Jehanabad District: An Overview
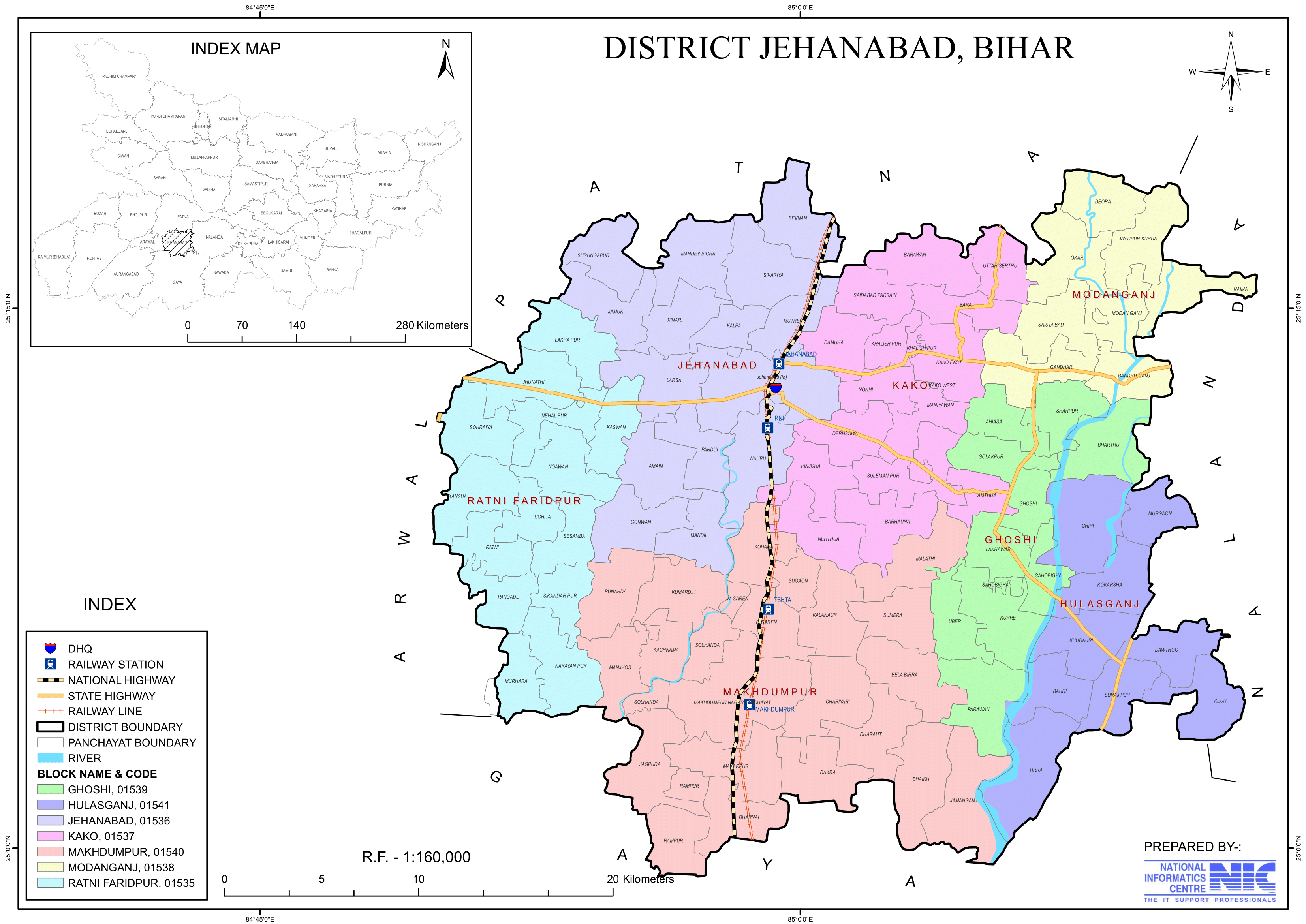
Jehanabad District is one of the 38-districts, located in central part of Bihar state, India. Spanning an area of 932 square kilometers (360 square miles), jehanabad lies at 25.1981°N latitude and 84.9859°E longitude, and shares borders with Patna district to the north, Gaya district to the south, Nalanda district to the east, and Arwal district to the west. The district’s administrative center is located at Jehanabad town, and it comes under Magadh Division.
Jehanabad was established as a subdivision of Gaya district in 1872. On 1st August 1986, Jehanabad gained prominence as a separate district, carving its identity in the administrative map of Bihar. The primary goal of establishing this district was to speed development while also addressing issues of extremism, poverty, unemployment, and underdeveloped areas.
The district known for its historical significance, agricultural prominence, and its role in social and political movements. Despite being one of the smaller districts of Bihar, Jehanabad holds a unique place due to its proximity to ancient sites and its fertile lands.
History
Jehanabad holds a unique place in Indian history, with its origins dating back to the Mughal era. The district is mentioned in the famous book Ain-e-Akbari, which recounts the devastating famine that struck the area in the 17th-Century, leading to widespread hunger and suffering.
To address the crisis, Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb established a relief market, or Mandi, under the supervision of Jahanara Begum, his sister. This market, named “Jahanara”, was set up to provide food and resources to the affected population. Jahanara is believed to have spent considerable time in the area, overseeing the relief efforts. Over time, the settlement around the Mandi came to be known as “Jahanarabad”, which eventually evolved into “Jehanabad”.
This historical connection reflects the region’s significance during the Mughal period and its enduring legacy.
Key Facts About Jehanabad District
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Division: Magadh
- Established: 1st August 1986
- Coordinates: 24°45′N 85°00′E
- District Headquarters: Jehanabad
- District Magistrate: Alankrita Pandey, I.A.S.
- Superintendent of Police: Arvind Pratap Singh I.P.S.
- Area: 932 km2 (360 sq mi)
- Population (2011):
- Total: 1,125,313
- Density: 1,200/km2 (3,100/sq mi)
- Literacy Rate: 68.27%
- Sex Ratio: 918/1000
- Gram Panchayats: 93
- Villages: 918
- No. of Subdivision: 1 (Jehanabad)
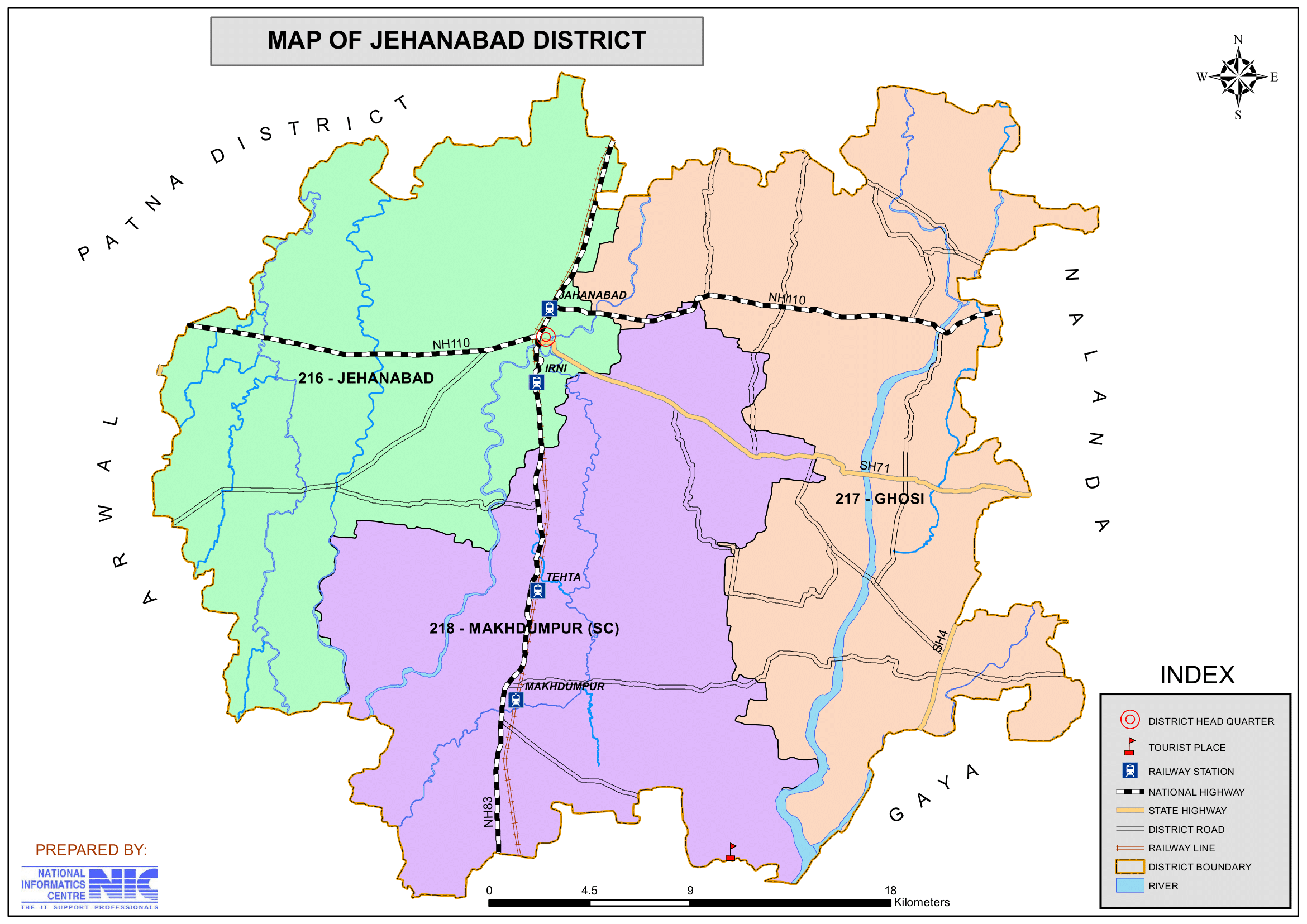
- No. of Blocks: 7 (Jehanabad, Makhdumpur, Ghosi, Hulasganj, Ratni Faridpur, Modanganj, Kako)
- Police Station: 13
- Tehta O.P., Okari O.P., Karauna O.P., Hulasganj, Pali, Makhdumpur, Kako, Kalpa O.P., Bhelawar O.P., Jehanabad, Ghosi, Sakurabad, Paras Bigha.
- Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad): 1( Jehanabad)
- Nagar Panchayat: Makhdumpur
- Lok Sabha constituency: 1 (Jehanabad)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 3 (Jehanabad, Ghosi, Makhdumpur)
- Key Features:
- Primarily an agricultural district producing paddy, wheat, and pulses.
- Known for its association with historical and cultural traditions.
- Important landmarks include Barabar Caves, ancient rock-cut caves linked to the Mauryan period.
- Significance: A blend of agricultural and historical importance.
- Time Zone: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- Pin Code: 8044xx (Jehanabad)
- Major Highways: NH-83
- Average annual precipitation: 1074 mm
- Official Website: jehanabad.nic.in
Geography
- Location: Jehanabad is situated in central Bihar and shares borders with Patna to the north, Gaya to the south, Nalanda to the east, and Arwal to the west.
- Area: The district spans an area of 932 square kilometers, making it one of the smaller districts in Bihar.
- Topography: The region is primarily plain, with fertile alluvial soil that supports agriculture. The Falgu River, a seasonal river, flows through the district.
- Climate: Jehanabad experiences a subtropical climate, characterized by hot summers, a monsoon season, and mild winters.
History
- Ancient Period:
- The region was historically part of the Magadha Empire and is linked to Buddhist and Jain traditions.
- Nearby historical sites like Rajgir and Bodh Gaya highlight the district’s ancient cultural connection.
- Medieval Era:
- Jehanabad saw the influence of various dynasties, including the Mauryas, Guptas, and Mughals.
- Modern Era:
- During British rule, Jehanabad was part of the Gaya district. It gained prominence due to its role in the freedom struggle.
- Jehanabad became a separate district on 1 August 1986, carved out of Gaya.
Demographics (According to the 2011 Census)
- Population:
- Total Population: Jehanabad district has a population of approximately 1,125,313.
- Ranking: 412th in India (out of 640 districts).
- Density: 1,206 persons per square kilometer (3,120/sq mi).
- Population Growth (2001–2011): 21.34% reflecting significant population increase.
- Sex Ratio: 918 females per 1,000 males, indicating a gender disparity.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate is 68.27%, higher than the state average, reflecting progress in education but with significant efforts being made to improve education access and quality.
- Urban Population: 12.01% of the total population lives in urban areas.
- Religious Composition (2011 Census):
- Hinduism: 92.87%
- Scheduled Castes: 19.81%
- Scheduled Tribes: 0.11%
- Islam: 6.73%
- Other or not stated: 0.40%
- Hinduism: 92.87%
- Languages: The primary languages spoken are Hindi, Magahi, and Urdu.
- Magahi: 79.5%
- Hindi: 18.01%
- Urdu: 2.00%
- Others: 0.16%
Administration
- Headquarters: The district headquarters is located in Jehanabad town.
- Subdivisions:
- The district has a single subdivision, Jehanabad Sadar.
- Each subdivision is led by a subdivisional magistrate who is in charge of development, revenue-related tasks, and maintaining law and order.
- Blocks and Circles:
- Jehanabad district comprises 7 administrative Blocks and Circles such as Jehanabad, Makhdumpur, Ghosi, Hulasganj, Ratni Faridpur, Modanganj and Kako, each responsible for local governance and development.
- A Circle officer (CO) leads each circle, while a Block Development Officer (BDO) leads each block.
- Governance: Jehanabad is part of the Magadh division and has representation in the Bihar Legislative Assembly and Parliament.
Organization Chart

Economy
The economy of Aurangabad district is predominantly agriculture-based, with no significant presence of industrial activities.
- Agriculture:
- Agriculture is the primary occupation, with crops like paddy, wheat, maize, and pulses being widely cultivated.
- The district benefits from the fertile soil and irrigation provided by the Falgu River and canals.
- Industries:
- Industrialization is minimal, with small-scale industries like rice mills and agro-processing units being prominent.
- Handicrafts and Pottery: Local artisans produce pottery and traditional handicrafts.
- Irrigation and Challenges:
- The district faces challenges such as limited industrial growth and dependency on agriculture.
- While a substantial portion of the district is well-irrigated, farmers face numerous challenges, including:
- Lack of proper infrastructure for advanced agricultural practices.
- Limited access to consistent power supply, affecting productivity and irrigation efficiency.
- Economic Reliance:
- The district’s economy is heavily reliant on agriculture, making it vulnerable to issues such as inadequate infrastructure, unpredictable weather patterns, and resource limitations.
- Despite its potential, the absence of industrial growth and infrastructural advancements hinders the economic development of the region.
Education
- Institutions:
- Jehanabad has several government and private schools, along with colleges affiliated with Magadh University.
- Institutions like Anugrah Narayan College and technical institutes cater to higher education.
- Some Schools/Colleges:
- S. S. College, Jehanabad
- Kendriya Vidyalaya, Main Road, Jehanabad
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Nauru, Jehanabad
- Skill Development:
- Vocational training centers aim to equip the youth with employable skills.
- Challenges:
- Rural areas face issues like inadequate infrastructure, teacher shortages, and limited access to higher education.
Culture
- Festivals:
- Major festivals like Chhath Puja, Durga Puja, Diwali, Holi, and Eid are celebrated with enthusiasm.
- Cuisine:
- The district’s cuisine includes traditional Bihari dishes like litti chokha, sattu paratha, thekua, and pitha.
- Folk Traditions:
- Folk music, dance, and storytelling are an integral part of Jehanabad’s cultural heritage.
Tourism
Jehanabad is not widely known for tourism, but it has several sites of historical and religious importance:


1. Dawthu, Hulasganj:
- This site features historical remains of ancient temples and sculptures.
- The structures resemble ancient mandapas (pillared halls) and Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum).
2. Amthua Sharif:
- Located 13 km from the district headquarters and 8 km from Kako block headquarters, Amthua Sharif honors Sufi Saint Sayyid Shah Hayat Rehma.
- Visitors from distant places come to seek blessings, making it a notable spiritual site.
3. Vishnu Temple, Kako:
- A site of historical and religious significance, formally established in 1950.
- Enshrines a historical idol of Lord Vishnu, attracting devotees and tourists alike.
- A large pond adjacent to the temple becomes a hub of activity during Chhath, when pilgrims gather to offer prayers to Lord Bhaskara (Sun God).
4. Barabar Caves:
- Situated near Makhdumpur, 25 km south of Jehanabad, the Barabar Caves are ancient rock-cut Buddhist chambers dating back to the 3rd century A.D.
- These caves are famous as the origin of the Ajivika sect, making them an important cultural and historical site.
- Nearby is the Baba Siddhnath Temple, also called Siddheshwar Nath Temple, a Gupta-period structure (7th century A.D.) believed to have been built by Bana Raja, the father-in-law of King Jarasandha.
5. Hazrat Bibi Kamal ka Mukbara:
- This is the dargah of Hazrat Bibi Kamal, India’s first woman Sufi saint, known for her holy healing powers.
- She is believed to be the aunt of Hazrat Makhdum Saheb of Bihar Sharif.
- Devotees come here with faith in her mystic powers, especially for healing mental and incurable diseases.
These sites reflect Jehanabad’s rich cultural and spiritual heritage, offering a unique blend of history, religion, and architecture.
Transportation
- Roadways:
- Jehanabad is well-connected by roads, with National Highway 83 passing through the district, linking it to Patna and Gaya.
- Regular bus services connect the district to nearby cities.
- Railways:
- Jehanabad Railway Station lies on the Patna-Gaya railway line, making it an important transit point.
- Airways:
- The nearest airport is Gaya International Airport, approximately 50 km away, providing domestic and international connectivity.
Challenges
- Economic Development: The district faces slow industrial growth and limited employment opportunities.
- Infrastructure: Rural areas lack adequate road, healthcare, and educational infrastructure.
- Flooding: Parts of the district are prone to flooding during the monsoon, affecting agriculture and livelihoods.
Conclusion
Jehanabad, though a small district, holds significant historical and cultural importance. Its fertile lands make it a key agricultural hub, while its proximity to major cities like Patna and Gaya offers potential for economic growth. The district’s rich heritage, seen in sites like the Barabar Caves, adds to its historical significance. Addressing challenges like infrastructure development and industrialization can unlock the district’s full potential and contribute to its progress.
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below or Checkout these topics
जहानाबाद जिला: विशेष प्राचीन स्थलों वाली भूमि
अवलोकन
जहानाबाद जिला भारत के बिहार राज्य के मध्य भाग में स्थित 38-जिलों में से एक है। 932 वर्ग किलोमीटर (360 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र में फैला जहानाबाद 25.1981 डिग्री उत्तरी अक्षांश और 84.9859 डिग्री पूर्वी देशांतर पर स्थित है, और उत्तर में पटना जिले, दक्षिण में गया जिले, पूर्व में नालंदा जिले और पश्चिम में अरवल जिले के साथ सीमा साझा करता है। जिले का प्रशासनिक केंद्र जहानाबाद शहर में स्थित है, और यह मगध डिवीजन के अंतर्गत आता है।
जहानाबाद की स्थापना 1872 में गया जिले के एक उपखंड के रूप में की गई थी। 1 अगस्त 1986 को, जहानाबाद ने एक अलग जिले के रूप में प्रमुखता हासिल की, जिसने बिहार के प्रशासनिक मानचित्र में अपनी पहचान बनाई। इस जिले की स्थापना का प्राथमिक लक्ष्य विकास को गति देना था, साथ ही उग्रवाद, गरीबी, बेरोजगारी और अविकसित क्षेत्रों के मुद्दों को संबोधित करना था। यह जिला अपने ऐतिहासिक महत्व, कृषि प्रधानता और सामाजिक तथा राजनीतिक आंदोलनों में अपनी भूमिका के लिए जाना जाता है। बिहार के छोटे जिलों में से एक होने के बावजूद, जहानाबाद प्राचीन स्थलों और अपनी उपजाऊ भूमि के निकट होने के कारण एक अद्वितीय स्थान रखता है।
इतिहास
जहानाबाद भारतीय इतिहास में एक अद्वितीय स्थान रखता है, इसकी उत्पत्ति मुगल काल से हुई है। जिले का उल्लेख प्रसिद्ध पुस्तक आइन-ए-अकबरी में किया गया है, जो 17वीं शताब्दी में इस क्षेत्र में आए विनाशकारी अकाल का वर्णन करती है, जिसके कारण व्यापक भूख और पीड़ा हुई।
संकट से निपटने के लिए, मुगल सम्राट औरंगजेब ने अपनी बहन जहाँआरा बेगम की देखरेख में एक राहत बाजार या मंडी की स्थापना की। “जहानआरा” नामक यह बाजार प्रभावित आबादी को भोजन और संसाधन उपलब्ध कराने के लिए स्थापित किया गया था। माना जाता है कि जहाँआरा ने राहत प्रयासों की देखरेख करते हुए इस क्षेत्र में काफी समय बिताया था। समय के साथ, मंडी के आसपास की बस्ती को “जहानआराबाद” के नाम से जाना जाने लगा, जो अंततः “जहानाबाद” में विकसित हो गया।
यह ऐतिहासिक संबंध मुगल काल के दौरान इस क्षेत्र के महत्व और इसकी स्थायी विरासत को दर्शाता है।
जहानाबाद जिले के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - प्रमंडल: मगध
- स्थापना: 26 जनवरी 1973
- निर्देशांक: 1 अगस्त 1986
- निर्देशांक: 24°45′N 85°00′E
- जिला मुख्यालय: जहानाबाद
- जिला मजिस्ट्रेट: अलंकृता पांडे, IAS
- पुलिस अधीक्षक: अरविंद प्रताप सिंह, IPS
- क्षेत्रफल: 932 km2 (360 वर्ग मील)
- जनसंख्या (2011):
- कुल: 1,125,313
- घनत्व: 1,200/km2 (3,100/वर्ग मील)
- साक्षरता दर: 68.27%
- लिंगानुपात: 918/1000
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 93
- गांव: 918
- उपखंड की संख्या: 1 (जहानाबाद)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 7 (जहानाबाद, मखदुमपुर, घोसी, हुलासगंज, रतनी फरीदपुर, मोदनगंज, काको)
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 13
- टेहटा ओ.पी., ओकरी ओ.पी., करौना ओ.पी., हुलासगंज, पाली, मखदुमपुर, काको, कल्पा ओ.पी., भेलावर ओ.पी., जहानाबाद, घोसी, सकुराबाद, पारस बिगहा।
- नगर परिषद: 1 (जहानाबाद)
- नगर पंचायत: मखदुमपुर
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र: 1 (जहानाबाद)
- विधानसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र: 3 (जहानाबाद, घोसी, मखदुमपुर)
- मुख्य विशेषताएं:
- मुख्य रूप से धान, गेहूं और दालों का उत्पादन करने वाला एक कृषि जिला।
- ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक परंपराओं के साथ अपने जुड़ाव के लिए जाना जाता है।
- महत्वपूर्ण स्थलों में बराबर गुफाएँ, मौर्य काल से जुड़ी प्राचीन चट्टान-कट गुफाएँ शामिल हैं।
- महत्व: कृषि और ऐतिहासिक महत्व का मिश्रण।
- समय क्षेत्र: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- पिन कोड: 8044xx (जहानाबाद)
- प्रमुख राजमार्ग: NH-83
- औसत वार्षिक वर्षा: 1074 मिमी
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: jehanabad.nic.in
भूगोल
- स्थान: जहानाबाद मध्य बिहार में स्थित है और उत्तर में पटना, दक्षिण में गया, पूर्व में नालंदा और पश्चिम में अरवल के साथ सीमा साझा करता है।
- क्षेत्र: यह जिला 932 वर्ग किलोमीटर के क्षेत्र में फैला हुआ है, जो इसे बिहार के छोटे जिलों में से एक बनाता है।
- स्थलाकृति: यह क्षेत्र मुख्य रूप से समतल है, जिसमें उपजाऊ जलोढ़ मिट्टी है जो कृषि का समर्थन करती है। फल्गु नदी, एक मौसमी नदी, जिले से होकर बहती है।
- जलवायु: जहानाबाद में उपोष्णकटिबंधीय जलवायु होती है, जिसमें गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल, मानसून का मौसम और हल्की सर्दियाँ होती हैं।
इतिहास
- प्राचीन काल:
- यह क्षेत्र ऐतिहासिक रूप से मगध साम्राज्य का हिस्सा था और बौद्ध और जैन परंपराओं से जुड़ा हुआ है।
- राजगीर और बोधगया जैसे आस-पास के ऐतिहासिक स्थल जिले के प्राचीन सांस्कृतिक संबंध को उजागर करते हैं।
- मध्यकालीन युग:
- जहानाबाद ने मौर्य, गुप्त और मुगलों सहित विभिन्न राजवंशों का प्रभाव देखा।
- आधुनिक युग:
- ब्रिटिश शासन के दौरान, जहानाबाद गया जिले का हिस्सा था। स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में अपनी भूमिका के कारण इसे प्रमुखता मिली।
- 1 अगस्त 1986 को गया से अलग होकर जहानाबाद एक अलग जिला बन गया।
जनसांख्यिकी (2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार)
- जनसंख्या:
- कुल जनसंख्या: जहानाबाद जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 1,125,313 है।
- रैंकिंग: भारत में 412वाँ (640 जिलों में से)।
- घनत्व: 1,206 व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर (3,120/वर्ग मील)।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि (2001-2011): 21.34%, जो महत्वपूर्ण जनसंख्या वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- लिंग अनुपात: प्रति 1,000 पुरुषों पर 918 महिलाएँ, जो लैंगिक असमानता को दर्शाता है।
- साक्षरता दर: साक्षरता दर 68.27% है, जो राज्य औसत से अधिक है, जो शिक्षा में प्रगति को दर्शाती है, लेकिन शिक्षा की पहुँच और गुणवत्ता में सुधार के लिए महत्वपूर्ण प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं।
- शहरी जनसंख्या: कुल जनसंख्या का 12.01% शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- धार्मिक संरचना (2011 की जनगणना):
- हिंदू धर्म: 92.87%
- अनुसूचित जाति: 19.81%
- अनुसूचित जनजाति: 0.11%
- इस्लाम: 6.73%
- अन्य या नहीं बताया गया: 0.40%
- भाषाएँ: बोली जाने वाली मुख्य भाषाएँ हिंदी, मगही और उर्दू हैं।
- मगही: 79.5%
- हिंदी: 18.01%
- उर्दू: 2.00%
- अन्य: 0.16%
प्रशासन
- मुख्यालय: जिला मुख्यालय जहानाबाद शहर में स्थित है।
- उपखंड:
- जिले में एक ही उपखंड है, जहानाबाद सदर।
- प्रत्येक उपखंड का नेतृत्व एक उपखंड मजिस्ट्रेट करता है जो विकास, राजस्व संबंधी कार्यों और कानून व्यवस्था बनाए रखने का प्रभारी होता है।
- ब्लॉक और सर्किल:
- जहानाबाद जिले में 7 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और सर्किल शामिल हैं जैसे जहानाबाद, मखदुमपुर, घोसी, हुलासगंज, रतनी फरीदपुर, मोदनगंज और काको, जिनमें से प्रत्येक स्थानीय शासन और विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
- प्रत्येक सर्किल का नेतृत्व एक सर्किल अधिकारी (सीओ) करता है, जबकि प्रत्येक ब्लॉक का नेतृत्व एक ब्लॉक विकास अधिकारी (बीडीओ) करता है।
- शासन: जहानाबाद मगध प्रमंडल का हिस्सा है और इसका बिहार विधानसभा और संसद में प्रतिनिधित्व है।
अर्थव्यवस्था
औरंगाबाद जिले की अर्थव्यवस्था मुख्य रूप से कृषि आधारित है, जिसमें औद्योगिक गतिविधियों की कोई महत्वपूर्ण उपस्थिति नहीं है।
- कृषि:
- कृषि प्राथमिक व्यवसाय है, जिसमें धान, गेहूं, मक्का और दालों जैसी फसलें व्यापक रूप से उगाई जाती हैं।
- जिले को उपजाऊ मिट्टी और फल्गु नदी और नहरों द्वारा प्रदान की जाने वाली सिंचाई से लाभ होता है।
- उद्योग:
- औद्योगीकरण न्यूनतम है, चावल मिलों और कृषि प्रसंस्करण इकाइयों जैसे छोटे पैमाने के उद्योग प्रमुख हैं।
- हस्तशिल्प और मिट्टी के बर्तन: स्थानीय कारीगर मिट्टी के बर्तन और पारंपरिक हस्तशिल्प बनाते हैं।
- सिंचाई और चुनौतियाँ:
- जिले को सीमित औद्योगिक विकास और कृषि पर निर्भरता जैसी चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है।
- जबकि जिले का एक बड़ा हिस्सा अच्छी तरह से सिंचित है, किसानों को कई चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है, जिनमें शामिल हैं:
- उन्नत कृषि पद्धतियों के लिए उचित बुनियादी ढाँचे की कमी।
- लगातार बिजली आपूर्ति तक सीमित पहुँच, जो उत्पादकता और सिंचाई दक्षता को प्रभावित करती है।
- आर्थिक निर्भरता:
- जिले की अर्थव्यवस्था कृषि पर बहुत अधिक निर्भर है, जिससे यह अपर्याप्त बुनियादी ढांचे, अप्रत्याशित मौसम पैटर्न और संसाधन सीमाओं जैसे मुद्दों के प्रति संवेदनशील है।
- अपनी क्षमता के बावजूद, औद्योगिक विकास और बुनियादी ढांचे की प्रगति की अनुपस्थिति क्षेत्र के आर्थिक विकास में बाधा डालती है।
शिक्षा
- संस्थान:
- जहानाबाद में मगध विश्वविद्यालय से संबद्ध कॉलेजों के साथ-साथ कई सरकारी और निजी स्कूल हैं।
- अनुग्रह नारायण कॉलेज और तकनीकी संस्थान जैसे संस्थान उच्च शिक्षा प्रदान करते हैं।
- कुछ स्कूल/कॉलेज:
- एस.एस. कॉलेज, जहानाबाद
- केन्द्रीय विद्यालय, मेन रोड, जहानाबाद
- जवाहर नवोदय विद्यालय, नाउरू, जहानाबाद
- कौशल विकास:
- व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण केंद्रों का उद्देश्य युवाओं को रोजगार योग्य कौशल से लैस करना है।
- चुनौतियाँ:
- ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अपर्याप्त बुनियादी ढांचे, शिक्षकों की कमी और उच्च शिक्षा तक सीमित पहुँच जैसी समस्याएँ हैं।
संस्कृति
- त्यौहार:
- छठ पूजा, दुर्गा पूजा, दिवाली, होली और ईद जैसे प्रमुख त्यौहार उत्साह के साथ मनाए जाते हैं।
- व्यंजन:
- जिले के व्यंजनों में लिट्टी चोखा, सत्तू पराठा, ठेकुआ और पीठा जैसे पारंपरिक बिहारी व्यंजन शामिल हैं।
- लोक परंपराएँ:
- लोक संगीत, नृत्य और कहानी सुनाना जहानाबाद की सांस्कृतिक विरासत का अभिन्न अंग हैं।
पर्यटन
जहानाबाद पर्यटन के लिए बहुत प्रसिद्ध नहीं है, लेकिन यहाँ ऐतिहासिक और धार्मिक महत्व के कई स्थल हैं:
1. दावथु, हुलासगंज:
- इस स्थल पर प्राचीन मंदिरों और मूर्तियों के ऐतिहासिक अवशेष हैं।
- ये संरचनाएँ प्राचीन मंडपों (स्तंभों वाले हॉल) और गर्भगृह (गर्भगृह) जैसी हैं।
2. अमथुआ शरीफ:
- जिला मुख्यालय से 13 किमी और काको ब्लॉक मुख्यालय से 8 किमी दूर स्थित, अमथुआ शरीफ सूफी संत सैय्यद शाह हयात रहमा का सम्मान करता है।
- आशीर्वाद लेने के लिए दूर-दूर से पर्यटक आते हैं, जो इसे एक उल्लेखनीय आध्यात्मिक स्थल बनाता है।
3. विष्णु मंदिर, काको:
- ऐतिहासिक और धार्मिक महत्व का स्थल, औपचारिक रूप से 1950 में स्थापित।
- भगवान विष्णु की एक ऐतिहासिक मूर्ति स्थापित है, जो भक्तों और पर्यटकों को समान रूप से आकर्षित करती है।
- मंदिर से सटा एक बड़ा तालाब छठ के दौरान गतिविधि का केंद्र बन जाता है, जब तीर्थयात्री भगवान भास्कर (सूर्य देव) की पूजा करने के लिए एकत्र होते हैं।
4. बराबर गुफाएँ:
- जहानाबाद से 25 किलोमीटर दक्षिण में मखदुमपुर के पास स्थित बराबर गुफाएँ तीसरी शताब्दी ई. की प्राचीन चट्टान-काटे गए बौद्ध कक्ष हैं।
- ये गुफाएँ आजीविक संप्रदाय की उत्पत्ति के रूप में प्रसिद्ध हैं, जो उन्हें एक महत्वपूर्ण सांस्कृतिक और ऐतिहासिक स्थल बनाती हैं।
- पास में ही बाबा सिद्धनाथ मंदिर है, जिसे सिद्धेश्वर नाथ मंदिर भी कहा जाता है, यह गुप्तकालीन संरचना (7वीं शताब्दी ई.) है, जिसके बारे में माना जाता है कि इसका निर्माण राजा जरासंध के ससुर बाना राजा ने करवाया था।
5. हज़रत बीबी कमाल का मुकबरा:
- यह भारत की पहली महिला सूफी संत हज़रत बीबी कमाल की दरगाह है, जो अपनी पवित्र उपचार शक्तियों के लिए जानी जाती हैं।
- माना जाता है कि वे बिहार शरीफ के हज़रत मखदूम साहब की मौसी थीं।
- भक्तगण उनकी रहस्यमयी शक्तियों में आस्था रखते हुए यहाँ आते हैं, खास तौर पर मानसिक और असाध्य रोगों के उपचार के लिए।
ये स्थल जहानाबाद की समृद्ध सांस्कृतिक और आध्यात्मिक विरासत को दर्शाते हैं, जो इतिहास, धर्म और वास्तुकला का एक अनूठा मिश्रण पेश करते हैं।
परिवहन
- सड़क मार्ग:
- जहानाबाद सड़कों से अच्छी तरह जुड़ा हुआ है, राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग 83 जिले से होकर गुजरता है, जो इसे पटना और गया से जोड़ता है।
- नियमित बस सेवाएँ जिले को आस-पास के शहरों से जोड़ती हैं।
- रेलवे:
- जहानाबाद रेलवे स्टेशन पटना-गया रेलवे लाइन पर स्थित है, जो इसे एक महत्वपूर्ण पारगमन बिंदु बनाता है।
- वायुमार्ग:
- निकटतम हवाई अड्डा गया अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डा है, जो लगभग 50 किमी दूर है, जो घरेलू और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संपर्क प्रदान करता है।
चुनौतियाँ
- आर्थिक विकास: जिले में धीमी औद्योगिक वृद्धि और सीमित रोजगार के अवसर हैं।
- बुनियादी ढाँचा: ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में पर्याप्त सड़क, स्वास्थ्य सेवा और शैक्षिक बुनियादी ढाँचे का अभाव है।
- बाढ़: जिले के कुछ हिस्से मानसून के दौरान बाढ़ की चपेट में आ जाते हैं, जिससे कृषि और आजीविका प्रभावित होती है।
निष्कर्ष
जहानाबाद, हालांकि एक छोटा जिला है, लेकिन इसका ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व बहुत अधिक है। इसकी उपजाऊ भूमि इसे एक प्रमुख कृषि केंद्र बनाती है, जबकि पटना और गया जैसे प्रमुख शहरों से इसकी निकटता आर्थिक विकास की संभावना प्रदान करती है। जिले की समृद्ध विरासत, जिसे बराबर गुफाओं जैसे स्थलों में देखा जा सकता है, इसके ऐतिहासिक महत्व को बढ़ाती है। बुनियादी ढांचे के विकास और औद्योगीकरण जैसी चुनौतियों का समाधान करके जिले की पूरी क्षमता को खोला जा सकता है और इसकी प्रगति में योगदान दिया जा सकता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

4 thoughts on “Jehanabad District: A Land with Special Ancient Sites”