.
- Religious Importance:
- It is associated with the Mahabharata, with references to various events occurring in the region.
- The region is also tied to Buddhism and Jainism, with remnants of stupas and inscriptions found in certain areas.
- Medieval Period: During the medieval period, the region saw the rise of various local chieftains and was later under the control of the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughals.
- Colonial Period: Saran gained importance as an administrative and trade center during British rule. Moreover, it was a key region in the Indigo Movement and played an active role in the Indian independence struggle, with leaders like Dr. Rajendra Prasad, the first President of India, being associated with the division.
Cultural Significance
- Languages: The primary languages spoken in the division include Bhojpuri, Hindi, and Urdu.
- Festivals:
- Chhath Puja is the most significant festival, celebrated with great devotion on the banks of rivers.
- Other popular festivals include Holi, Diwali, Durga Puja, and Eid.
- Folk Traditions: The region is rich in Bhojpuri folk songs, dances, and literature. Bhojpuri cinema has also contributed to popularizing the cultural identity of the region.
- Cuisine: The division is known for its Bhojpuri cuisine, with dishes like litti chokha, dal puri, thekua, and bhuja (puffed rice) being popular.
Economy
- Agriculture:
- The division is a primarily agrarian economy, with a focus on crops like rice, wheat, pulses, sugarcane, and vegetables.
- The fertile soil and irrigation from rivers make it one of the most productive agricultural regions in Bihar.
- Dairy and Livestock: The division has a thriving dairy industry, with many families engaged in milk production and livestock farming.
- Trade and Commerce:
- Chhapra serves as a regional trade hub, with markets for agricultural produce, textiles, and consumer goods.
- Small-scale industries, such as sugar mills and rice mills, are prevalent in the division.
- Challenges: Despite its agricultural prominence, the division faces challenges like seasonal flooding, unemployment, and lack of industrial development, leading to outmigration for jobs.
Education and Institutions
- Key Institutions:
- Jai Prakash University (Chhapra): A leading university in the division, offering higher education in various disciplines.
- Rajendra College (Chhapra): One of the oldest and most prestigious colleges in the region.
- Several schools and colleges contribute to the educational development of the region, but higher education opportunities are still limited.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in the division has improved over the years but still lags behind the state and national averages due to inadequate infrastructure in rural areas.
- Focus Areas: There is an emphasis on promoting vocational education and skill development to curb unemployment and migration.
Transportation and Connectivity
- Roadways:
- The division is well-connected through a network of national and state highways, including NH-19 (formerly NH-31) and NH-85, which link it to Patna and other major cities.
- The Digha-Sonepur Rail-Cum-Road Bridge (JP Setu) and the Chhapra-Hajipur Bridge over the Ganga have improved connectivity significantly.
- Railways:
- Chhapra Junction and Siwan Junction are major railway stations, providing links to Delhi, Kolkata, Patna, and other cities.
- The division is a critical rail corridor for freight and passenger movement in the region.
- Waterways: Historically, the Ganga and Ghaghara rivers were used for navigation and trade, and there are proposals to revive inland water transport.
- Airways: The nearest airport is Jay Prakash Narayan International Airport in Patna, around 70 km from Chhapra. Plans for regional air connectivity are under consideration.
Tourism
Saran Division boasts several cultural, historical, and natural attractions:
- Sonepur (Saran): Famous for the Sonepur Cattle Fair, one of the largest and oldest cattle fairs in Asia.
- Chirand (Saran): An archaeological site on the banks of the Ganga, showcasing remnants of the Neolithic and Chalcolithic periods.
- Ami Temple (Saran): A revered Hindu temple dedicated to Goddess Durga.
- Siwan City (Siwan): Known for its religious sites and association with historical figures.
- Thawe Temple (Gopalganj): A popular temple dedicated to Goddess Durga, attracting devotees from across Bihar.
- Gopalganj Sugar Mill Area: Once a hub of sugarcane cultivation and processing, now an emerging tourist spot for eco-tourism initiatives.
Challenges
- Flooding: Seasonal floods from the Ganga and Ghaghara rivers cause widespread damage to crops, infrastructure, and homes.
- Infrastructure Deficiency: Rural areas suffer from poor road connectivity, healthcare facilities, and educational infrastructure.
- Unemployment and Migration: Limited industrial development has resulted in high unemployment, with many residents migrating to other states or abroad for work.
- Environmental Concerns: Soil erosion and pollution from agricultural and urban waste are pressing environmental issues.
Development Initiatives
- Flood Control Projects: Construction of embankments and flood-resistant infrastructure to mitigate the impact of seasonal floods.
- Skill Development Programs: Vocational training centers are being set up to enhance employment opportunities for youth.
- Agricultural Development: Promotion of modern farming techniques, better irrigation facilities, and crop diversification to boost productivity.
- Industrialization: Efforts are being made to attract investment in small and medium-scale industries.
- Tourism Promotion: Development of better facilities at major tourist sites, such as Chirand and Sonepur, to attract more visitors.
Key Highlights
- Agricultural Heartland: Saran Division is one of the most fertile regions of Bihar, sustaining a predominantly agrarian economy.
- Historical Significance: Its association with ancient civilizations and the Indian freedom movement makes it historically significant.
- Cultural Hub: Rich in Bhojpuri culture, Saran is a center of traditional art, music, and festivals.
- Tourism Potential: From archaeological sites to vibrant fairs, the division has immense potential for cultural and eco-tourism.
Conclusion
The Saran Division is a vital administrative and cultural region in Bihar, combining its historical roots, agricultural prosperity, and traditional values. Furthermore, it is a vibrant region that combines a rich historical legacy with immense potential for economic and cultural development. In addition, while agriculture remains its backbone, tourism, education, and small-scale industries are emerging as growth sectors. Moreover, addressing challenges like flooding, infrastructure gaps, and unemployment can transform Saran into a model region for balanced and sustainable development in Bihar. Ultimately, with districts like Siwan and Gopalganj contributing to its legacy, the division holds great importance in the overall development and cultural heritage of the state.
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below 😊
सारण प्रमंडल और उसके जिले
सारण प्रमंडल बिहार के प्रशासनिक प्रमंडलों में से एक है। यह राज्य के उत्तर-पश्चिमी भाग में स्थित है, और इस प्रमंडल का नाम प्राचीन सारण क्षेत्र से लिया गया है, जिसका उल्लेख विभिन्न ऐतिहासिक और पौराणिक ग्रंथों में मिलता है। इसके अलावा, प्रमंडल का प्रशासनिक केंद्र छपरा में स्थित है। 2005 तक, यह प्रमंडल सारण (छपरा जिला के रूप में भी जाना जाता है), सीवान और गोपालगंज जिलों से बना है। यह प्रमंडल बिहार का एकमात्र ऐसा प्रमंडल है, जहां हर जिला उत्तर प्रदेश के साथ सीमा साझा करता है।
प्राचीन काल में, आधुनिक सारण प्रमंडल कोसल देश का हिस्सा था। इसके अलावा, सारन डिवीजन का इतिहास कोसल के इतिहास से अभिन्न रूप से जुड़ा हुआ है, जिसमें सारन डिवीजन की वर्तमान सीमाओं से परे के क्षेत्र शामिल हैं। विशेष रूप से, कोसल राज्य की सीमा उत्तर में नेपाल, पूर्व में गंडक, दक्षिण में सर्पिका (सई) नदी और पश्चिम में पंचाल से लगती थी। उत्तर प्रदेश और बिहार में आधुनिक फैजाबाद, गोंडा, बस्ती, गोरखापुर, देवरिया और सारन कोसल का हिस्सा थे।
‘आइन-ए-अकबरी’ में दी गई जिले की ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि के अनुसार, सारन वास्तव में बिहार प्रांत को बनाने वाले छह सरकारों (राजस्व प्रभागों) में से एक है। 1765 में जब ईस्ट इंडिया कंपनी को दीवानी दी गई थी, तब सारन और चंपारण सहित आठ सरकारें थीं। बाद में, इन दोनों को मिलाकर एक इकाई बनाई गई जिसे सारन के नाम से जाना जाता है। जब 1829 में कमिश्नरी डिवीजन की स्थापना की गई, तो सारण (चंपारण के साथ) को पटना डिवीजन में शामिल कर लिया गया। जब 1866 में चंपारण को एक अलग जिले के रूप में स्थापित किया गया, तो इसे चंपारण से अलग कर दिया गया। अंत में, जब 1908 में तिरहुत डिवीजन की स्थापना की गई, तो सारण इसका एक हिस्सा बन गया।
जिलों का अवलोकन
इस बिंदु पर, जिले को तीन उपखंडों में विभाजित किया गया: सारण, सीवान और गोपालगंज। इसके बाद, पूर्व सारण जिले के प्रत्येक उपखंड एक अलग जिला बन गए और 1981 में सारण डिवीजन का हिस्सा बन गए।
जनरल कनिंघम के अनुसार, सारण को पहले सारण या शरण के नाम से जाना जाता था, जो सम्राट अशोक द्वारा निर्मित एक स्तूप (स्तंभ) का नाम था। “सारण” नाम की उत्पत्ति कई सिद्धांतों का विषय रही है। दूसरी ओर, एक अलग सिद्धांत के अनुसार, जिले का नाम, सारण, सारंग-अरण्य, या हिरण वन से लिया गया है, जो प्रागैतिहासिक काल में अपने विशाल जंगल और हिरणों के लिए प्रसिद्ध था। शायद इस जिले के बारे में सबसे पुराना विश्वसनीय ऐतिहासिक रिकॉर्ड या तथ्य 898 ई. का है, जब यह सुझाव दिया गया था कि राजा महेंद्र पालदेव के शासनकाल के दौरान जारी एक ताम्रपत्र सारण के दिघवारा दुबौली गाँव द्वारा आपूर्ति किया गया था। विशेष रूप से, यह अपने ऐतिहासिक महत्व, उपजाऊ कृषि भूमि और सांस्कृतिक विरासत के लिए जाना जाता है।
हथवा राज बिहार के सारण प्रमंडल में एक भूमिहार ज़मींदारी थी। विशेष रूप से, इसमें 1,365 गाँव, 391,000 से अधिक निवासी थे, और सालाना लगभग दस लाख रुपये किराया आय उत्पन्न करते थे।
सारण जिला
“सारण जिला” उत्तर बिहार के नवगठित सारण डिवीजन के दक्षिणी भाग में स्थित है, विशेष रूप से 25°36′ से 26°13′ उत्तरी अक्षांश और 84°24′ से 85°15′ पूर्वी देशांतर के बीच। उल्लेखनीय रूप से, गंगा जिले की दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है, जिसके आगे भोजपुर और पटना जिले हैं। इसके अलावा, सारण के उत्तर में सीवान और गोपालगंज जिले हैं। इसके अलावा, गंडक पूर्व में वैशाली और मुजफ्फरपुर जिलों को विभाजित करती है। इस बीच, सारण के पश्चिम में उत्तर प्रदेश के सिवान और बलिया जिले हैं, जहाँ घाघरा नदी दोनों के बीच प्राकृतिक सीमा का काम करती है।
सीवान जिला
छपरा जिला 25-39′ से 26°-14′ उत्तर और 84°-23′ से 85°-12′ पूर्व के बीच स्थित है। इसके अतिरिक्त, सिवान जिला पश्चिम में उत्तर प्रदेश के गोरखपुर जिले से, उत्तर और उत्तर-पश्चिम में गोपालगंज जिले से, पूर्व और दक्षिण-पूर्व में सदर अनुमंडल से और दक्षिण में गोगरा नदी से घिरा है।
गोपालगंज जिला
इस बीच, गोपालगंज 26°-12′ से 26°-39′ उत्तर और 83°-54′ से 84°-55′ पूर्व के बीच स्थित है, जिसका क्षेत्रफल 786 वर्ग मील है। इसके अलावा, यह पूर्व में गंडक नदी, दक्षिण में सिवान और उत्तर में उत्तर प्रदेश के गोरखपुर जिले से घिरा हुआ था।
सारण प्रमंडल के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - स्थापित: 1908
- क्षेत्रफल: 6,893 km2 (2,661 वर्ग मील)
- निर्देशांक: 25.7848°N 84.7274°E
- विभाजन मुख्यालय: छपरा
- प्रमंडलीय आयुक्त: नर्मदेश्वर लाल
- जनसंख्या (2011): 9,819,311
- जिलों की संख्या: 3 (सारण, सीवान, गोपालगंज)
- अनुमंडल: 7 (सदर, मढ़ौरा, सोनपुर, सीवान सदर, महाराजगंज, गोपालगंज, हथुआ)
- ब्लॉक: 52
- गोपालगंज – बैकुंठपुर, बरौली, गोपालगंज, कुचायकोट, मांझा, थावे, सिधवलिया, भोरे, हथुआ, कटेया, पंचदेवरी, फुलवरिया, उचकागांव और विजयीपुर।
- सीवान – सीवान, मैरवा, दरौली, गुठनी, हुसैनगंज, आंदर, रघुनाथपुर, सिसवन, बड़हरिया, पचरुखी, महाराजगंज, दुरौंधा, गोरेयाकोठी, बसंतपुर, भगवानपुर और लकरी नबीगंज।
- सारण – अमनौर, बनियापुर, छपरा, दरियापुर, दिघवारा, एकमा, गरखा, ईशुपुर, जलालपुर, लहलादपुर, मकेर, मांझी, मढ़ौरा, मशरख, नगरा, पानापुर, परसा, रेवेलगंज, सोनपुर और तरैया।
- ग्राम पंचायत: 837
- गांव: 4903 (लगभग)
- नदियाँ: बूढ़ी गंडक, गंडकी, गंगा
- भूगोल:
- गंगा, गंडक और घाघरा जैसी नदियों से घिरा हुआ, जो भूमि को उपजाऊ बनाता है।
- पश्चिमी बिहार में स्थित, राज्य के बाकी हिस्सों से अच्छी कनेक्टिविटी के साथ।
- परिवहन:
- NH-727, NH-531, NH-331, NH-722
- दीघा-सोनपुर ब्रिज
- बरौनी-गोरखपुर लाइनें
- रक्सौल और जयनगर लाइनें
- आरा-छपरा पुल
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: 4 (गोपालगंज, महाराजगंज, सारण, सीवान)
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 24
- (एकमा, मांझी, बनियापुर, तरैया, मढ़ौरा, छपरा, गरखा, अमनौर, परसा, सोनपुर
- सीवान, जीरादेई, दरौली, रघुनाथपुर, दरौंधा, बड़हरिया, गोरियाकोठी, महाराजगंज
- बैकुंठपुर, बरौली, गोपालगंज, कुचायकोट, भोरे , हथुआ
- सामुदायिक विकास खंड: सोनपुर, दरियापुर, कुचायकोट, जीरादेई
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: sarandivision.bih.nic.in
सारण प्रमंडल के जिले: एक अवलोकन
सारण प्रमंडल में तीन जिले शामिल हैं:
1. सारण (छपरा) ज़िला:
- क्षेत्रफल: 2,641 km2 (1,020 वर्ग मील)
- जनसंख्या (2011): 3,951,862
- साक्षरता दर: 72.57%
- जिला मुख्यालय: छपरा।
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 310
- गांव: 1807
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 20
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 30
- अनुमण्डल की संख्या: 3 (सदर, मढ़ौरा, सोनपुर)
- नगर निगम: 1 (छपरा)
- नगर पंचायत: 7 (दिघवारा, मांझी, मशरख, रिविलगंज, सोनपुर, परसा बाजार, एकमा, कोपा, मढ़ौरा)
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 10
- एकमा, मांझी, बनियापुर, तरैया, मढ़ौरा, छपरा, गरखा, अमनौर, परसा, सोनपुर
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: 2 (सारण, महाराजगंज)
- प्रमुख विशेषताऐं:
- एशिया के सबसे बड़े पशु मेलों में से एक सोनपुर पशु मेले के लिए जाना जाता है।
- प्राचीन भारतीय इतिहास से जुड़ी महत्वपूर्ण सांस्कृतिक विरासत।
- पर्यटक आकर्षणों में आमी मंदिर और ढोरह आश्रम शामिल हैं।
- यह जिला चावल, गेहूं और गन्ने का प्रमुख उत्पादक है।
- महत्व: संभाग का केंद्रीय भाग, सांस्कृतिक और आर्थिक महत्व वाला।
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: saran.nic.in
2. सीवान ज़िला:
- क्षेत्रफल: 2,219 km2 (857 वर्ग मील)
- जनसंख्या (2011): 3,330,465
- साक्षरता दर: 79.61%
- जिला मुख्यालय: सीवान शहर।
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 293
- गांव: 1530
- अनुमण्डल की संख्या: 2 (महाराजगंज, सीवान सदर)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 19
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 28
- नगर परिषद: 1 (सीवान)
- नगर पंचायत: 8 (महाराजगंज, मैरवा, आंदर, बड़हरिया, बसंतपुर, गोपालपुर, गुठनी, हसनपुरा
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: 2 (सीवान, महाराजगंज)
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 8
- सीवान, जीरादेई, दरौली, रघुनाथपुर, दरौंधा, बड़हरिया, गोरियाकोठी, महाराजगंज
- प्रमुख विशेषताऐं:
- भारत के प्रथम राष्ट्रपति डॉ. राजेंद्र प्रसाद का जन्मस्थान।
- ऐतिहासिक रूप से भारतीय स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन में अपने योगदान के लिए जाना जाता है।
- धान, मक्का और दालों का उत्पादन करने वाली मुख्य रूप से कृषि अर्थव्यवस्था।
- महत्व: ऐतिहासिक और राजनीतिक महत्व का जिला बिहार में.
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: siwan.nic.in
3. गोपालगंज ज़िला:
- क्षेत्रफल: 2,033 km2 (785 वर्ग मील)
- जनसंख्या (2011): 2,562,012
- साक्षरता दर: 65.47%
- जिला मुख्यालय: गोपालगंज शहर
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 234
- गांव: 1566
- उपखंड की संख्या: 2 (हथुआ, गोपालगंज)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 14
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 22
- नगर परिषद: 1 (गोपालगंज)
- नगर पंचायत: 3 (बरौली, कटेया, मीरगंज)
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: 1 (गोपालगंज)
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 6
- बैकुंठपुर, बरौली, गोपालगंज, कुचायकोट, भोरे, हथुआ
- प्रमुख विशेषताऐं:
- उपजाऊ कृषि भूमि, गन्ना, धान और गेहूँ का उत्पादन।
- अपनी हरी-भरी हरियाली और नदियों के नज़दीकी के लिए जाना जाता है।
- मंदिरों और पारंपरिक त्योहारों के कारण सांस्कृतिक महत्व।
- महत्व: कृषि की रीढ़ और सांस्कृतिक समृद्धि वाला एक जिला।
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: gopalganj.nic.in
प्रत्येक जिला संभाग के आर्थिक, सांस्कृतिक और राजनीतिक परिदृश्य में अद्वितीय योगदान देता है।
भौगोलिक अवलोकन
- स्थान: सारण प्रमंडल बिहार के उत्तर-पश्चिमी भाग में स्थित है और इसकी सीमा गंगा और घाघरा नदियों से मिलती है, जो इसके भूगोल और अर्थव्यवस्था को परिभाषित करती हैं।
- नदियाँ:
- गंगा नदी इसकी दक्षिणी सीमा बनाती है और कृषि, परिवहन और आजीविका में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती है।
- घाघरा नदी इसके पश्चिमी किनारे से बहती है, गंगा में मिल जाती है और प्रमंडल की बाढ़ के मैदान की पारिस्थितिकी को प्रभावित करती है।
- स्थलाकृति: प्रमंडल की विशेषता जलोढ़ मैदान है, जो इसे बिहार के सबसे उपजाऊ क्षेत्रों में से एक बनाता है।
- जलवायु: प्रमंडल में गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल, मानसूनी वर्षा और ठंडी सर्दियाँ के साथ आर्द्र उपोष्णकटिबंधीय जलवायु होती है।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- प्राचीन इतिहास: सारन क्षेत्र प्राचीन काल से ही भारतीय इतिहास का एक प्रमुख हिस्सा रहा है। यह वैदिक काल के दौरान कोसल साम्राज्य का हिस्सा था और बाद में मगध साम्राज्य में एकीकृत हो गया।
- धार्मिक महत्व:
- यह महाभारत से जुड़ा हुआ है, जिसमें इस क्षेत्र में होने वाली विभिन्न घटनाओं का उल्लेख है।
- यह क्षेत्र बौद्ध धर्म और जैन धर्म से भी जुड़ा हुआ है, जहाँ कुछ क्षेत्रों में स्तूप और शिलालेखों के अवशेष पाए गए हैं।
- मध्यकालीन काल: मध्यकालीन काल के दौरान, इस क्षेत्र में विभिन्न स्थानीय सरदारों का उदय हुआ और बाद में यह दिल्ली सल्तनत और मुगलों के नियंत्रण में आ गया।
- औपनिवेशिक काल: ब्रिटिश शासन के दौरान सारन ने एक प्रशासनिक और व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में महत्व प्राप्त किया। यह नील आंदोलन में एक महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्र था और इसने भारतीय स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में सक्रिय भूमिका निभाई थी, जिसमें भारत के पहले राष्ट्रपति डॉ. राजेंद्र प्रसाद जैसे नेता इस विभाजन से जुड़े थे।
सांस्कृतिक महत्व
- भाषाएँ: संभाग में बोली जाने वाली मुख्य भाषाओं में भोजपुरी, हिंदी और उर्दू शामिल हैं।
- त्यौहार:
- छठ पूजा सबसे महत्वपूर्ण त्यौहार है, जिसे नदियों के किनारे बड़ी श्रद्धा के साथ मनाया जाता है।
- अन्य लोकप्रिय त्यौहारों में होली, दिवाली, दुर्गा पूजा और ईद शामिल हैं।
- लोक परंपराएँ: यह क्षेत्र भोजपुरी लोकगीतों, नृत्यों और साहित्य से समृद्ध है। भोजपुरी सिनेमा ने भी इस क्षेत्र की सांस्कृतिक पहचान को लोकप्रिय बनाने में योगदान दिया है।
- व्यंजन: यह संभाग अपने भोजपुरी व्यंजनों के लिए जाना जाता है, जिसमें लिट्टी चोखा, दाल पूरी, ठेकुआ और भुजा (फूला हुआ चावल) जैसे व्यंजन लोकप्रिय हैं।
अर्थव्यवस्था
- कृषि:
- यह प्रभाग मुख्य रूप से कृषि अर्थव्यवस्था वाला है, जिसमें चावल, गेहूं, दालें, गन्ना और सब्जियों जैसी फसलों पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया जाता है।
- उपजाऊ मिट्टी और नदियों से सिंचाई इसे बिहार के सबसे अधिक उत्पादक कृषि क्षेत्रों में से एक बनाती है।
- डेयरी और पशुधन: इस प्रभाग में एक संपन्न डेयरी उद्योग है, जिसमें कई परिवार दूध उत्पादन और पशुपालन में लगे हुए हैं।
- व्यापार और वाणिज्य:
- छपरा एक क्षेत्रीय व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता है, जहाँ कृषि उपज, कपड़ा और उपभोक्ता वस्तुओं के लिए बाज़ार हैं।
- चीनी मिलों और चावल मिलों जैसे लघु उद्योग प्रभाग में प्रचलित हैं।
- चुनौतियाँ: अपनी कृषि प्रधानता के बावजूद, प्रभाग को मौसमी बाढ़, बेरोजगारी और औद्योगिक विकास की कमी जैसी चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है, जिससे नौकरियों के लिए पलायन होता है।
शिक्षा और संस्थान
- प्रमुख संस्थान:
- जय प्रकाश विश्वविद्यालय (छपरा): संभाग का एक अग्रणी विश्वविद्यालय, जो विभिन्न विषयों में उच्च शिक्षा प्रदान करता है।
- राजेंद्र कॉलेज (छपरा): क्षेत्र के सबसे पुराने और सबसे प्रतिष्ठित कॉलेजों में से एक।
- कई स्कूल और कॉलेज क्षेत्र के शैक्षिक विकास में योगदान देते हैं, लेकिन उच्च शिक्षा के अवसर अभी भी सीमित हैं।
- साक्षरता दर: संभाग में साक्षरता दर में पिछले कुछ वर्षों में सुधार हुआ है, लेकिन ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अपर्याप्त बुनियादी ढांचे के कारण यह अभी भी राज्य और राष्ट्रीय औसत से पीछे है।
- फोकस क्षेत्र: बेरोजगारी और पलायन को रोकने के लिए व्यावसायिक शिक्षा और कौशल विकास को बढ़ावा देने पर जोर दिया जा रहा है।
परिवहन और संपर्क
- सड़क मार्ग:
- यह संभाग राष्ट्रीय और राज्य राजमार्गों के नेटवर्क के माध्यम से अच्छी तरह से जुड़ा हुआ है, जिसमें NH-19 (पूर्व में NH-31) और NH-85 शामिल हैं, जो इसे पटना और अन्य प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ते हैं।
- दीघा-सोनपुर रेल-सह-सड़क पुल (जेपी सेतु) और गंगा पर छपरा-हाजीपुर पुल ने संपर्क में उल्लेखनीय सुधार किया है।
- रेलवे:
- छपरा जंक्शन और सीवान जंक्शन प्रमुख रेलवे स्टेशन हैं, जो दिल्ली, कोलकाता, पटना और अन्य शहरों को जोड़ते हैं।
- यह संभाग क्षेत्र में माल और यात्री आवागमन के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण रेल गलियारा है।
- जलमार्ग: ऐतिहासिक रूप से, गंगा और घाघरा नदियों का उपयोग नौवहन और व्यापार के लिए किया जाता था, और अंतर्देशीय जल परिवहन को पुनर्जीवित करने के प्रस्ताव हैं।
- वायुमार्ग: निकटतम हवाई अड्डा पटना में जय प्रकाश नारायण अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डा है, जो छपरा से लगभग 70 किमी दूर है। क्षेत्रीय हवाई संपर्क की योजनाएँ विचाराधीन हैं।
पर्यटन
सारण संभाग में कई सांस्कृतिक, ऐतिहासिक और प्राकृतिक आकर्षण हैं:
- सोनपुर (सारण): एशिया के सबसे बड़े और सबसे पुराने पशु मेलों में से एक, सोनपुर पशु मेले के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।
- चिरांद (सारण): गंगा के तट पर स्थित एक पुरातात्विक स्थल, जिसमें नवपाषाण और ताम्रपाषाण काल के अवशेष प्रदर्शित हैं।
- अमी मंदिर (सारण): देवी दुर्गा को समर्पित एक प्रतिष्ठित हिंदू मंदिर।
- सीवान शहर (सीवान): अपने धार्मिक स्थलों और ऐतिहासिक हस्तियों के साथ जुड़ाव के लिए जाना जाता है।
- थावे मंदिर (गोपालगंज): देवी दुर्गा को समर्पित एक लोकप्रिय मंदिर, जो पूरे बिहार से भक्तों को आकर्षित करता है।
- गोपालगंज चीनी मिल क्षेत्र: कभी गन्ने की खेती और प्रसंस्करण का केंद्र रहा, अब इको-टूरिज्म पहल के लिए एक उभरता हुआ पर्यटन स्थल है।
चुनौतियाँ
- बाढ़: गंगा और घाघरा नदियों से आने वाली मौसमी बाढ़ से फसलों, बुनियादी ढांचे और घरों को व्यापक नुकसान होता है।
- बुनियादी ढांचे की कमी: ग्रामीण इलाकों में खराब सड़क संपर्क, स्वास्थ्य सेवा सुविधाएँ और शैक्षिक बुनियादी ढाँचा है।
- बेरोज़गारी और पलायन: सीमित औद्योगिक विकास के कारण बेरोज़गारी बहुत बढ़ गई है, जिसके कारण कई निवासी काम के लिए दूसरे राज्यों या विदेश चले गए हैं।
- पर्यावरण संबंधी चिंताएँ: मिट्टी का कटाव और कृषि और शहरी कचरे से होने वाला प्रदूषण पर्यावरणीय मुद्दों को गंभीर बना रहे हैं।
विकास पहल
- बाढ़ नियंत्रण परियोजनाएँ: मौसमी बाढ़ के प्रभाव को कम करने के लिए तटबंधों और बाढ़ प्रतिरोधी बुनियादी ढाँचे का निर्माण।
- कौशल विकास कार्यक्रम: युवाओं के लिए रोज़गार के अवसर बढ़ाने के लिए व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण केंद्र स्थापित किए जा रहे हैं।
- कृषि विकास: उत्पादकता बढ़ाने के लिए आधुनिक कृषि तकनीकों, बेहतर सिंचाई सुविधाओं और फसल विविधीकरण को बढ़ावा देना।
- औद्योगीकरण: छोटे और मध्यम स्तर के उद्योगों में निवेश आकर्षित करने के प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं।
- पर्यटन को बढ़ावा देना: चिरांद और सोनपुर जैसे प्रमुख पर्यटन स्थलों पर बेहतर सुविधाओं का विकास, ताकि अधिक से अधिक पर्यटकों को आकर्षित किया जा सके।
मुख्य बातें
- कृषि क्षेत्र: सारण प्रमंडल बिहार के सबसे उपजाऊ क्षेत्रों में से एक है, जो मुख्य रूप से कृषि अर्थव्यवस्था को बनाए रखता है।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व: प्राचीन सभ्यताओं और भारतीय स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन के साथ इसका जुड़ाव इसे ऐतिहासिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण बनाता है।
- सांस्कृतिक केंद्र: भोजपुरी संस्कृति से समृद्ध, सारण पारंपरिक कला, संगीत और त्योहारों का केंद्र है।
- पर्यटन संभावना: पुरातात्विक स्थलों से लेकर जीवंत मेलों तक, इस प्रमंडल में सांस्कृतिक और पारिस्थितिकी पर्यटन की अपार संभावनाएं हैं।
निष्कर्ष
सारण प्रमंडल बिहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रशासनिक और सांस्कृतिक क्षेत्र है, जो अपनी ऐतिहासिक जड़ों, कृषि समृद्धि और पारंपरिक मूल्यों को जोड़ता है। इसके अलावा, यह एक जीवंत क्षेत्र है जो आर्थिक और सांस्कृतिक विकास की अपार संभावनाओं के साथ एक समृद्ध ऐतिहासिक विरासत को जोड़ता है। इसके अलावा, जबकि कृषि इसकी रीढ़ बनी हुई है, पर्यटन, शिक्षा और लघु उद्योग विकास क्षेत्रों के रूप में उभर रहे हैं। इसके अलावा, बाढ़, बुनियादी ढांचे की कमी और बेरोजगारी जैसी चुनौतियों का समाधान करके सारण को बिहार में संतुलित और सतत विकास के लिए एक आदर्श क्षेत्र में बदला जा सकता है। अंततः, सिवान और गोपालगंज जैसे जिलों ने इसकी विरासत में योगदान दिया है, यह प्रमंडल राज्य के समग्र विकास और सांस्कृतिक विरासत में बहुत महत्व रखता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

5 thoughts on “Saran Division and its Special Districts of Bihar”