Patna District: An Overview
Patna District is one of the 38-districts, located in the South-central of Bihar State, India. The largest city in Bihar, Patna serves as the state capital and the administrative headquarters of Patna district. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world, with a rich history dating back over 2,500 years. Known as Pataliputra in ancient times, it has been the center of power, education, culture and historical significance in India. Besides being an administrative hub, today, Patna is the political, economic, and educational hub of Bihar, making it one of the most important districts in the state.
Spanning an area of 3,202 square kilometers (1,236 square miles), Patna lies at 25.35° North latitude and 85.12° East longitude, and shares borders with Vaishali District and Ganges to the North, Bhojpur District and Sone River to the West, Saran District to the Northwest, Begusarai District to the East, Samastipur District to the Northeast, Jehanabad District to the South, Arwal District to the Southwest, and Nalanda District to the Southeast.
Situated on the southern bank of the Ganges, it is well connected by railways and road networks. District collectors, also known as district magistrates, are in charge of Patna’s revenue district. The district’s administrative headquarters or DM’s office is located is in Patna Collectorate. The Patna district is part of the Patna Division and it is divided into 6-Subdivision i.e. Patna Sadar, Patna City, Danapur, Masaurhi, Barh, and Paliganj. It is the most populous district of Bihar and 15th most populous district in India (As of 2011).
History of Patna
The history and tradition of Patna date back to the earliest dawn of civilization. Originally known as Pataliputra or Patalipattan, its recorded history begins around 600 B.C. Over time, the city’s name evolved through various stages, including Pataligram, Kusumpur, Patliputra, and Azimabad, before finally settling on its present name, Patna.
In the 4th century B.C., Chandragupta Maurya made Pataliputra the capital of his empire. However, after the decline of the Mauryan Empire, the city lost its prominence until the 16th century A.D., when Sher Shah Suri rose to power. Another historical perspective suggests that Patna developed from a village named Pattan or Patthan, which later transformed into Patna. According to historical accounts, Ajatashatru founded Pataliputra by expanding a village named Patali, adding the suffix Pattan to form its name. Ancient Greek texts refer to the city as Palibothra, which is believed to be Pataliputra.
Ancient Period
Ajatashatru fortified Pataliputra against repeated Lichchavi invasions, leveraging its natural riverine defenses formed by three rivers. His son Udayin shifted the capital from Rajagriha to Pataliputra, a status maintained under the Mauryas and Guptas.
During this time, Ashoka the Great governed his vast empire from Pataliputra. The city was also home to renowned warriors like Chandragupta Maurya and Samudragupta, who launched military campaigns from here. Chandragupta Vikramaditya repelled invaders such as the Shakas and Huns from this city.
Pataliputra was a center of learning and administration, hosting influential figures like Kautilya (Chanakya), who wrote the Arthashastra here. Greek ambassador Megasthenes resided in the city during Chandragupta Maurya’s reign. Chinese travelers Fa-Hien (5th century A.D.) and Hiuen-Tsang (7th century A.D.) also documented its significance.
Medieval and Mughal Era
In 1703, Prince Azim-us-Shan, grandson of Aurangzeb, was appointed Governor of Patna and attempted to transform the city, renaming it Azimabad. However, the local population continued to call it Patna. Earlier, Sher Shah Suri had moved his capital from Biharsharif to Patna, further strengthening its importance. Old Patna was once a walled city, remnants of which can still be seen today.
Geography and Agriculture
After the formation of the new district, Patna does not contain any hilly terrain. Patna’s landscape is entirely alluvial and flat, making it one of the most highly fertile and heavily cultivated regions in India. The district is divided into two natural regions:
- A narrow strip (~8 km wide) along the southern bank of the Ganges, characterized by highly fertile soil.
- Alluvial plains covering the remaining area, ideal for agriculture.
The region lacks significant forest wealth, but the alluvial soil supports extensive agricultural land which is interspersed with mango orchards, palmyra, date palm and bamboo groves. Common trees include bel, siris, jackfruit, and red cotton trees. Rice is the dominant crop, covering more than one-third of the cultivated area. Other major crops include maize, pulses, wheat, and oilseeds, while cash crops like vegetables and watermelons thrive in the Diara belt. The Ganga and its tributaries play a crucial role in irrigation and agriculture, enhancing the region’s prosperity. Weeds like ammannia, citriculari, hygrophile, and sesbania grow in the areas that border the Ganges. Dry shrub jungles are sometimes seen in the villages away from the rivers.
Climate
Due to being so close to four huge rivers, Patna experiences a tropical climate with hot summers, high humidity, and cold winters:
- Summer (April–July): Temperatures soar up to 46°C, with intense heat till the moisture laiden monsoon wind bring some much-needed relief to the parched fields.
- Monsoon (August–September): Heavy rainfall provides relief from the heat.
- Winter (November–February): Chilly nights and sunny days characterize this season till the arrival of the spring that brings the weather to a full cycle.
- Spring (March-April): Marks the transition from winter to summer.
The local almanac traditionally divides the year into six seasons, including mild summer and mild winter, in addition to the four primary seasons.
Patna’s rich historical, cultural, and geographical significance makes it a vital part of India’s heritage, embodying centuries of evolution and development.
Key Facts About patna District
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Division: Patna
- Established: 1764
- Area: 3,202 km2 (1,236 sq mi)
- Coordinates: 25°25′N 85°10′E
- District Headquarters: Patna city
- District Magistrate: Dr. Chandrashekhar Singh, IAS
- No. of Subdivision: 6 (Patna Sadar, Patna City, Barh, Masaurhi, Paliganj, Danapur)
- Population:
- Total: 58,38,465
- Density: 1,823/km2 (4,720/sq mi)
- Literacy Rate: 70.68%
- Sex Ratio: 897/1000
- Gram Panchayats: 322
- Villages: 1395
- No. of Blocks: 23
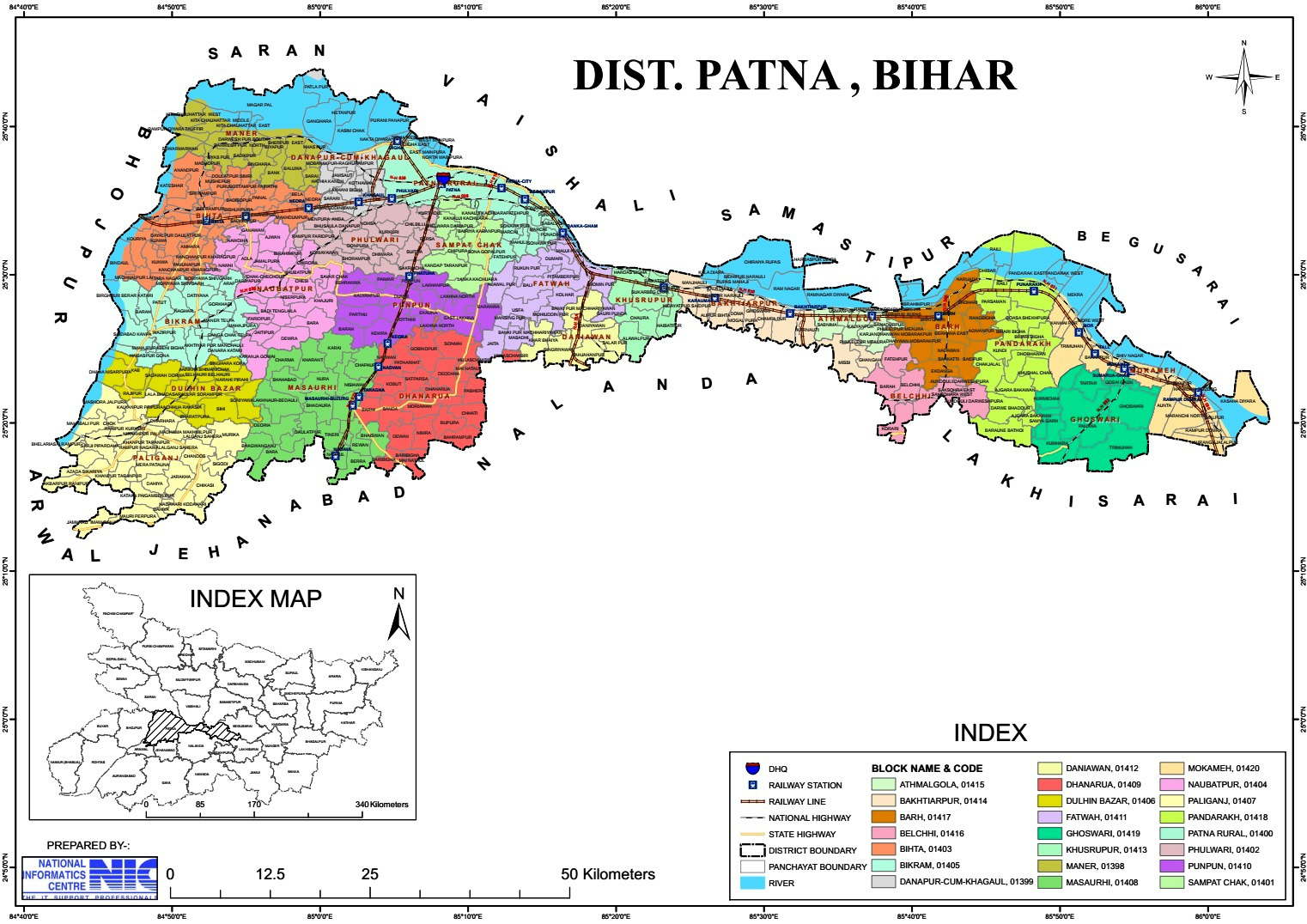
- Patna Sadar, Sampatchak, Phulwari Sharif, Fatuha, Daniyawaan, Khusrupur, Athmalgola, Mokama, Belchi, Ghoswari, Pandarak, Bakhtiyarpur, Barh, Masaurhi, Punpun, Dhanarua, Danapur, Maner, Bihta, Naubatpur, Paliganj, Dulhin Bazar and Bikram.
- Municipal Corporation (Nagar Nigam): 1 (Patna)
- Municipal Council (Nagar Parisad): 6 (Barh, Danapur, Khagaul, Masaurhi, Mokama, Phulwari)
- Nagar Panchayat: 6 (Bakhtiyapur, Fatuha, Khusrupur, Maner, Naubatpur, Vikram)
- Lok Sabha Constituency: The district has 3 parliament constituencies:
- 30-Patna Sahib, covers Bakhtiarpur, Digha, Bankipur, Kumhrar, Patna Sahib and Fatuha.
- 31-Pataliputra, covers Danapur, Maner, Phulwari, Masaurhi, Paliganj, and Bikram.
- 28-Munger/Monghyr, covers Barh and Mokama and shared with Munger district.
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies:
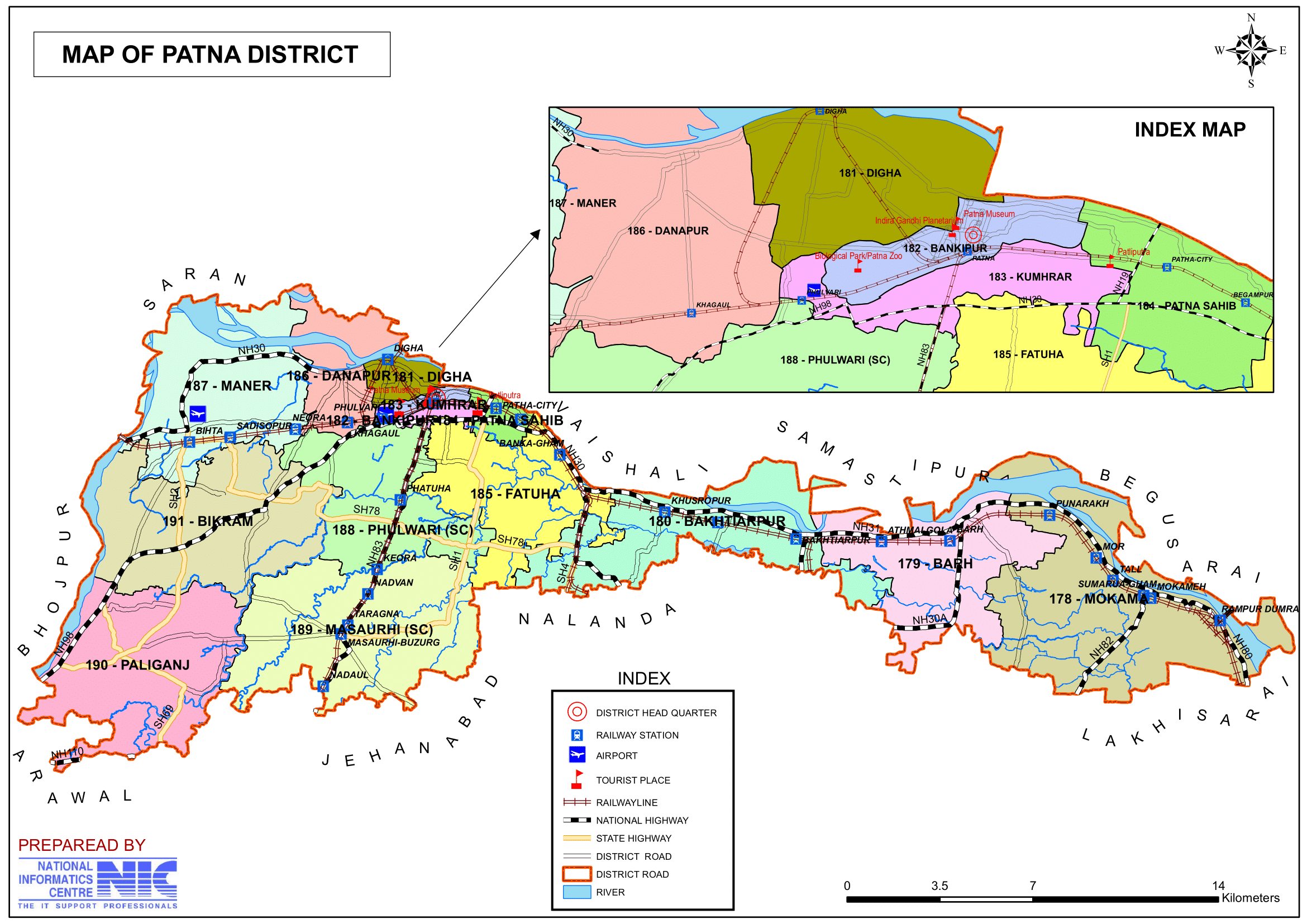
- 178-Mokama, 179-Barh, 180-Bakhtiarpur, 181-Digha, 182-Bankipur, 183-Kumhrar, 184-Patna Sahib, 185-Fatuha, 186-Danapur, 187-Maner, 188-Phulwari (SC), 189-Masaurhi (SC), 190-Paliganj, 191-Bikram.
- Altitude: 53 meters
- Postal Code: 800001
- Telephone Code: +0612
- Vehicle Code: BR-01
- Time Zone: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- Major Highways: NH-30, NH-83
- Human Development Index (2016): 0.811 (High)
- Official Website: patna.nic.in
Police Stations: 67
- Agamkuan, Air Port, Akilpur, Alamganj, Athmalgola, Bahadurpur, Bakhtiyarpur, Barh, Belachii, Beur, Bhagwanganj, Bhaudaur, Bihta, Bikram, Buddha Colony, Bypass, Chowk, Danapur, Daniyawa, Dhanarua, Didarganj, Digha, Dulhin Bazar, Fathua, Fulwarisarif, Gandhi Maidan, Gardanibagh, Gaurichak, Ghoswari, Gopalpur, Hathidah, Jakkanpur, Janipur, Kadamkuan, Kadirganj, Kankarbagh, Khajekala, Khaugal, Khushrupur, Kotwali, Malsalami, Maner, Marachii, Masaudhi, Mehndiganj, Mokama, Naubatpur, Paliganj, Panchmahla, Pandarak, Parsa Bazar, Patliputra, Patrakar Nagar, Pirbahor, Punpun, Rajeev Nagar, Ramkrishna Nagar, Rani Talab, Rupaspur, S K Puri, Sachiwalya, Sahjahapur, Sahpur, Saksohra, Shastri Nagar, Sigaudi.
Hospitals:
- Ford Hospital and Research Centre
- Mediversal Multi Superspecialty Hospital
- PMCH – Patna Medical College and Hospital
- Mahavir Cancer Institute and Research Centre
- NMCH – Nalanda Medical College and Hospital
- IGIMS – Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences
- AIIMS – All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna
Key Features:
- Capital of Bihar and the oldest continuously inhabited city in India.
- Major historical sites: Golghar, Patna Sahib Gurudwara, and Kumhrar.
- Economic hub with industries, education centers, and administrative importance.
- Significance: It is the administrative and economic heart of Bihar.
Geography
- Location: Located in south-central Bihar, Patna is situated on the southern bank of the Ganga River.
- Bordering Districts:
- North: Saran, Vaishali, and Samastipur
- South: Jehanabad, Nalanda, and Gaya
- East: Lakhisarai and Begusarai
- West: Bhojpur and Arwal
- Area: 3,202 square kilometers
- Topography:
- Flat alluvial plains of the Indo-Gangetic region, making it highly fertile.
- Several rivers flow through the district, including Ganga, Son, Punpun, and Gandak.
- Climate:
- Hot summers (April-June) with temperatures reaching 45°C.
- Monsoon (July-September) brings heavy rainfall.
- Cool winters (December-February) with temperatures dropping to 5°C.
History
Ancient Period
- Ancient Origins:
- Patna, an ancient city with a glorious past, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world.
- Founded in 490 BCE by the king of Magadha.
- Ancient Patna (Pataliputra):
- Known as Pataliputra, it served as the capital of the Magadha Empire.
- Ruled by successive dynasties including the Haryanka, Nanda, Mauryan, Shunga, Gupta, and Pala empires.
- Magadha Empire (600 BCE – 300 BCE)
- Maurya Empire (321 BCE – 185 BCE) – Chandragupta Maurya and Samrat Ashoka (who promoted Buddhism) ruled from here.
- Gupta Empire (4th – 6th century CE)
- Acted as a major seat of power, learning, and fine arts.
- Home to renowned scholars and figures such as Gautam Buddha, Aryabhata, Panini, Vātsyāyana, Chanakya (whose Arthashastra remains influential), and Kālidāsa.
- During the Mauryan period (around 400 BCE), the population of Pataliputra was approximately 400,000.
- Patna has also been significant for Jain traditions, Persian studies, and is the birthplace of Sikh Guru Gobind Singh (the tenth Guru).
- Famous Travelers like Megasthenes, Fa-Hien, and Hiuen Tsang visited Pataliputra and praised its grandeur.
- Cultural and Political Centre:
- Patna (Pataliputra) was a vibrant political and cultural centre of the Indian subcontinent.
- Decline and Revival:
- With the fall of the Gupta Empire, Patna lost much of its ancient glory.
- In the 17th century, the British revived Patna as a centre of international trade.
Medieval Period
- During the Mughal period, Patna became a center for trade, learning, and Sufi culture.
- Sher Shah Suri renamed the city Patna and built roads and forts.
Colonial & Modern Era
- The British East India Company established Patna as an administrative center in 1764 after the Battle of Buxar.
- It played a key role in India’s Independence Movement, with leaders like Rajendra Prasad and Jayaprakash Narayan.
- Post-independence, Patna became the political and economic center of Bihar.
- Establishment as a Provincial Council (1770):
- The modern district of Patna was created in September 1770 by the British.
- It was established as a provincial council to supervise revenue matters in Bihar.
- Formation as a Judicial District (1793):
- In 1793, Patna was designated as a separate judicial district.
- This change marked the foundation of the modern administrative structure of the district.
- Re-Organization in 1972:
- The re-organization of districts in Bihar took effect in 1972.
- On November 9, 1972, Nalanda district was formed by carving out the Bihar Sharif sub-division from Patna district.
This historical evolution laid the groundwork for the modern governance and administrative framework in Patna, shaping it into the influential district it is today.
Demographics (As per the 2011 Census)
- Population:
- Total Population: Patna district has a population of approximately 5,838,465 (Now estimated over 7 million)
- Males Population: 3078512
- Females Population: 2759953
- Total Population: Patna district has a population of approximately 5,838,465 (Now estimated over 7 million)
- Ranking: st in India (out of 640 districts).
- Density: 1,823 persons per square kilometer (4,720/sq mi) (one of the highest in Bihar).
- Population Growth (2001–2011): 23.73% reflecting significant population increase.
- Sex Ratio: 897 females per 1,000 males.
- Literacy Rate: 70.68%, one of the highest in Bihar and with significant efforts being made to improve education access and quality.
- Male Literacy Rate: 78.48%
- Female Literacy Rate: 61.96%
- Urban Population: (2514590) 43.07% of the total population lives in urban areas.
- Rural Population: (3323875) 56.93% of the total population lives in rural areas.
- Population within the age group of (0 to 6 years): 943552 (16.16%) of Total Population.
- Total Number of Households: 975578
- Religious Composition (2011 Census): The majority of the population follows Hinduism, with a significant Muslim community and other communities forming a significant part.
- Hinduism: 91.74%
- Scheduled Castes: (920918) 15.77% of the total population.
- Scheduled Tribes: (9069) 0.15% of the total population.
- Islam: 7.54%
- Other or not stated: 0.72%
- Hinduism: 91.74%
- Urban vs. Rural:
- Urban – Patna city is the largest urban center in Bihar.
- Rural – Several villages are still dependent on agriculture.
- Languages Spoken: Hindi, Magahi, Bhojpuri, Urdu, and English.
- Magahi: 46.35%
- Hindi: 43.77%
- Urdu: 5.19%
- Bhojpuri: 2.67%
- Maithili: 1.24%
- Others: 0.78% (Bengali and Oriya)
Administration
- The district is headed by an IAS officer of the rank of District Magistrate (DM).
- Administrative headquarters (DM’s office): Patna city
- The district is divided into Sub-divisions or Tehsils, and these Tehsils are further divided into Blocks.
- Subdivisions:
- The district has 6 subdivisions or Tehsils: Patna Sadar, Barh, Masaurhi, Danapur, Paliganj and Patna City (Old Patna area)
- Each subdivision is led by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM) who is in charge of development, revenue-related tasks, and maintaining law and order.
- Blocks and Circles:
- Patna district comprises 23 administrative Blocks and Circles under 6 subdivisions are: Each block responsible for local governance and development.
- Patna Sadar – Patna Sadar, Sampatchak and Phulwari Sharif
- Masaurhi – Masaurhi, Punpun and Dhanarua
- Patna City – Fatuha, Daniyawaan and Khusrupur
- Paliganj – Paliganj, Dulhin Bazar and Bikram
- Danapur – Danapur, Maner, Bihta and Naubatpur
- Barh – Athmalgola, Mokama, Belchi, Ghoswari, Pandarak, Bakhtiyarpur and Barh
- A Circle officer (CO) leads each circle, while a Block Development Officer (BDO) leads each block.
- Patna district comprises 23 administrative Blocks and Circles under 6 subdivisions are: Each block responsible for local governance and development.
- Lok Sabha Constituencies:
- The district has 3 parliament constituencies: 30-Patna Sahib, 31-Pataliputra and 28-Munger/Monghyr.
- Vidhan Sabha Constituencies: The district has 14 Assembly seats.
- 178-Mokama, 179-Barh, 180-Bakhtiarpur, 181-Digha, 182-Bankipur, 183-Kumhrar, 184-Patna Sahib, 185-Fatuha, 186-Danapur, 187-Maner, 188-Phulwari (SC), 189-Masaurhi (SC), 190-Paliganj, 191-Bikram.
Organization Chart

Overall Roles and responsibilities of the Collectorate:
Plays a pivotal role in district administration and Responsible for maintaining law and order, planning, development, revenue, and disaster management within the district.
- Collector (I.A.S Cadre):
- Head of the District: Acts as the chief executive and District Magistrate.
- Law and Order: Maintains peace and enforces law and order in the district.
- Planning & Development: Oversees planning and development projects.
- Administration of Scheduled/Agency Areas: Manages areas designated as scheduled or under special agency administration.
- Election Management & Arms Licensing: Handles general elections and oversees the licensing of arms.
- Additional Collector (B.A.S Cadre):
- Revenue Administration: Runs revenue-related functions across various district departments.
- Additional District Magistrate: Shares responsibilities in maintaining law and order and administering civil functions.
- Key Responsibilities: Oversees civil supplies, land matters, management of mines and minerals, and supervises village officers.
- District Development Commissioner (B.A.S Cadre):
- Developmental Activities: Manages and coordinates various developmental initiatives across the district.
- Key Departments Overseen:
- District Medical and Health Department.
- Social Welfare Department.
- BC (Backward Classes) Welfare and BC Corporation.
- Disabled Welfare.
- Housing and other related departments.
- Additional Collector (Disaster) (B.A.S Cadre):
- Disaster Management: Focuses on planning and coordinating activities related to disaster management.
- Key Responsibilities: Oversees the disaster section and other related developmental departments during emergencies.
These roles collectively ensure that the district is well-governed, with a focus on maintaining law and order, efficient revenue collection, effective disaster management, and sustainable development across various sectors.
Economy
Patna has historically been a significant agricultural and trade hub, with grain, sugarcane, sesame, and medium-grained Patna rice being its primary exports. The city has evolved into an important business and luxury brand center in eastern India.
Economic Growth
- Patna’s economy has experienced sustained growth since 2005, driven by:
- Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry
- Service sector
- Green revolution businesses
- World Bank Report (2009): Ranked 2nd best city in India to start a business.
- GDP per capita (2015): ₹1,06,000 (As of 2015)
- GDP growth rate (2015): 7.29%.
- Fastest Growing City:
- 21st fastest-growing city in the world.
- 5th fastest-growing city in India.
- Expected to grow at 3.72% annually.
Agriculture
- Despite urbanization, agriculture remains significant in rural areas.
- Major crops include:
- Paddy, maize, pulses, wheat, oilseeds.
- One-third of sown area is dedicated to rice (paddy).
- Cash crops: Vegetables, watermelons (grown in the Diara belt).
- Dairy farming and fisheries are also important.
Industrial Sector & Business Hub
- Patna is one of the fastest-growing cities in India.
- Sugar Industry: Several sugar mills are located in and around Patna.
- Agro-processing Industry: Plays a major role in the region’s economy.
- Other Key Industries:
- Leather Industry
- Handicrafts
- Retail & Luxury Brands
- Food processing (Rice mills, dairy, sugar mills, biscuit factories)
- Handloom & textile industry
- IT & Software Services – Patna is emerging as an IT hub.
- Real estate boom due to urban expansion.
Industries, Organizations and companies associated with Bihar:
1. Bihar State Road Transport Corporation (BSRTC):
- Type: State-owned corporation.
- Function: Provides road transport services within Bihar and to neighboring states.
- Services: Operates intercity and interstate bus services, aiming to offer affordable and efficient transportation to the public.
2. Bihar State Tourism Development Corporation (BSTDC):
- Established: 1980.
- Purpose: Develop and promote tourism in Bihar.
- Initiatives: Manages tourist bungalows, cafeterias, restaurants, transportation facilities, and a ropeway at various tourist spots.
- Website: bstdc.bihar.gov.in
3. Taasir:
- Type: Urdu-language daily newspaper.
- Headquarters: Patna, Bihar.
- Coverage: Focuses on regional, national, and international news, catering to the Urdu-speaking population.
4. Barh Super Thermal Power Station:
- Location: Barh, Bihar.
- Operator: National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC).
- Capacity: Planned total capacity of 3,300 MW, with 1,320 MW currently operational and 1,980 MW under construction.
- Significance: Aims to meet the growing power demands of Bihar and neighboring regions.
5. Bihar State Power Holding Company Limited (BSPHCL):
- Formerly: Bihar State Electricity Board (BSEB).
- Function: Acts as the apex holding company for electricity generation, transmission, and distribution in Bihar.
- Subsidiaries:
- Bihar State Power Generation Company Limited.
- North Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited.
- Bihar State Power Transmission Company Limited.
- South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited.
- Website: bsphcl.co.in
6. South Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited (SBPDCL):
- Function: Distributes electricity in the southern regions of Bihar.
- Services: Provides new electricity connections, billing, and customer support.
- Website: sbpdcl.co.in
7. North Bihar Power Distribution Company Limited (NBPDCL):
- Function: Distributes electricity in the northern regions of Bihar.
- Services: Offers electricity distribution, billing, and customer services.
- Website: nbpdcl.co.in
8. Husk Power Systems:
- Founded: 2008.
- Type: Private company.
- Focus: Provides renewable energy solutions in rural areas.
- Technology: Utilizes rice husks and other biomass to generate electricity, establishing microgrids in off-grid villages.
- Impact: Aims to promote sustainable development and improve the quality of life in rural communities.
9. Sattuz:
- Type: Food and beverage brand.
- Product: Specializes in traditional Indian beverages, particularly “Sattu,” a roasted gram flour-based drink popular in Bihar.
- Goal: Revitalizes traditional recipes with modern packaging and marketing.
10. Muskan Constructions Pvt. Ltd.:
- Type: Private construction company.
- Services: Engages in infrastructure development, including residential and commercial projects.
- Reputation: Known for quality construction and timely project delivery in Bihar.
11. SAIJA Finance Private Limited:
- Established: 2007.
- Type: Non-Banking Financial Company-Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI).
- Services: Provides microloans to low-income households and small entrepreneurs in Bihar and neighboring states.
- Objective: Aims to promote financial inclusion and support economic development at the grassroots level.
These organizations and companies play significant roles in the development and economy of Bihar, contributing across sectors such as transportation, tourism, energy, media, construction, and finance.
Economic Challenges
- Backward Region: In 2006, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj identified Patna as one of India’s 250 most backward districts.
- Receives aid from the Backward Regions Grant Fund (BRGF) for economic development.
- Unemployment and migration to metro cities.
- Need for more large-scale industries.
Patna is an emerging economic center in eastern India, with robust growth in FMCG, services, agriculture, and industry. Despite its challenges, it remains one of the fastest-growing cities in India and the world.
Education
School Education:
- Types of Schools:
- Government-run schools
- Private schools
- Affiliations:
- Bihar School Examination Board (BSEB)
- Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE)
- National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS)
- Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE)
- Medium of Instruction: Primarily Hindi and English
Higher Secondary & Degree Education (10+2+3/4 Plan):
- Structure:
- 10 years of schooling (secondary education)
- Enrollment in higher secondary schools (affiliated with Bihar State Intermediate Board, CISCE, NIOS, or CBSE)
- Streams Offered: Arts, Commerce and Science
- Post-Secondary Options:
- General degree courses in various fields
- Professional degree courses (e.g., law, engineering, medicine)
- Some prestigious schools like:
- Loyola High School
- Notre Dame Academy
- St. Xavier’s High School
- Don Bosco Academy
- St. Michael’s High School
- Delhi Public School, Patna
- DAV BSEB
Major Higher Educational Institutions in Patna:
- Patna University (Established 1917, Seventh oldest modern university in the Indian subcontinent).
- IIT Patna (Indian Institute of Technology).
- A N College
- Patna College
- Magadh University
- Patna Dental College
- Bihar National College
- Amity University, Patna
- Patna Women’s College
- Magadh Mahila College
- Nalanda Open University
- St. Xavier’s College, Patna
- Patliputra University, Patna
- Central University of South Bihar
- Aryabhatta Knowledge University
- Chanakya National Law University
- Birla Institute of Technology, Patna
- R.P. Sharma Institute of Technology
- Chandragupt Institute of Management
- Bihar Animal Sciences University, Patna
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Patna
- National Institute of Technology, Patna (NIT-P)
- Maulana Azad College of Engineering and Technology
- National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT Patna)
- Maulana Mazharul Haque Arabic and Persian University
- Rajendra Memorial Research Institute of Medical Sciences
- Nalanda Medical College & Hospital, Patna
- Patna Medical College Hospital (PMCH), Patna
- Additionally, Patna is home to various other universities, primary schools, and secondary schools.
Educational infrastructure in Patna, ranging from primary schooling to higher education, and highlighting its longstanding tradition of academic excellence.
Challenges
- High competition and lack of quality colleges in some sectors.
- Students often migrate to Delhi, Pune, and Bangalore for higher education.
Festivals, Culture & Heritage
Festivals:
- Chhath Puja:
- The biggest festival in Patna, celebrated grandly on the banks of the Ganga River.
- A major Hindu festival dedicated to the Sun God (Surya), celebrated with immense faith.
- Held twice a year:
- In Chaitra (summer)
- In Kartik (beginning of winter)
- Devotees observe rigorous rituals including holy bathing, fasting, and offering water (arghya) to the setting and rising sun.
- Makar Sankranti (Tila Sankranti):
- Celebrated at the beginning of summer and marks the harvest season.
- Considered auspicious as it symbolizes the commencement of a new year in Indian culture.
- Holi:
- One of the biggest and most colorful festivals in the district.
- Celebrated with great enthusiasm, where people engage in joyous, vibrant festivities that light up the atmosphere.
- Durga Puja, Diwali, Janamashtami, Kali Pooja, Sarswati Pooja, Nag Panchemi, Shiv Ratri, Bakarid, Eid and Muharram are also widely celebrated.
- Bhojpuri folk songs and dances are a major part of the cultural identity.
- Patna Kalam (Mughal painting style) has historical significance.
- Bhojpuri, Magahi, and Hindi literature flourish in the district.
Cuisines:
- Traditional Staples:
- Daily meals typically include dishes such as sabzi (vegetable curry), roti (flatbread), dal (lentils), and bhaji (stir-fried vegetables).
- Signature Dishes:
- Litti Chokha: A popular Bihari delicacy made with roasted wheat balls (litti) served with mashed vegetables (chokha).
- Kadhi: A yogurt-based curry often spiced with traditional seasonings.
- Jhal Moori: A spicy snack mix, beloved by locals.
- Sattu: Roasted gram flour, used in various dishes and beverages like Sattu Paratha, Dal Pitha and Dal Puri.
- Sweets & Desserts:
- Renowned for its mouthwatering sweets made with pure desi ghee, which are available in local sweet shops and are commonly prepared at home during ceremonial occasions.
- Sweets like Khaja, Balushahi, Tilkut, Thekua and Malpua are famous.
Costumes:
- Traditional Male Attire:
- Dhotis, kurtas, and pajamas are commonly worn.
- Young men may also be seen in shirts and trousers, blending traditional and modern styles.
- Traditional Female Attire:
- Women traditionally wear Ghaghara (long skirts), choli (blouses) and Saree, reflecting the rich Hindu cultural heritage.
- Attire of the Muslim Community:
- Men: Typically dress in kurta and pajama.
- Women: Often wear burkas, following traditional Muslim attire.
Religions:
- Religious Composition:
- The district is predominantly Hindu, but it also has a significant Muslim community.
- Tribal communities also reside under Patna district, with many adhering to their own indigenous religious practices.
- Cultural Integration:
- The region’s cultural landscape is a vibrant mix of various religious traditions, with communities having coexisted for many decades.
- Social Harmony:
- Despite the diversity, there is a strong sense of social unity and hospitality, which leaves a lasting impression on visitors.
- Heritage and Tradition:
- The rich tapestry of religious traditions contributes to a unique cultural heritage, which is evident in festivals, rituals, and everyday practices in Patna.
Tourism & Historical Heritage
1. Mahavir Mandir, Patna: A Sacred Haven of Devotion
Mahavir Mandir, one of the most revered Hindu temples dedicated to Lord Hanuman, is located in Patna, Bihar. Renowned as one of North India’s most prominent religious sites, the temple attracts millions of devotees annually. The idol of Sankat Mochan Hanuman holds a special place in the hearts of worshippers, especially during the grand celebrations of Ram Navami.
Historical Significance:
- The temple’s origins date back centuries, with records indicating its establishment by Swami Balanand of the Ramanandi sect in 1730 AD. It was officially declared a public temple by the Patna High Court in 1948. The temple has been under the Ramanandi sect since 1900 AD and was previously under the Gosain Sanyasi sect until 1948. Over time, Mahavir Mandir has grown into a significant religious and charitable institution.
- Following India’s partition in 1947, the temple saw a surge in devotees, leading to its reconstruction between 1983 and 1985. The newly built grand marble structure, completed with voluntary donations and ‘Kar Seva,’ stands as a testament to unwavering faith.
Architectural Grandeur:
Spread over 10,000 square feet, the temple complex consists of multiple sanctums:
- Ground Floor: Houses two idols of Lord Hanuman, representing his roles in protecting the virtuous and eliminating evil. The corridor surrounding the sanctum also features Lord Shiva’s presence.
- First Floor: Enshrines deities including Lord Rama, Lord Krishna, Goddess Durga, Lord Shiva, and Goddess Parvati. A notable attraction is the Ram Setu Shila, a floating stone believed to be from the Ramayana’s legendary bridge.
- Second Floor: Features the Sanskar Mandap, a dedicated space for religious rituals, mantras, and recitations from scriptures like the Valmiki Ramayana. Scenes from the Ramayana are artistically depicted here.
- Temple Premises: The complex includes an office, a bookstore, a religious goods shop, and an astrologer’s center. Devotees can also visit the Peepal tree where Lord Shani is worshipped.
Spiritual and Charitable Initiatives:
Mahavir Mandir is not only a spiritual center but also a hub of humanitarian efforts. The Shri Mahavir Sthan Nyas Samiti, the managing trust, runs several charitable hospitals and initiatives, including:
- Mahavir Vatsalya Hospital
- Mahavir Cancer Institute and Research Center
- The trust provides financial aid for cancer treatment and supports the underprivileged through orphanages and other welfare programs.
- Mahavir Arogya Sansthan
- Mahavir Netralaya
Unique Features:
- Naivedyam Prasadam: A famous offering made from gram flour, sugar, cashews, raisins, cardamom, and Kashmiri saffron, prepared by experts from Tirupati.
- Inclusive Worship: The temple welcomes priests from various backgrounds, including Sanskrit scholars of the Ramanandi sect, Bairagi sadhus, and Dalit priests.
- Shravan Kumar Award: Instituted to honor individuals dedicated to parental care, with financial awards up to ₹1,00,000.
Festivals and Celebrations:
- Ram Navami: The grandest festival at Mahavir Mandir, drawing thousands of devotees.
- Hanuman Jayanti: Celebrated on the 14th night of the Kartika month with great fervor.
Mahavir Mandir stands as a beacon of faith, devotion, and service. Its historical legacy, magnificent architecture, and philanthropic contributions make it one of the most revered temples in India. Whether seeking spiritual solace or engaging in charitable efforts, a visit to Mahavir Mandir is an enriching experience for devotees and visitors alike. Official Websites of Temple: mahavirmandirpatna.org
2. Bapu Tower: A monumental tribute to Mahatma Gandhi in Patna, Bihar:
- Location & Significance:
- Situated in Gardanibagh, Patna, Bihar.
- Dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi, the Father of the Nation.
- The first-ever tower in India specifically built as a tribute to Gandhi’s legacy.
- Architectural Features:
- Height & Structure:
- Tower stands at 120 feet tall and comprises six stories.
- Designed with both circular and rectangular sections that create an immersive narrative of Gandhi’s life.
- Exterior Design:
- The exterior is clad with 42,000 kg of copper, which transforms into beautiful rainbow hues due to the natural reaction of oxygen and nitrogen.
- Green Technology:
- Incorporates sustainable development practices and environmentally friendly construction methods.
- Height & Structure:
- Purpose & Function:
- Serves as an architectural marvel as well as a hub for learning and reflection on Gandhi’s contributions to India’s freedom struggle.
- Houses various galleries, research centers, lounges for distinguished guests, and administrative offices.
- Offers an interactive turntable theatre show on the ground floor that brings Gandhi’s biography to life for visitors.
- Exhibition & Investment:
- Features an extensive exhibition on the history of Gandhi and Bihar, costing approximately Rs 45 crore.
- The exhibition includes sculptures and artifacts meticulously crafted in Ahmedabad.
- Construction & Timeline:
- Construction began on October 2, 2018 under the visionary guidance of Chief Minister Nitish Kumar.
- Despite several extensions beyond the initial completion target, the tower is scheduled to be inaugurated on February 4, 2024.
- The total construction cost is Rs 129 crore.
- The tower spans seven acres of land.
- Cultural & Educational Impact:
- Bapu Tower is designed to be a vital educational resource for children, students, and researchers.
- It offers visitors an enlightening experience, showcasing historical events, Gandhi’s philosophical thoughts, and his deep connection with Bihar.
- The tower is set to become a prominent cultural landmark and a source of inspiration for future generations.
3. Gandhi Sangrahalaya (Gandhi Museum) in Patna:
- Location: Situated in Patna, Bihar.
- Year of Construction: Built in 1967.
- Purpose & Significance:
- A public service institution dedicated to showcasing the life and principles of Mahatma Gandhi.
- Highlights Gandhi’s role in Bihar during India’s freedom struggle.
- Serves as a key monument to honor the legacy of the “Father of the Nation.”
- Exhibits & Features:
- Photograph Section: Displays a collection of photographs of Mahatma Gandhi, documenting different stages of his life.
- Library: Houses a rich collection of books, periodicals, literature, and audio-video material related to Gandhi’s life and philosophy.
- Visitor Experience:
- Recognized as one of the best places to see in Patna for those interested in the historical and cultural contributions of Mahatma Gandhi.
4. Khuda Baksh Oriental Library:
- Historical Overview:
- Founded as a Private Collection:
- Began in the mid-18th century with 1,400 manuscripts and rare books.
- Initiated by Khuda Bakhsh, a government officer who inherited the collection from his father.
- Public Opening: The library was first opened to the public in 1891.
- Founded as a Private Collection:
- Current Collection:
- Manuscripts: Over 21,000 manuscripts.
- Printed Books: Approximately 250,000 printed books.
- Languages Represented: Persian, Arabic, Urdu, Hindi, English, Turkish, and many other languages.
- Notable Items in the Collection:
- Tarikh-e-Khandan-e-Timuriyah:
- A lavishly illustrated text detailing the history of Taimur and his descendants.
- The only extant copy of this work is housed in the library.
- Lord Byron’s “Ode to Napoleon”: A copy with two additional stanzas believed to be in Byron’s own handwriting.
- Sword of Nadir Shah: An important historical artifact.
- Miniature Copy of the Quran: Remarkably small at just 2.5 mm wide.
- Tarikh-e-Khandan-e-Timuriyah:
- Manuscript Conservation Efforts:
- Functions as a Manuscript Conservation Centre.
- Preventive Conservation: Over 8,468 manuscripts have been safeguarded.
- Curative Conservation: Conservation treatment has been undertaken for 247 manuscripts.
- A significant number of manuscripts have been digitized and made available online.
- Research and Global Importance:
- Recognized as one of the largest repositories of rare and unique manuscripts in the world.
- Attracts researchers and scholars from across the globe.
- Notable Visitors:
- The library has welcomed at least six viceroys.
- Prominent figures such as Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Rabindranath Tagore.
- Four Presidents of India have visited, including APJ Abdul Kalam.
The Khuda Baksh Oriental Library is a treasure trove of historical documents and rare manuscripts, playing a critical role in preserving and promoting cultural heritage and scholarship worldwide.
5. Kumhrar’s Park:
- Location & Historical Significance:
- Kumhrar’s Park is situated in the middle of the city (Patna) and is considered the ancient heart of the city.
- Excavations around Patna have uncovered remains of the ancient city of Pataliputra.
- Major Archaeological Findings at Kumhrar:
- 80-Pillared Hall:
- An impressive hall with 80 pillars and a wooden platform was discovered in Kumhrar.
- Initially, this hall was thought to be a royal durbar (a hall for royal audiences).
- Later findings revealed that it served as an assembly hall for Buddhists and was built during the time of Emperor Ashoka.
- Monastery-cum-Hospital (Arogya Vihar):
- Within the park, a structure known as Arogya Vihar was uncovered.
- This building functioned both as a monastery and a hospital.
- It dates back to the 4th-5th century CE.
- 80-Pillared Hall:
- Additional Artifact:
- A small potsherd inscribed with the word ‘Dharvantareh’ was found at the site, adding to the historical and archaeological significance of the park.
These findings collectively highlight Kumhrar’s importance in understanding the ancient history of Pataliputra and the Buddhist heritage of the region.
6. Takhat Sri Harimandir Ji Patna Sahib:
- Significance as a Takhat:
- Considered the second holiest Takhat (seat of temporal authority) in Sikhism.
- One of the five Takhts that represent the highest seats of Sikh authority.
- Historical and Religious Importance:
- Revered as the birthplace of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji Maharaj, the tenth Sikh Guru.
- The shrine has been consecrated by three Sikh Gurus, enhancing its sacred status.
- Known as a symbol of valor and fearlessness, inspiring great piety among its devotees.
- Cultural Impact:
- Holds a prominent place in the glorious heritage of Patna City.
- Also referred to as Patna Sahib, reflecting its integral role in the cultural and spiritual landscape of the region.
7. Gol Ghar in Patna:
- Historical Background:
- Built in 1786 by Captain John Garstin for the British Army.
- Constructed in response to the devastating impact of the 1770 famine in the region.
- Purpose & Structure:
- An enormous granary designed to store grain.
- Pillar-less design:
- The structure is built without internal pillars.
- Features a massive wall that is 3.6 meters thick at the base.
- Height: Stands at 29 meters tall.
- Architectural Features:
- Spiral Staircase:
- Consists of 145 steps that wind around the exterior of the granary.
- Originally designed to facilitate the transport of grain:
- Workers would carry loads up through a hole at the top and then descend via separate stairs.
- Spiral Staircase:
- Visitor Experience:
- Climbing the staircase offers a panoramic view of Patna city.
- Provides a brilliant view of the nearby Ganga River.
8. Bihar Museum:
- Location: Situated on Bailey Road, Patna.
- Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Acts as a hub of historical knowledge and showcases a multitude of artifacts.
- Designed to highlight the rich history and culture of India.
- Every statue and exhibit reflects the glorious past of the region.
- Visitor Experience:
- The museum premises are well-maintained and clean.
- It offers various sections catering to different interests.
- Children’s Favorite: An artificial wildlife sanctuary is a hit among young visitors.
- Operating Hours: Open for visitors from 10:30 AM to 5:00 PM.
- Ideal For: A perfect place to hang out with friends and family while learning about history and culture.
9. Buddha Smriti Park:
- Purpose & Commemoration:
- Developed by the Government of Bihar to commemorate the 2554th birthday of Lord Buddha.
- Also known as Buddha Memorial Park.
- Location & Size:
- Located on Frazer Road near Patna Junction, opposite the Mahavir Mandir.
- An urban oasis spanning 22 acres.
- Key Features & Attractions:
- Two Bodhi Trees:
- Planted by the Dalai Lama, these trees flank a statue of Lord Buddha, serving as a major visual highlight.
- Pataliputra Karuna Stupa:
- A 200-foot-high circular stupa that is the most prominent feature of the park.
- Houses a relic of Lord Buddha—one of the eight original relics excavated from Vaishali—in a glass enclosure.
- The stupa has multiple entrances.
- Meditation Centre:
- Modeled on the architectural plans of Nalanda University monasteries.
- Contains 60 cells from which visitors can view the stupa.
- Library & Museum:
- The library holds numerous books on Buddhism.
- The museum features artifacts and offers audio-visual and multimedia presentations about the life and teachings of Lord Buddha.
- Park of Memories: An additional section dedicated to preserving the legacy of Buddha.
- Two Bodhi Trees:
- Additional Relics:
- Several other relics, brought by His Holiness the Dalai Lama and monks from countries like Thailand, Myanmar, Japan, South Korea, and Sri Lanka, are housed in different caskets within the park.
These features make Buddha Smriti Park a comprehensive cultural and educational hub that highlights the rich legacy and teachings of Lord Buddha.
10. Sanjay Gandhi Botanical Garden (Patna Zoo):
- Location: Situated on the famous Bailey Road in Patna.
- Biodiversity:
- Home to a diverse array of birds and animals.
- Features flora and fauna from various parts of India as well as other countries.
- The on-site zoo is particularly popular among children.
- Attractions & Amenities:
- Artificial Lake: Offers boating facilities for visitors.
- Unique Wooden House: A wooden structure built on a tree that attracts visitors for its novelty.
- Visitor Experience:
- Open year-round.
- Especially busy during New Year’s Day and other holidays.
- The park becomes a vibrant hub for local families and tourists from neighboring towns.
- Popular activities include picnics and cookouts, with visitors often dressed in colorful attire to celebrate festive occasions.
11. Patna Kalam (Patna Painting Style):
- Definition & Origins:
- Patna Kalam is a unique style of Indian painting that emerged in the 18th century.
- Developed by Mughal artists, it was the first school of painting to specifically depict the lifestyle of the common people.
- Historical Significance:
- Has been in existence for almost 200 years and continues to be popular.
- Initially, the British bought these paintings as souvenirs.
- Artistic Technique:
- The process is known as “Kaji Seahi”, which distinguishes the style and technique of Patna Kalam.
12. Old Secretariat, Patna:
- Architectural Importance:
- Completed in 1917 in the Indo-Saracenic style by the British, making it one of the largest government buildings in the city.
- Features a huge bell tower set amidst a lush green garden; the bell tower stands at approximately 184 feet in height.
- Notable Elements:
- Houses a bronze statue of Bihar’s first Chief Minister, Shri Krishna Sinha (Bihar Kesari), a key attraction.
- Designed by the renowned Sydney architect Joseph Munnings and constructed by Martin Byrne of Calcutta.
- Administrative Role: Serves as the administrative headquarters for the Bihar State Government.
13. Sabhyata Dwar:
- Overview & Inauguration:
- A modern monument inaugurated by Chief Minister Nitish Kumar in 2018.
- Architectural Features:
- Located in the northern part of Gandhi Maidan.
- Constructed using red sandstone with a small stupa on top.
- Cultural Significance:
- Serves as a reminder of historical achievements and is designed as a masterpiece of architecture.
- A popular gathering spot in the evenings for locals and tourists.
14. Kalidas Rangalaya:
- Cultural Hub:
- One of Bihar’s renowned theatres located in the southeast corner of Gandhi Maidan.
- Managed by Bihar Art Theater, the regional center of the International Theatre Institute.
- Facilities:
- Includes a stage, auditorium, and the Bihar Institute of Dramatics office.
- Also houses a cafeteria named “Annapurna”.
- The complex further includes Shakuntala Janta Theater, Priyambada Children’s Theater, Anasuya Art Gallery, and Abhyathna Guest House for artists.
- Educational Programs: Offers classes in dance, music, painting, and photography.
- Role: Serves as a center for cultural performances and artistic expression in Patna.
15. Premchand Rangashala:
- Historical Background:
- Located in Rajendra Nagar, set up by the Government of Bihar in 1971.
- Considered one of the largest theatres in Eastern India.
- Administration & Renovation:
- After a period of inactivity and use by the CRPF, the auditorium was reopened for regular plays after pressure from cultural activists.
- Underwent major renovations in 2011-2012 at an estimated cost of ₹5.91 crore, increasing its seating capacity and improving its structure.
- Inauguration:
- The state-of-the-art renovated theatre was inaugurated by Chief Minister Nitish Kumar in February 2012.
16. Rabindra Parishad:
- Multi-Purpose Cultural Centre:
- Located on Beer Chand Patel Path in Patna.
- Named After:
- Rabindranath Tagore, reflecting his influence on art and literature.
- Components of the Centre:
- A musical school (Geet Bhawan).
- A library with books on and by Tagore.
- An auditorium (Rabindra Bhavan), a significant venue for cultural and theatrical events.
- Programming:
- Hosts a range of performances including theatre, live music, dance, comedy, visual art, spoken word, and children’s events.
- Renovation Details:
- Renovated between 2008 to 2010 at a cost of ₹1.5 crore.
- Increased the auditorium’s seating from 655 to 1,000.
- The updated facility was inaugurated in February 2011 by Chief Minister Nitish Kumar.
17. Bhartiya Nritya Kala Mandir:
- Institution Overview:
- A renowned institute dedicated to the promotion and preservation of Indian classical dance forms.
- Establishment:
- Founded in 1963 by Padmashree Pandit Hari Uppal Ji.
- Registered under the Bihar Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Programs and Training:
- Offers comprehensive training in various classical dance forms, including Bharatanatyam, Kathak, Odissi, Kuchipudi, and Manipuri.
- Conducts workshops, seminars, and performances to promote classical dance and cultural heritage.
- Cultural Impact:
- Plays a vital role in nurturing artistic talent and preserving the rich tradition of Indian classical dance in Patna and beyond.
Some Other Major attractions:
- Overall Importance of Patna:
- Patna attracts 41% of all tourists visiting Bihar.
- While Bodh Gaya is the most popular among foreign visitors, Patna boasts a rich blend of historical, cultural, and modern attractions.
- Additional Gurdwaras in Patna:
- Pahila Bara Gurdwara
- Gobind Ghat Gurdwara
- Guru ka Bagh Gurdwara
- Bal Leela Gurdwara
- Handi Sahib Gurdwara
- British Colonial Architecture:
- Padri Ki Haveli, High Court, Golghar, and Secretariat Building: Fine examples of British-era architecture.
- Gandhi Maidan: A historic ground where numerous freedom movement rallies took place.
- Ancient Heritage & Cultural Monuments:
- Kumhrar and Agam Kuan:
- Ruins of the ancient city of Pataliputra.
- An ancient well from the Mauryan era.
- Key sites where Ashokan architecture and ancient urban planning are evident.
- Didarganj Yakshi:
- A notable example of Mauryan art that reflects the region’s early cultural legacy.
- Kumhrar and Agam Kuan:
- Patna Planetarium (Indira Gandhi Planetarium):
- Located within the Indira Gandhi Science Complex.
- One of the largest planetariums in Asia, drawing a large number of visitors.
- Upcoming State-of-the-Art Art Landmark Museum:
- Being built on a 13.9-acre site on Bailey Road at an approximate cost of Rs. 530 crores.
- Partially opened, with full completion expected soon.
These attractions collectively showcase Patna’s rich historical legacy, vibrant religious traditions, and ongoing modern developments, making it a must-visit destination in Bihar.
Transportation
Roadways
- Extensive Road Network: Well served by a network of roads throughout the district.
- NH-31, NH-30, NH-83, and NH-98 connect Patna to other major cities.
- National Highway 31:
- Passes through Danapur, Patna, and Patna City.
- One branch of NH-31 leads to Barauni via Barh.
- Another branch proceeds to Nawada via Bihar.
- Nearly all sub-divisional headquarters (except Masaurhi) are located on this highway.
- Patna Metro (under construction) will improve urban transport.
- Inter-City Connectivity:
- Provides a vital link between North and South Bihar.
- Convenient road access to key destinations such as Bodhgaya, Rajgir, Ranchi, and Siliguri.
- Intra-City Transportation: Efficient local transportation options within Patna.
- Loknayak Ganga Path, Mahatma Gandhi Setu, Digha–Sonpur Bridge
Railways
- Main Railway Line:
- The East Central Railway main line runs parallel to the Ganga across the district.
- Patna Junction:
- The principal railway station in Patna.
- Connects Patna with major cities including Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Guwahati, Varanasi, Amritsar, Bangalore, Lucknow, and Chennai through express and super fast trains.
- Railway Lines:
- Three main railway lines running from north to south:
- Patna-Gaya Branch Line
- Fatwah-Islampur Light Railway
- Bakhtiarpur-Rajgir Branch Line
- Three main railway lines running from north to south:
- Other stations – Rajendra Nagar Terminal, Patliputra Junction, Patna Saheb, Gulzarbagh Station, Phulwari Sharif railway station, Danapur Station, Fatuha Junction railway station, Patna Metro.
Airways
- Patna Airport – One of the busiest airports in eastern India.
- Known as Jaiprakash Narayan International Airport.
- Offers excellent air connectivity with important cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, and Kolkata.
- Several airlines operate regular flights to and from this airport.
- Named after “Lok Nayak” Jayaprakash Narayan (1902–1979), a prominent independence activist and political leader.
- Bihta Air Force Station
- Upcoming Bihta Airport to handle more air traffic.
Waterways (By River):
- Navigability of the Ganges:
- The Ganges is navigable throughout the year, facilitating cargo transport.
- Smaller Rivers:
- Rivers like Punpun and Dardha become navigable only during the rainy season.
- These rivers are used for transporting agricultural produce to the grain market at Fatwah.
Challenges & Issues
- Traffic congestion and pollution.
- Urban flooding during monsoons.
- Unemployment and skill gap.
- Healthcare facilities need improvement.
Conclusion
Patna is the cultural, economic, and political hub of Bihar. With historical sites, strong education infrastructure, and growing industries, it is developing rapidly. However, infrastructure, traffic, and job opportunities need improvement to make Patna a truly modern city.
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below 😊
पटना जिला: विरासत, संस्कृति और विकास की एक विशेष भूमि
अवलोकन
पटना जिला भारत के बिहार राज्य के दक्षिण-मध्य में स्थित 38-जिलों में से एक है। बिहार का सबसे बड़ा शहर, पटना राज्य की राजधानी और पटना जिले का प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय है। यह दुनिया के सबसे पुराने लगातार बसे हुए स्थानों में से एक है, जिसका इतिहास 2,500 साल से भी पुराना है। प्राचीन काल में पाटलिपुत्र के नाम से जाना जाने वाला यह भारत में सत्ता, शिक्षा, संस्कृति और ऐतिहासिक महत्व का केंद्र रहा है। प्रशासनिक केंद्र होने के अलावा, आज पटना बिहार का राजनीतिक, आर्थिक और शैक्षिक केंद्र है, जो इसे राज्य के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण जिलों में से एक बनाता है।
3,202 वर्ग किलोमीटर (1,236 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र में फैला, पटना 25.35 डिग्री उत्तरी अक्षांश और 85.12 डिग्री पूर्वी देशांतर पर स्थित है, और उत्तर में वैशाली जिले और गंगा, पश्चिम में भोजपुर जिला और सोन नदी, उत्तरपश्चिम में सारण जिला, पूर्व में बेगूसराय जिला, पूर्वोत्तर में समस्तीपुर जिला, दक्षिण में जहानाबाद जिला, दक्षिणपश्चिम में अरवल जिला और दक्षिणपूर्व में नालंदा जिला के साथ सीमाएं साझा करता है।
गंगा के दक्षिणी तट पर स्थित, यह रेलवे और सड़क नेटवर्क द्वारा अच्छी तरह से जुड़ा हुआ है। जिला कलेक्टर, जिन्हें जिला मजिस्ट्रेट भी कहा जाता है, पटना के राजस्व जिले के प्रभारी हैं। जिले का प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय या डीएम का कार्यालय पटना कलेक्ट्रेट में स्थित है। पटना जिला पटना डिवीजन का हिस्सा है यह बिहार का सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला जिला है और भारत का 15वां सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला जिला है (2011 तक)।
पटना का इतिहास
पटना का इतिहास और परंपरा सभ्यता के आरंभिक दौर से जुड़ी हुई है। मूल रूप से पाटलिपुत्र या पाटलीपट्टन के नाम से जाना जाने वाला, इसका दर्ज इतिहास लगभग 600 ईसा पूर्व से शुरू होता है। समय के साथ, शहर का नाम विभिन्न चरणों से गुज़रा, जिसमें पाटलिग्राम, कुसुमपुर, पाटलिपुत्र और अज़ीमाबाद शामिल हैं, और अंत में इसका वर्तमान नाम पटना रखा गया।
ईसा पूर्व चौथी शताब्दी में, चंद्रगुप्त मौर्य ने पाटलिपुत्र को अपने साम्राज्य की राजधानी बनाया। हालाँकि, मौर्य साम्राज्य के पतन के बाद, शहर ने 16वीं शताब्दी ईस्वी तक अपनी प्रमुखता खो दी, जब शेर शाह सूरी सत्ता में आए। एक अन्य ऐतिहासिक परिप्रेक्ष्य से पता चलता है कि पटना का विकास पट्टन या पठान नामक एक गाँव से हुआ, जो बाद में पटना में बदल गया। ऐतिहासिक विवरणों के अनुसार, अजातशत्रु ने पाटलिपुत्र की स्थापना पाटलि नामक एक गाँव का विस्तार करके की थी, और इसके नाम में पट्टन शब्द जोड़कर इसे बनाया था। प्राचीन यूनानी ग्रंथों में इस शहर का उल्लेख पालिबोथरा के रूप में किया गया है, जिसे पाटलिपुत्र माना जाता है।
प्राचीन काल
अजातशत्रु ने तीन नदियों द्वारा निर्मित प्राकृतिक नदी सुरक्षा का लाभ उठाते हुए, बार-बार लिच्छवी आक्रमणों के खिलाफ पाटलिपुत्र को मजबूत किया। उनके बेटे उदयिन ने राजधानी को राजगृह से पाटलिपुत्र में स्थानांतरित कर दिया, जो मौर्य और गुप्त के अधीन बनी रही।
इस दौरान, महान अशोक ने पाटलिपुत्र से अपने विशाल साम्राज्य पर शासन किया। यह शहर चंद्रगुप्त मौर्य और समुद्रगुप्त जैसे प्रसिद्ध योद्धाओं का भी घर था, जिन्होंने यहीं से सैन्य अभियान शुरू किए थे। चंद्रगुप्त विक्रमादित्य ने इस शहर से शक और हूण जैसे आक्रमणकारियों को खदेड़ दिया था।
पाटलिपुत्र शिक्षा और प्रशासन का केंद्र था, जहाँ कौटिल्य (चाणक्य) जैसे प्रभावशाली व्यक्ति रहते थे, जिन्होंने यहाँ अर्थशास्त्र लिखा था। चंद्रगुप्त मौर्य के शासनकाल के दौरान यूनानी राजदूत मेगस्थनीज ने शहर में निवास किया था। चीनी यात्री फा-हियान (5वीं शताब्दी ई.) और ह्वेन-त्सांग (7वीं शताब्दी ई.) ने भी इसके महत्व का दस्तावेजीकरण किया है।
मध्यकालीन और मुगल काल
1703 में, औरंगजेब के पोते, राजकुमार अजीम-उस-शान को पटना का गवर्नर नियुक्त किया गया और उन्होंने शहर को बदलने का प्रयास किया, इसका नाम बदलकर अजीमाबाद कर दिया। हालाँकि, स्थानीय लोग इसे पटना ही कहते रहे। इससे पहले, शेरशाह सूरी ने अपनी राजधानी बिहारशरीफ से पटना स्थानांतरित कर दी थी, जिससे इसका महत्व और बढ़ गया। पुराना पटना कभी दीवारों से घिरा शहर था, जिसके अवशेष आज भी देखे जा सकते हैं।
भूगोल और कृषि
नए जिले के गठन के बाद, पटना में कोई पहाड़ी इलाका नहीं है। पटना का परिदृश्य पूरी तरह से जलोढ़ और समतल है, जो इसे भारत के सबसे उपजाऊ और भारी खेती वाले क्षेत्रों में से एक बनाता है। जिला दो प्राकृतिक क्षेत्रों में विभाजित है:
- गंगा के दक्षिणी तट के साथ एक संकरी पट्टी (~ 8 किमी चौड़ी), जिसकी विशेषता अत्यधिक उपजाऊ मिट्टी है।
- शेष क्षेत्र को कवर करने वाले जलोढ़ मैदान, कृषि के लिए आदर्श हैं।
इस क्षेत्र में महत्वपूर्ण वन संपदा का अभाव है, लेकिन जलोढ़ मिट्टी व्यापक कृषि भूमि का समर्थन करती है, जो आम के बागों, ताड़ के पेड़ों, खजूर और बांस के पेड़ों से घिरी हुई है। आम पेड़ों में बेल, सिरिस, कटहल और लाल कपास के पेड़ शामिल हैं। चावल प्रमुख फसल है, जो खेती वाले क्षेत्र के एक तिहाई से अधिक हिस्से को कवर करती है। अन्य प्रमुख फसलों में मक्का, दालें, गेहूं और तिलहन शामिल हैं, जबकि सब्जियां और तरबूज जैसी नकदी फसलें दियारा बेल्ट में पनपती हैं। गंगा और उसकी सहायक नदियाँ सिंचाई और कृषि में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती हैं, जिससे क्षेत्र की समृद्धि बढ़ती है। गंगा के किनारे के इलाकों में अम्मानिया, सिट्रिकुलरी, हाइग्रोफाइल और सेसबानिया जैसे खरपतवार उगते हैं। नदियों से दूर गांवों में कभी-कभी सूखे झाड़ीदार जंगल देखे जाते हैं।
जलवायु
चार विशाल नदियों के इतने करीब होने के कारण, पटना में गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल, उच्च आर्द्रता और ठंडी सर्दियाँ वाली उष्णकटिबंधीय जलवायु होती है:
- ग्रीष्मकाल (अप्रैल-जुलाई): तापमान 46 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक बढ़ जाता है, जब तक नमी से भरी मानसूनी हवाएँ सूखे खेतों को कुछ राहत नहीं पहुँचातीं।
- मानसून (अगस्त-सितंबर): भारी वर्षा गर्मी से राहत देती है।
- सर्दी (नवंबर-फरवरी): ठंडी रातें और धूप वाले दिन इस मौसम की विशेषता हैं, जब तक कि वसंत का आगमन नहीं हो जाता, जो मौसम को एक पूर्ण चक्र में ले आता है।
- वसंत (मार्च-अप्रैल): सर्दियों से गर्मियों में संक्रमण का प्रतीक है।
स्थानीय पंचांग पारंपरिक रूप से वर्ष को छह मौसमों में विभाजित करता है, जिसमें चार प्राथमिक मौसमों के अलावा हल्की गर्मी और हल्की सर्दी शामिल है।
पटना का समृद्ध ऐतिहासिक, सांस्कृतिक और भौगोलिक महत्व इसे भारत की विरासत का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा बनाता है, जो सदियों के विकास और प्रगति का प्रतीक है।
पटना जिले के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - प्रमंडल: पटना
- स्थापना: 1764
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,202 km2 (1,236 वर्ग मील)
- निर्देशांक: 25°25′N 85°10′E
- जिला मुख्यालय: पटना शहर
- जिलाधिकारी: डॉ. चन्द्रशेखर सिंह, आईएएस
- अनुमंडल की संख्या: 6 (पटना सदर, पटना सिटी, बाढ़, मसौढ़ी, पालीगंज, दानापुर)
- जनसंख्या:
- कुल: 58,38,465
- घनत्व: 1,823/km2 (4,720/वर्ग मील)
- साक्षरता दर: 70.68%
- लिंगानुपात: 897/1000
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 322
- गांव: 1395
- नगर निगम: 1 (पटना)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 23
- पटना सदर, संपतचक, फुलवारीशरीफ, फतुहा, दनियावां, खुसरूपुर, अथमलगोला, मोकामा, बेलछी, घोसवरी, पंडारक, बख्तियारपुर, बाढ़, मसौढ़ी, पुनपुन, धनरुआ, दानापुर, मनेर, बिहटा, नौबतपुर, पालीगंज, दुल्हिन बाजार और बिक्रम।
- नगर परिषद: 6 (बाढ़, दानापुर, खगौल, मसौढ़ी, मोकामा, फुलवारी)
- नगर पंचायत: 6 (बख्तियापुर, फतुहा, खुसरूपुर, मनेर, नौबतपुर, विक्रम)
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र: जिले में 3 संसदीय क्षेत्र हैं:
- 30-पटना साहिब, बख्तियारपुर, दीघा, बांकीपुर, कुम्हरार, पटना साहिब और फतुहा को कवर करता है।
- 31-पाटलिपुत्र, दानापुर, मनेर, फुलवारी, मसौढ़ी, पालीगंज और बिक्रम को कवर करता है।
- 28-मुंगेर/मोंगहिर, बाढ़ और मोकामा को कवर करता है और मुंगेर जिले के साथ साझा किया जाता है।
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 14
- 178-मोकामा, 179-बाढ़, 180-बख्तियारपुर, 181-दीघा, 182-बांकीपुर, 183-कुम्हरार, 184-पटना साहिब, 185-फतुहा, 186-दानापुर, 187-मनेर, 188-फुलवारी (एससी), 189-मसौढ़ी (एससी), 190-पालीगंज, 191-बिक्रम.
- ऊँचाई: 53 मीटर
- पोस्टल कोड: 800001
- टेलीफ़ोन कोड: +0612
- वाहन कोड: BR-01
- समय क्षेत्र: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- प्रमुख राजमार्ग: NH-30, NH-83
- मानव विकास सूचकांक (2016): 0.811 (उच्च)
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: patna.nic.in
पुलिस स्टेशन: 67
- अगमकुआं, एयर पोर्ट, अकिलपुर, आलमगंज, अथमलगोला, बहादुरपुर, बख्तियारपुर, बाढ़, बेलाची, बेउर, भगवानगंज, भौदौर, बिहटा, बिक्रम, बुद्धा कॉलोनी, बाइपास, चौक, दानापुर, दनियावा, धनरूआ, दीदारगंज, दीघा, दुल्हिन बाजार, फथुआ, फुलवारीशरीफ, गांधी मैदान, गर्दनीबाग, गौरीचक, घोसवारी, गोपालपुर, हाथीदह, जक्कनपुर, जानीपुर, कदमकुआं, कादिरगंज, कंकड़बाग, खाजेकला, खौगल, खुशरूपुर, कोतवाली, मालसलामी, मनेर, मराची, मसौढ़ी, मेहंदीगंज, मोकामा, नौबतपुर, पालीगंज, पंचमहला, पंडारक, परसा बाजार, पाटलिपुत्र, पत्रकार नगर, पीरबहोर, पुनपुन, राजीव नगर, रामकृष्ण नगर, रानी तालाब, रूपसपुर, एस के पुरी, सचिवालय, सहजापुर, साहपुर, सकसोहरा, शास्त्री नगर, सिगौड़ी।
अस्पताल:
- फोर्ड अस्पताल और अनुसंधान केंद्र
- मेडिवर्सल मल्टी सुपरस्पेशलिटी अस्पताल
- पीएमसीएच – पटना मेडिकल कॉलेज और अस्पताल
- महावीर कैंसर संस्थान और अनुसंधान केंद्र
- एनएमसीएच – नालंदा मेडिकल कॉलेज और अस्पताल
- आईजीआईएमएस – इंदिरा गांधी आयुर्विज्ञान संस्थान
- एम्स – अखिल भारतीय आयुर्विज्ञान संस्थान, पटना
मुख्य विशेषताएं:
- बिहार की राजधानी और भारत में सबसे पुराना लगातार बसा हुआ शहर।
- प्रमुख ऐतिहासिक स्थल: गोलघर, पटना साहिब गुरुद्वारा और कुम्हरार।
- उद्योगों, शिक्षा केंद्रों और प्रशासनिक महत्व के साथ आर्थिक केंद्र।
- महत्व: यह बिहार का प्रशासनिक और आर्थिक हृदय है।
भूगोल
- स्थान: दक्षिण-मध्य बिहार में स्थित, पटना गंगा नदी के दक्षिणी तट पर स्थित है।
- सीमावर्ती जिले:
- उत्तर: सारण, वैशाली और समस्तीपुर
- दक्षिण: जहानाबाद, नालंदा और गया
- पूर्व: लखीसराय और बेगूसराय
- पश्चिम: भोजपुर और अरवल
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,202 वर्ग किलोमीटर
- स्थलाकृति:
- भारत-गंगा क्षेत्र के समतल जलोढ़ मैदान, जो इसे अत्यधिक उपजाऊ बनाते हैं।
- जिले से होकर कई नदियाँ बहती हैं, जिनमें गंगा, सोन, पुनपुन और गंडक शामिल हैं।
- जलवायु:
- गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल (अप्रैल-जून) जिसमें तापमान 45 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक पहुँच जाता है।
- मानसून (जुलाई-सितंबर) में भारी वर्षा होती है।
- ठंडी सर्दियाँ (दिसंबर-फरवरी) जिसमें तापमान 5 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक गिर जाता है।
इतिहास
प्राचीन काल
- प्राचीन उत्पत्ति:
- पटना, एक गौरवशाली अतीत वाला प्राचीन शहर, दुनिया में सबसे पुराने लगातार बसे हुए स्थानों में से एक है।
- मगध के राजा द्वारा 490 ईसा पूर्व में स्थापित।
- प्राचीन पटना (पाटलिपुत्र):
- पाटलिपुत्र के रूप में जाना जाता है, यह मगध साम्राज्य की राजधानी के रूप में कार्य करता था।
- हर्यंका, नंदा, मौर्य, शुंग, गुप्त और पाल साम्राज्यों सहित क्रमिक राजवंशों द्वारा शासित।
- मगध साम्राज्य (600 ईसा पूर्व – 300 ईसा पूर्व)
- मौर्य साम्राज्य (321 ईसा पूर्व – 185 ईसा पूर्व) – चंद्रगुप्त मौर्य और सम्राट अशोक (जिन्होंने बौद्ध धर्म को बढ़ावा दिया) ने यहां से शासन किया।
- गुप्त साम्राज्य (चौथी – छठी शताब्दी ई.पू.)
- शक्ति, शिक्षा और ललित कलाओं की एक प्रमुख सीट के रूप में कार्य किया।
- गौतम बुद्ध, आर्यभट्ट, पाणिनि, वात्स्यायन, चाणक्य (जिनका अर्थशास्त्र प्रभावशाली बना हुआ है) और कालिदास जैसे प्रसिद्ध विद्वानों और हस्तियों का घर।
- मौर्य काल (लगभग 400 ईसा पूर्व) के दौरान, पाटलिपुत्र की आबादी लगभग 400,000 थी।
- पटना जैन परंपराओं, फारसी अध्ययनों के लिए भी महत्वपूर्ण रहा है, और यह सिख गुरु गोबिंद सिंह (दसवें गुरु) का जन्मस्थान है।
- मेगास्थनीज, फा-हियान और ह्वेन त्सांग जैसे प्रसिद्ध यात्रियों ने पाटलिपुत्र का दौरा किया और इसकी भव्यता की प्रशंसा की।
- सांस्कृतिक और राजनीतिक केंद्र:
- पटना (पाटलिपुत्र) भारतीय उपमहाद्वीप का एक जीवंत राजनीतिक और सांस्कृतिक केंद्र था।
- पतन और पुनरुद्धार:
- गुप्त साम्राज्य के पतन के साथ, पटना ने अपना अधिकांश प्राचीन गौरव खो दिया।
- 17वीं शताब्दी में, अंग्रेजों ने पटना को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के केंद्र के रूप में पुनर्जीवित किया।
मध्यकालीन काल
- मुगल काल के दौरान, पटना व्यापार, शिक्षा और सूफी संस्कृति का केंद्र बन गया।
- शेर शाह सूरी ने शहर का नाम बदलकर पटना रख दिया और सड़कें और किले बनवाए।
औपनिवेशिक और आधुनिक युग
- बक्सर की लड़ाई के बाद 1764 में ब्रिटिश ईस्ट इंडिया कंपनी ने पटना को प्रशासनिक केंद्र के रूप में स्थापित किया।
- इसने राजेंद्र प्रसाद और जयप्रकाश नारायण जैसे नेताओं के साथ भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई।
- स्वतंत्रता के बाद, पटना बिहार का राजनीतिक और आर्थिक केंद्र बन गया।
- प्रांतीय परिषद के रूप में स्थापना (1770):
- पटना का आधुनिक जिला सितंबर 1770 में अंग्रेजों द्वारा बनाया गया था।
- इसे बिहार में राजस्व मामलों की निगरानी के लिए एक प्रांतीय परिषद के रूप में स्थापित किया गया था।
- न्यायिक जिले के रूप में गठन (1793):
- 1793 में, पटना को एक अलग न्यायिक जिले के रूप में नामित किया गया था।
- इस परिवर्तन ने जिले के आधुनिक प्रशासनिक ढांचे की नींव रखी।
- 1972 में पुनर्गठन:
- बिहार में जिलों का पुनर्गठन 1972 में प्रभावी हुआ।
- 9 नवंबर, 1972 को पटना जिले से बिहार शरीफ उप-मंडल को अलग करके नालंदा जिले का गठन किया गया।
इस ऐतिहासिक विकास ने पटना में आधुनिक शासन और प्रशासनिक ढांचे की नींव रखी, जिसने इसे आज के प्रभावशाली जिले के रूप में आकार दिया।
जनसांख्यिकी (2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार)
- जनसंख्या:
- कुल जनसंख्या: पटना जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 5,838,465 है (अब अनुमानतः 7 मिलियन से अधिक)
- पुरुष जनसंख्या: 3078512
- महिला जनसंख्या: 2759953
- कुल जनसंख्या: पटना जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 5,838,465 है (अब अनुमानतः 7 मिलियन से अधिक)
- रैंकिंग: भारत में 14 (640 जिलों में से)।
- घनत्व: 1,823 व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर (4,720/वर्ग मील) (बिहार में सबसे अधिक में से एक)।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि (2001-2011): 23.73% जो महत्वपूर्ण जनसंख्या वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- लिंग अनुपात: प्रति 1,000 पुरुषों पर 897 महिलाएँ।
- साक्षरता दर: 70.68%, जो बिहार में सबसे अधिक है और शिक्षा की पहुँच और गुणवत्ता में सुधार के लिए महत्वपूर्ण प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं।
- पुरुष साक्षरता दर: 78.48%
- महिला साक्षरता दर: 61.96%
- शहरी जनसंख्या: (2514590) कुल जनसंख्या का 43.07% शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- ग्रामीण जनसंख्या: (3323875) कुल जनसंख्या का 56.93% ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- (0 से 6 वर्ष) आयु वर्ग की जनसंख्या: कुल जनसंख्या का 943552 (16.16%)
- कुल घरों की संख्या: 975578
- धार्मिक संरचना (2011 की जनगणना): अधिकांश आबादी हिंदू धर्म का पालन करती है, जिसमें एक महत्वपूर्ण मुस्लिम समुदाय और अन्य समुदाय एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा बनाते हैं।
- हिंदू धर्म: 91.74%
- अनुसूचित जाति: (920918) कुल जनसंख्या का 15.77%
- अनुसूचित जनजातियाँ: (9069) कुल जनसंख्या का 0.15%
- इस्लाम: 7.54%
- अन्य या नहीं बताया गया: 0.72%
- हिंदू धर्म: 91.74%
- शहरी बनाम ग्रामीण:
- शहरी – पटना शहर बिहार का सबसे बड़ा शहरी केंद्र है।
- ग्रामीण – कई गाँव अभी भी कृषि पर निर्भर हैं।
- बोली जाने वाली भाषाएँ: हिंदी, मगही, भोजपुरी, उर्दू और अंग्रेजी।
- मगही: 46.35%
- हिंदी: 43.77%
- उर्दू: 5.19%
- भोजपुरी: 2.67%
- मैथिली: 1.24%
- अन्य: 0.78% (बंगाली और उड़िया)
प्रशासन
- इस जिले का नेतृत्व जिला मजिस्ट्रेट (डीएम) रैंक के एक आईएएस अधिकारी द्वारा किया जाता है।
- प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय (डीएम कार्यालय): पटना शहर
- जिले को उप-विभागों या तहसीलों में विभाजित किया गया है, और इन तहसीलों को आगे ब्लॉकों में विभाजित किया गया है।
- उप-विभाग:
- जिले में 6 उप-विभाग या तहसील हैं: पटना सदर, बाढ़, मसौढ़ी, दानापुर, पालीगंज और पटना सिटी (पुराना पटना क्षेत्र)
- प्रत्येक उप-विभाग का नेतृत्व एक उप-विभागीय मजिस्ट्रेट (SDM) करता है, जो विकास, राजस्व-संबंधी कार्यों और कानून-व्यवस्था बनाए रखने का प्रभारी होता है।
- ब्लॉक और सर्किल:
- पटना जिले में 6 उप-विभागों के अंतर्गत 23 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और सर्किल शामिल हैं: प्रत्येक ब्लॉक स्थानीय शासन और विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
- पटना सदर-पटना सदर, संपतचक और फुलवारीशरीफ
- मसौढ़ी– मसौढ़ी, पुनपुन और धनरूआ
- पटना सिटी– फतुहा, दनियावां और खुसरूपुर
- पालीगंज – पालीगंज, दुल्हिन बाजार और बिक्रम
- दानापुर- दानापुर, मनेर, बिहटा और नौबतपुर
- बाढ़ – अथमलगोला, मोकामा, बेलछी, घोसवारी, पंडारक, बख्तियारपुर और बाढ़
- पटना जिले में 6 उप-विभागों के अंतर्गत 23 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और सर्किल शामिल हैं: प्रत्येक ब्लॉक स्थानीय शासन और विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
- प्रत्येक सर्कल का नेतृत्व एक सर्कल अधिकारी (सीओ) करता है, जबकि प्रत्येक ब्लॉक का नेतृत्व एक खंड विकास अधिकारी (बीडीओ) करता है।
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र:
- जिले में 3 संसद क्षेत्र हैं: 30-पटना साहिब, 31-पाटलिपुत्र और 28-मुंगेर/मोंगहिर।
- विधानसभा क्षेत्र: जिले में 14 विधानसभा सीटें हैं।
- 178-मोकामा, 179-बाढ़, 180-बख्तियारपुर, 181-दीघा, 182-बांकीपुर, 183-कुम्हरार, 184-पटना साहिब, 185-फतुहा, 186-दानापुर, 187-मनेर, 188-फुलवारी (एससी), 189-मसौढ़ी (एससी), 190-पालीगंज, 191-बिक्रम.
कलेक्टरेट की समग्र भूमिकाएँ और जिम्मेदारियाँ:
जिला प्रशासन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है और जिले के भीतर कानून और व्यवस्था, योजना, विकास, राजस्व और आपदा प्रबंधन को बनाए रखने के लिए जिम्मेदार होता है।
- कलेक्टर (आई.ए.एस. कैडर):
- जिले का मुखिया: मुख्य कार्यकारी और जिला मजिस्ट्रेट के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- कानून और व्यवस्था: जिले में शांति बनाए रखता है और कानून और व्यवस्था लागू करता है।
- योजना और विकास: योजना और विकास परियोजनाओं की देखरेख करता है।
- अनुसूचित/एजेंसी क्षेत्रों का प्रशासन: अनुसूचित या विशेष एजेंसी प्रशासन के तहत नामित क्षेत्रों का प्रबंधन करता है।
- चुनाव प्रबंधन और शस्त्र लाइसेंसिंग: आम चुनावों को संभालता है और शस्त्रों के लाइसेंसिंग की देखरेख करता है।
- अतिरिक्त कलेक्टर (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- राजस्व प्रशासन: विभिन्न जिला विभागों में राजस्व संबंधी कार्यों को चलाता है।
- अतिरिक्त जिला मजिस्ट्रेट: कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने और नागरिक कार्यों को संचालित करने में जिम्मेदारियों को साझा करता है।
- प्रमुख जिम्मेदारियाँ: नागरिक आपूर्ति, भूमि मामलों, खानों और खनिजों के प्रबंधन की देखरेख करना और ग्राम अधिकारियों की देखरेख करना।
- जिला विकास आयुक्त (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- विकासात्मक गतिविधियाँ: जिले भर में विभिन्न विकासात्मक पहलों का प्रबंधन और समन्वय करना।
- देखरेख करने वाले प्रमुख विभाग:
- जिला चिकित्सा और स्वास्थ्य विभाग।
- समाज कल्याण विभाग।
- बीसी (पिछड़ा वर्ग) कल्याण और बीसी निगम।
- विकलांग कल्याण।
- आवास और अन्य संबंधित विभाग।
- अतिरिक्त कलेक्टर (आपदा) (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- आपदा प्रबंधन: आपदा प्रबंधन से संबंधित गतिविधियों की योजना बनाने और समन्वय करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना।
- प्रमुख जिम्मेदारियाँ: आपात स्थिति के दौरान आपदा अनुभाग और अन्य संबंधित विकास विभागों की देखरेख करना।
ये भूमिकाएँ सामूहिक रूप से सुनिश्चित करती हैं कि जिला अच्छी तरह से शासित हो, जिसमें कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने, कुशल राजस्व संग्रह, प्रभावी आपदा प्रबंधन और विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में सतत विकास पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया जाता है।
अर्थव्यवस्था
पटना ऐतिहासिक रूप से एक महत्वपूर्ण कृषि और व्यापार केंद्र रहा है, जहाँ अनाज, गन्ना, तिल और मध्यम दाने वाला पटना चावल इसके प्राथमिक निर्यात हैं। शहर पूर्वी भारत में एक महत्वपूर्ण व्यवसाय और लक्जरी ब्रांड केंद्र के रूप में विकसित हुआ है।
आर्थिक विकास
- पटना की अर्थव्यवस्था ने 2005 से निरंतर विकास का अनुभव किया है, जिसके पीछे कारण हैं:
- फास्ट-मूविंग कंज्यूमर गुड्स (FMCG) उद्योग
- सेवा क्षेत्र
- हरित क्रांति व्यवसाय
- विश्व बैंक रिपोर्ट (2009): व्यवसाय शुरू करने के लिए भारत में दूसरा सबसे अच्छा शहर।
- प्रति व्यक्ति सकल घरेलू उत्पाद (2015): ₹1,06,000 (2015 तक)
- जीडीपी विकास दर (2015): 7.29%
- सबसे तेजी से बढ़ने वाला शहर:
- दुनिया का 21वाँ सबसे तेजी से बढ़ने वाला शहर।
- भारत का 5वाँ सबसे तेजी से बढ़ने वाला शहर।
- सालाना 3.72% की दर से बढ़ने की उम्मीद है।
कृषि
- शहरीकरण के बावजूद, ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में कृषि महत्वपूर्ण बनी हुई है।
- मुख्य फसलों में शामिल हैं:
- धान, मक्का, दालें, गेहूं, तिलहन।
- एक तिहाई बोया गया क्षेत्र चावल (धान) के लिए समर्पित है।
- नकदी फसलें: सब्जियाँ, तरबूज (दियारा बेल्ट में उगाए गए)।
- डेयरी फार्मिंग और मत्स्य पालन भी महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
औद्योगिक क्षेत्र और व्यापार केंद्र
- पटना भारत के सबसे तेजी से बढ़ते शहरों में से एक है।
- चीनी उद्योग: पटना और उसके आसपास कई चीनी मिलें स्थित हैं।
- कृषि प्रसंस्करण उद्योग: क्षेत्र की अर्थव्यवस्था में एक प्रमुख भूमिका निभाता है।
- अन्य प्रमुख उद्योग:
- चमड़ा उद्योग
- हस्तशिल्प
- खुदरा और लक्जरी ब्रांड
- खाद्य प्रसंस्करण (चावल मिलें, डेयरी, चीनी मिलें, बिस्किट कारखाने)
- हथकरघा और कपड़ा उद्योग
- आईटी और सॉफ्टवेयर सेवाएँ – पटना एक आईटी हब के रूप में उभर रहा है।
- शहरी विस्तार के कारण रियल एस्टेट में उछाल।
बिहार से जुड़े उद्योग, संगठन और कंपनियाँ:
1. बिहार राज्य सड़क परिवहन निगम (BSRTC):
- प्रकार: राज्य के स्वामित्व वाला निगम।
- कार्य: बिहार के भीतर और पड़ोसी राज्यों को सड़क परिवहन सेवाएँ प्रदान करता है।
- सेवाएँ: लोगों को किफ़ायती और कुशल परिवहन प्रदान करने के उद्देश्य से अंतर-शहर और अंतरराज्यीय बस सेवाएँ संचालित करता है।
2. बिहार राज्य पर्यटन विकास निगम (BSTDC):
- स्थापना: 1980.
- उद्देश्य: बिहार में पर्यटन का विकास और प्रचार-प्रसार करना।
- पहल: विभिन्न पर्यटन स्थलों पर पर्यटक बंगले, कैफेटेरिया, रेस्तरां, परिवहन सुविधाएँ और रोपवे का प्रबंधन करता है।
- वेबसाइट: bstdc.bihar.gov.in
3. तासीर:
- प्रकार: उर्दू भाषा का दैनिक समाचार पत्र।
- मुख्यालय: पटना, बिहार।
- कवरेज: उर्दू भाषी आबादी के लिए क्षेत्रीय, राष्ट्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय समाचारों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
4. बाढ़ सुपर थर्मल पावर स्टेशन:
- स्थान: बाढ़, बिहार।
- संचालक: राष्ट्रीय ताप विद्युत निगम (एनटीपीसी)।
- क्षमता: 3,300 मेगावाट की नियोजित कुल क्षमता, जिसमें से 1,320 मेगावाट वर्तमान में चालू है और 1,980 मेगावाट निर्माणाधीन है।
- महत्व: बिहार और पड़ोसी क्षेत्रों की बढ़ती बिजली मांगों को पूरा करना है।
5. बिहार स्टेट पावर होल्डिंग कंपनी लिमिटेड (बीएसपीएचसीएल):
- पूर्व में: बिहार राज्य विद्युत बोर्ड (बीएसईबी)।
- कार्य: बिहार में बिजली उत्पादन, संचरण और वितरण के लिए शीर्ष होल्डिंग कंपनी के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- सहायक:
- बिहार स्टेट पावर जनरेशन कंपनी लिमिटेड।
- बिहार स्टेट पावर ट्रांसमिशन कंपनी लिमिटेड।
- उत्तर बिहार पावर डिस्ट्रीब्यूशन कंपनी लिमिटेड।
- दक्षिण बिहार पावर डिस्ट्रीब्यूशन कंपनी लिमिटेड।
- वेबसाइट: bsphcl.co.in
6. साउथ बिहार पावर डिस्ट्रीब्यूशन कंपनी लिमिटेड (एसबीपीडीसीएल):
- कार्य: बिहार के दक्षिणी क्षेत्रों में बिजली वितरित करता है।
- सेवाएँ: नए बिजली कनेक्शन, बिलिंग और ग्राहक सहायता प्रदान करता है।
- वेबसाइट: sbpdcl.co.in
7. नॉर्थ बिहार पावर डिस्ट्रीब्यूशन कंपनी लिमिटेड (NBPDCL):
- कार्य: बिहार के उत्तरी क्षेत्रों में बिजली वितरित करता है।
- सेवाएँ: बिजली वितरण, बिलिंग और ग्राहक सेवाएँ प्रदान करता है।
- वेबसाइट: nbpdcl.co.in
8. हस्क पावर सिस्टम्स:
- स्थापना: 2008.
- प्रकार: निजी कंपनी।
- फ़ोकस: ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अक्षय ऊर्जा समाधान प्रदान करता है।
- प्रौद्योगिकी: बिजली उत्पन्न करने के लिए चावल की भूसी और अन्य बायोमास का उपयोग करता है, ऑफ-ग्रिड गाँवों में माइक्रोग्रिड स्थापित करता है।
- प्रभाव: सतत विकास को बढ़ावा देना और ग्रामीण समुदायों में जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार करना।
9. सत्तूज़:
- प्रकार: खाद्य और पेय पदार्थ ब्रांड।
- उत्पाद: पारंपरिक भारतीय पेय पदार्थों में विशेषज्ञता, विशेष रूप से “सत्तू”, बिहार में लोकप्रिय भुना हुआ बेसन आधारित पेय।
- लक्ष्य: आधुनिक पैकेजिंग और मार्केटिंग के साथ पारंपरिक व्यंजनों को पुनर्जीवित करना।
10. मुस्कान कंस्ट्रक्शन प्राइवेट लिमिटेड:
- प्रकार: निजी निर्माण कंपनी।
- सेवाएँ: आवासीय और वाणिज्यिक परियोजनाओं सहित बुनियादी ढाँचे के विकास में संलग्न है।
- प्रतिष्ठा: बिहार में गुणवत्तापूर्ण निर्माण और समय पर परियोजना वितरण के लिए जाना जाता है।
11. सैजा फाइनेंस प्राइवेट लिमिटेड:
- स्थापना: 2007.
- प्रकार: गैर-बैंकिंग वित्तीय कंपनी-माइक्रो फाइनेंस इंस्टीट्यूशन (एनबीएफसी-एमएफआई)।
- सेवाएँ: बिहार और पड़ोसी राज्यों में कम आय वाले परिवारों और छोटे उद्यमियों को माइक्रोलोन प्रदान करता है।
- उद्देश्य: वित्तीय समावेशन को बढ़ावा देना और जमीनी स्तर पर आर्थिक विकास का समर्थन करना।
ये संगठन और कंपनियाँ बिहार के विकास और अर्थव्यवस्था में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती हैं, परिवहन, पर्यटन, ऊर्जा, मीडिया, निर्माण और वित्त जैसे क्षेत्रों में योगदान देती हैं।
आर्थिक चुनौतियाँ
- पिछड़ा क्षेत्र: 2006 में, पंचायती राज मंत्रालय ने पटना को भारत के 250 सबसे पिछड़े जिलों में से एक के रूप में पहचाना।
- आर्थिक विकास के लिए पिछड़ा क्षेत्र अनुदान निधि (BRGF) से सहायता प्राप्त करता है।
- बेरोजगारी और महानगरों की ओर पलायन।
- अधिक बड़े पैमाने के उद्योगों की आवश्यकता।
पटना पूर्वी भारत में एक उभरता हुआ आर्थिक केंद्र है, जहाँ FMCG, सेवाओं, कृषि और उद्योग में मजबूत वृद्धि हुई है। अपनी चुनौतियों के बावजूद, यह भारत और दुनिया में सबसे तेजी से बढ़ते शहरों में से एक बना हुआ है।
शिक्षा
स्कूल शिक्षा:
- स्कूलों के प्रकार:
- सरकारी स्कूल
- निजी स्कूल
- संबद्धता:
- बिहार स्कूल परीक्षा बोर्ड (BSEB)
- भारतीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा प्रमाणपत्र (ICSE)
- राष्ट्रीय मुक्त विद्यालयी शिक्षा संस्थान (NIOS)
- केंद्रीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा बोर्ड (CBSE)
- शिक्षा का माध्यम: मुख्य रूप से हिंदी और अंग्रेजी
उच्च माध्यमिक और डिग्री शिक्षा (10+2+3/4 योजना):
- संरचना:
- 10 साल की स्कूली शिक्षा (माध्यमिक शिक्षा)
- उच्च माध्यमिक विद्यालयों में नामांकन (बिहार राज्य इंटरमीडिएट बोर्ड, CISCE, NIOS, या CBSE से संबद्ध)
- प्रस्तावित स्ट्रीम: कला, वाणिज्य और विज्ञान
- माध्यमिकोत्तर विकल्प:
- विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में सामान्य डिग्री पाठ्यक्रम
- पेशेवर डिग्री पाठ्यक्रम (जैसे, कानून, इंजीनियरिंग, चिकित्सा)
- कुछ प्रतिष्ठित स्कूल जैसे:
- लोयोला हाई स्कूल
- नोट्रे डेम अकादमी
- सेंट जेवियर्स हाई स्कूल
- डॉन बॉस्को अकादमी
- सेंट माइकल्स हाई स्कूल
- दिल्ली पब्लिक स्कूल, पटना
- डीएवी बीएसईबी
पटना में प्रमुख उच्च शिक्षण संस्थान:
- पटना विश्वविद्यालय (1917 में स्थापित, भारतीय उपमहाद्वीप में सातवां सबसे पुराना आधुनिक विश्वविद्यालय)।
- आईआईटी पटना (भारतीय प्रौद्योगिकी संस्थान)।
- ए एन कॉलेज
- पटना कॉलेज
- मगध विश्वविद्यालय
- पटना डेंटल कॉलेज
- बिहार नेशनल कॉलेज
- एमिटी यूनिवर्सिटी, पटना
- पटना महिला कॉलेज
- मगध महिला कॉलेज
- नालंदा ओपन यूनिवर्सिटी
- सेंट जेवियर्स कॉलेज, पटना
- पाटलिपुत्र विश्वविद्यालय, पटना
- सेंट्रल यूनिवर्सिटी ऑफ साउथ बिहार
- आर्यभट्ट नॉलेज यूनिवर्सिटी
- चाणक्य नेशनल लॉ यूनिवर्सिटी
- बिरला इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ टेक्नोलॉजी, पटना
- आर.पी. शर्मा इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ टेक्नोलॉजी
- चंद्रगुप्त इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ मैनेजमेंट
- बिहार एनिमल साइंसेज यूनिवर्सिटी, पटना
- अखिल भारतीय आयुर्विज्ञान संस्थान (एम्स), पटना
- राष्ट्रीय प्रौद्योगिकी संस्थान, पटना (एनआईटी-पी)
- मौलाना आजाद कॉलेज ऑफ इंजीनियरिंग एंड टेक्नोलॉजी
- राष्ट्रीय फैशन प्रौद्योगिकी संस्थान (निफ्ट पटना)
- मौलाना मजहरुल हक अरबी और फारसी विश्वविद्यालय
- राजेंद्र मेमोरियल रिसर्च इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ मेडिकल साइंसेज
- नालंदा मेडिकल कॉलेज एंड हॉस्पिटल, पटना
- पटना मेडिकल कॉलेज हॉस्पिटल (पीएमसीएच), पटना
- इसके अतिरिक्त, पटना में कई अन्य विश्वविद्यालय, प्राथमिक विद्यालय और माध्यमिक विद्यालय हैं।
पटना में शैक्षणिक बुनियादी ढाँचा, प्राथमिक विद्यालय से लेकर उच्च शिक्षा तक, और अकादमिक उत्कृष्टता की इसकी दीर्घकालिक परंपरा को उजागर करता है।
चुनौतियाँ
- कुछ क्षेत्रों में उच्च प्रतिस्पर्धा और गुणवत्तापूर्ण कॉलेजों की कमी।
- छात्र अक्सर उच्च शिक्षा के लिए दिल्ली, पुणे और बैंगलोर जाते हैं।
त्यौहार, संस्कृति और विरासत
त्यौहार:
- छठ पूजा:
- पटना का सबसे बड़ा त्यौहार, जो गंगा नदी के तट पर भव्य रूप से मनाया जाता है।
- सूर्यदेव (सूर्य) को समर्पित एक प्रमुख हिंदू त्यौहार, जिसे अपार आस्था के साथ मनाया जाता है।
- वर्ष में दो बार मनाया जाता है:
- चैत्र (गर्मी)
- कार्तिक (सर्दियों की शुरुआत)
- भक्त पवित्र स्नान, उपवास और डूबते और उगते सूर्य को जल (अर्घ्य) अर्पित करने सहित कठोर अनुष्ठान करते हैं।
- मकर संक्रांति (तिला संक्रांति):
- गर्मी की शुरुआत में मनाया जाता है और फसल के मौसम का प्रतीक है।
- इसे शुभ माना जाता है क्योंकि यह भारतीय संस्कृति में नए साल की शुरुआत का प्रतीक है।
- होली:
- जिले में सबसे बड़े और सबसे रंगीन त्यौहारों में से एक।
- बहुत उत्साह के साथ मनाया जाता है, जहाँ लोग खुशी और जीवंत उत्सव मनाते हैं जो माहौल को रोशन कर देते हैं।
- दुर्गा पूजा, दिवाली, जन्माष्टमी, काली पूजा, सरस्वती पूजा, नाग पंचमी, शिव रात्रि, बकरीद, ईद और मुहर्रम भी व्यापक रूप से मनाए जाते हैं।
- भोजपुरी लोकगीत और नृत्य सांस्कृतिक पहचान का एक प्रमुख हिस्सा हैं।
- पटना कलम (मुगल चित्रकला शैली) का ऐतिहासिक महत्व है।
- जिले में भोजपुरी, मगही और हिंदी साहित्य का विकास हुआ है।
व्यंजन:
- पारंपरिक मुख्य खाद्य पदार्थ:
- दैनिक भोजन में आमतौर पर सब्जी, रोटी, दाल और भाजी जैसे व्यंजन शामिल होते हैं।
- विशिष्ट व्यंजन:
- लिट्टी चोखा: भुने हुए गेहूं के गोले (लिट्टी) से बना एक लोकप्रिय बिहारी व्यंजन जिसे मसली हुई सब्जियों (चोखा) के साथ परोसा जाता है।
- कढ़ी: दही से बनी करी जिसे अक्सर पारंपरिक मसालों के साथ मसालेदार बनाया जाता है।
- झाल मूरी: स्थानीय लोगों द्वारा पसंद किया जाने वाला मसालेदार नाश्ता मिश्रण।
- सत्तू: भुना हुआ बेसन, सत्तू पराठा, दाल पीठा और दाल पूरी जैसे विभिन्न व्यंजनों और पेय पदार्थों में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
- मिठाइयाँ और डेसर्ट:
- शुद्ध देसी घी से बनी अपनी मुंह में पानी लाने वाली मिठाइयों के लिए प्रसिद्ध, जो स्थानीय मिठाई की दुकानों में उपलब्ध हैं और आमतौर पर घर पर औपचारिक अवसरों के दौरान बनाई जाती हैं।
- खाजा, बालूशाही, तिलकुट, ठेकुआ और मालपुआ जैसी मिठाइयाँ प्रसिद्ध हैं।
वेशभूषा:
- पारंपरिक पुरुष पोशाक:
- धोती, कुर्ता और पायजामा आमतौर पर पहने जाते हैं।
- युवा पुरुषों को पारंपरिक और आधुनिक शैलियों को मिलाते हुए शर्ट और पतलून में भी देखा जा सकता है।
- पारंपरिक महिला पोशाक:
- महिलाएँ पारंपरिक रूप से घाघरा (लंबी स्कर्ट), चोली (ब्लाउज) और साड़ी पहनती हैं, जो समृद्ध हिंदू सांस्कृतिक विरासत को दर्शाती हैं।
- मुस्लिम समुदाय की पोशाक:
- पुरुष: आमतौर पर कुर्ता और पायजामा पहनते हैं।
- महिलाएँ: पारंपरिक मुस्लिम पोशाक का पालन करते हुए अक्सर बुर्का पहनती हैं।
धर्म:
- धार्मिक संरचना:
- यह जिला मुख्य रूप से हिंदू है, लेकिन इसमें एक महत्वपूर्ण मुस्लिम समुदाय भी है।
- पटना जिले में आदिवासी समुदाय भी रहते हैं, जिनमें से कई अपनी स्वदेशी धार्मिक प्रथाओं का पालन करते हैं।
- सांस्कृतिक एकीकरण:
- इस क्षेत्र का सांस्कृतिक परिदृश्य विभिन्न धार्मिक परंपराओं का एक जीवंत मिश्रण है, जिसमें कई समुदाय कई दशकों से सह-अस्तित्व में हैं।
- सामाजिक सद्भाव:
- विविधता के बावजूद, सामाजिक एकता और आतिथ्य की एक मजबूत भावना है, जो आगंतुकों पर एक स्थायी छाप छोड़ती है।
- विरासत और परंपरा:
- धार्मिक परंपराओं की समृद्ध टेपेस्ट्री एक अनूठी सांस्कृतिक विरासत में योगदान देती है, जो पटना में त्योहारों, अनुष्ठानों और रोजमर्रा की प्रथाओं में स्पष्ट है।
पर्यटन और ऐतिहासिक धरोहर
1. महावीर मंदिर, पटना: भक्ति का पवित्र स्थल
भगवान हनुमान को समर्पित सबसे प्रतिष्ठित हिंदू मंदिरों में से एक महावीर मंदिर, पटना, बिहार में स्थित है। उत्तर भारत के सबसे प्रमुख धार्मिक स्थलों में से एक के रूप में प्रसिद्ध, यह मंदिर हर साल लाखों भक्तों को आकर्षित करता है। संकट मोचन हनुमान की मूर्ति भक्तों के दिलों में एक विशेष स्थान रखती है, खासकर राम नवमी के भव्य समारोहों के दौरान।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
मंदिर की उत्पत्ति सदियों पहले हुई थी, अभिलेखों से पता चलता है कि इसकी स्थापना 1730 ई. में रामानंदी संप्रदाय के स्वामी बालानंद ने की थी। इसे आधिकारिक तौर पर 1948 में पटना उच्च न्यायालय द्वारा सार्वजनिक मंदिर घोषित किया गया था। यह मंदिर 1900 ई. से रामानंदी संप्रदाय के अधीन है और इससे पहले 1948 तक गोसाईं संन्यासी संप्रदाय के अधीन था। समय के साथ, महावीर मंदिर एक महत्वपूर्ण धार्मिक और धर्मार्थ संस्थान के रूप में विकसित हुआ है।
1947 में भारत के विभाजन के बाद, मंदिर में भक्तों की संख्या में भारी वृद्धि देखी गई, जिसके कारण 1983 और 1985 के बीच इसका पुनर्निर्माण किया गया। स्वैच्छिक दान और ‘कार सेवा’ से निर्मित नवनिर्मित भव्य संगमरमर संरचना, अटूट आस्था का प्रमाण है।
वास्तुशिल्प की भव्यता:
10,000 वर्ग फीट में फैले, मंदिर परिसर में कई गर्भगृह हैं:
- भूतल: भगवान हनुमान की दो मूर्तियाँ हैं, जो पुण्य की रक्षा और बुराई को खत्म करने में उनकी भूमिका को दर्शाती हैं। गर्भगृह के चारों ओर के गलियारे में भगवान शिव की उपस्थिति भी है।
- पहली मंजिल: भगवान राम, भगवान कृष्ण, देवी दुर्गा, भगवान शिव और देवी पार्वती सहित देवताओं की प्रतिमाएँ हैं। एक उल्लेखनीय आकर्षण राम सेतु शिला है, जो एक तैरता हुआ पत्थर है जिसे रामायण के पौराणिक पुल से माना जाता है।
- दूसरी मंजिल: संस्कार मंडप की विशेषता है, जो धार्मिक अनुष्ठानों, मंत्रों और वाल्मीकि रामायण जैसे शास्त्रों के पाठ के लिए समर्पित स्थान है। रामायण के दृश्यों को यहाँ कलात्मक रूप से दर्शाया गया है।
- मंदिर परिसर: परिसर में एक कार्यालय, एक किताबों की दुकान, एक धार्मिक सामान की दुकान और एक ज्योतिषी केंद्र शामिल हैं। भक्त पीपल के पेड़ पर भी जा सकते हैं जहाँ भगवान शनि की पूजा की जाती है।
आध्यात्मिक और धर्मार्थ पहल:
श्री महावीर मंदिर न केवल एक आध्यात्मिक केंद्र है, बल्कि मानवीय प्रयासों का केंद्र भी है। श्री महावीर स्थान न्यास समिति, जो इसका प्रबंधन ट्रस्ट है, कई धर्मार्थ अस्पताल और पहल चलाती है, जिनमें शामिल हैं:
- महावीर वात्सल्य अस्पताल
- महावीर कैंसर संस्थान और अनुसंधान केंद्र
- ट्रस्ट कैंसर के इलाज के लिए वित्तीय सहायता प्रदान करता है और अनाथालयों और अन्य कल्याणकारी कार्यक्रमों के माध्यम से वंचितों का समर्थन करता है।
- महावीर आरोग्य संस्थान
- महावीर नेत्रालय
अनोखी विशेषताएँ:
- नैवेद्यम प्रसादम: बेसन, चीनी, काजू, किशमिश, इलायची और कश्मीरी केसर से बना एक प्रसिद्ध प्रसाद, जिसे तिरुपति के विशेषज्ञों द्वारा तैयार किया जाता है।
- समावेशी पूजा: मंदिर में विभिन्न पृष्ठभूमि के पुजारी आते हैं, जिनमें रामानंदी संप्रदाय के संस्कृत विद्वान, बैरागी साधु और दलित पुजारी शामिल हैं।
- श्रवण कुमार पुरस्कार: माता-पिता की देखभाल के लिए समर्पित व्यक्तियों को सम्मानित करने के लिए स्थापित, जिसमें ₹1,00,000 तक के वित्तीय पुरस्कार दिए जाते हैं।
त्यौहार और उत्सव:
- राम नवमी: महावीर मंदिर का सबसे भव्य उत्सव, जिसमें हज़ारों भक्त आते हैं।
- हनुमान जयंती: कार्तिक महीने की 14वीं रात को बड़े उत्साह के साथ मनाई जाती है।
महावीर मंदिर आस्था, भक्ति और सेवा का प्रतीक है। इसकी ऐतिहासिक विरासत, शानदार वास्तुकला और परोपकारी योगदान इसे भारत के सबसे प्रतिष्ठित मंदिरों में से एक बनाते हैं। चाहे आध्यात्मिक शांति की तलाश हो या धर्मार्थ प्रयासों में संलग्न होना हो, महावीर मंदिर की यात्रा भक्तों और आगंतुकों दोनों के लिए एक समृद्ध अनुभव है। मंदिर की आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: mahavirmandirpatna.org
2. बापू टॉवर: पटना, बिहार में महात्मा गांधी को एक स्मारकीय श्रद्धांजलि:
- स्थान और महत्व:
- गर्दनीबाग, पटना, बिहार में स्थित है।
- राष्ट्रपिता महात्मा गांधी को समर्पित।
- भारत में पहली बार बनाया गया टॉवर विशेष रूप से गांधी की विरासत को श्रद्धांजलि देने के लिए बनाया गया है।
- वास्तुशिल्प विशेषताएँ:
- ऊँचाई और संरचना:
- टॉवर 120 फीट ऊँचा है और इसमें छह मंजिलें हैं।
- गोलाकार और आयताकार दोनों वर्गों के साथ डिज़ाइन किया गया है जो गांधी के जीवन की एक आकर्षक कहानी बनाते हैं।
- बाहरी डिज़ाइन:
- बाहरी भाग 42,000 किलोग्राम तांबे से बना है, जो ऑक्सीजन और नाइट्रोजन की प्राकृतिक प्रतिक्रिया के कारण सुंदर इंद्रधनुषी रंगों में बदल जाता है।
- हरित प्रौद्योगिकी:
- इसमें सतत विकास प्रथाओं और पर्यावरण के अनुकूल निर्माण विधियों को शामिल किया गया है।
- ऊँचाई और संरचना:
- उद्देश्य और कार्य:
- यह वास्तुकला के चमत्कार के साथ-साथ भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में गांधी के योगदान पर सीखने और चिंतन का केंद्र भी है।
- इसमें विभिन्न गैलरी, शोध केंद्र, विशिष्ट अतिथियों के लिए लाउंज और प्रशासनिक कार्यालय हैं।
- भूतल पर एक इंटरैक्टिव टर्नटेबल थिएटर शो पेश करता है जो आगंतुकों के लिए गांधी की जीवनी को जीवंत बनाता है।
- प्रदर्शनी और निवेश:
- इसमें गांधी और बिहार के इतिहास पर एक व्यापक प्रदर्शनी है, जिसकी लागत लगभग 45 करोड़ रुपये है।
- प्रदर्शनी में अहमदाबाद में सावधानीपूर्वक तैयार की गई मूर्तियां और कलाकृतियाँ शामिल हैं।
- निर्माण और समयरेखा:
- मुख्यमंत्री नीतीश कुमार के दूरदर्शी मार्गदर्शन में 2 अक्टूबर, 2018 को निर्माण शुरू हुआ।
- प्रारंभिक पूर्णता लक्ष्य से परे कई विस्तारों के बावजूद, टॉवर का उद्घाटन 4 फरवरी, 2024 को होना है।
- इसकी कुल निर्माण लागत 129 करोड़ रुपये है।
- यह टॉवर सात एकड़ भूमि पर फैला हुआ है।
सांस्कृतिक और शैक्षिक प्रभाव:
- बापू टॉवर को बच्चों, छात्रों और शोधकर्ताओं के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण शैक्षिक संसाधन के रूप में डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
- यह आगंतुकों को ऐतिहासिक घटनाओं, गांधी के दार्शनिक विचारों और बिहार के साथ उनके गहरे संबंध को प्रदर्शित करते हुए एक ज्ञानवर्धक अनुभव प्रदान करता है।
- यह टॉवर एक प्रमुख सांस्कृतिक स्थल और भावी पीढ़ियों के लिए प्रेरणा का स्रोत बनने के लिए तैयार है।
3. पटना में गांधी संग्रहालय:
- स्थान: पटना, बिहार में स्थित है।
- निर्माण का वर्ष: 1967 में निर्मित।
- उद्देश्य और महत्व:
- महात्मा गांधी के जीवन और सिद्धांतों को प्रदर्शित करने के लिए समर्पित एक सार्वजनिक सेवा संस्थान।
- भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम के दौरान बिहार में गांधी की भूमिका पर प्रकाश डालता है।
- “राष्ट्रपिता” की विरासत का सम्मान करने के लिए एक प्रमुख स्मारक के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- प्रदर्शनी और विशेषताएँ:
- फ़ोटोग्राफ़ अनुभाग: महात्मा गांधी की तस्वीरों का एक संग्रह प्रदर्शित करता है, जो उनके जीवन के विभिन्न चरणों का दस्तावेजीकरण करता है।
- पुस्तकालय: इसमें गांधी के जीवन और दर्शन से संबंधित पुस्तकों, पत्रिकाओं, साहित्य और ऑडियो-वीडियो सामग्री का समृद्ध संग्रह है।
- आगंतुक अनुभव:
- महात्मा गांधी के ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक योगदान में रुचि रखने वालों के लिए पटना में देखने के लिए सबसे अच्छी जगहों में से एक के रूप में पहचाना जाता है।
4. खुदा बख्श ओरिएंटल लाइब्रेरी:
- ऐतिहासिक अवलोकन:
- निजी संग्रह के रूप में स्थापित:
- 18वीं शताब्दी के मध्य में 1,400 पांडुलिपियों और दुर्लभ पुस्तकों के साथ शुरू हुआ।
- खुदा बख्श द्वारा शुरू किया गया, जो एक सरकारी अधिकारी थे, जिन्हें यह संग्रह उनके पिता से विरासत में मिला था।
- सार्वजनिक उद्घाटन: पुस्तकालय को पहली बार 1891 में जनता के लिए खोला गया था।
- निजी संग्रह के रूप में स्थापित:
- वर्तमान संग्रह:
- पांडुलिपियाँ: 21,000 से अधिक पांडुलिपियाँ।
- मुद्रित पुस्तकें: लगभग 250,000 मुद्रित पुस्तकें।
- प्रस्तुत भाषाएँ: फ़ारसी, अरबी, उर्दू, हिंदी, अंग्रेज़ी, तुर्की और कई अन्य भाषाएँ।
- संग्रह में उल्लेखनीय वस्तुएँ:
- तारीख-ए-खानदान-ए-तैमूरिया:
- तैमूर और उसके वंशजों के इतिहास का विस्तृत विवरण देने वाला एक भव्य सचित्र पाठ।
- इस कार्य की एकमात्र मौजूदा प्रति पुस्तकालय में रखी गई है।
- लॉर्ड बायरन का “ओड टू नेपोलियन”: दो अतिरिक्त छंदों वाली एक प्रति, जिसके बारे में माना जाता है कि यह बायरन की खुद की लिखावट है।
- नादिर शाह की तलवार: एक महत्वपूर्ण ऐतिहासिक कलाकृति।
- कुरान की लघु प्रति: केवल 2.5 मिमी चौड़ी, उल्लेखनीय रूप से छोटी।
- तारीख-ए-खानदान-ए-तैमूरिया:
- पांडुलिपि संरक्षण प्रयास:
- पांडुलिपि संरक्षण केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- निवारक संरक्षण: 8,468 से अधिक पांडुलिपियों को सुरक्षित रखा गया है।
- उपचारात्मक संरक्षण: 247 पांडुलिपियों के लिए संरक्षण उपचार किया गया है।
- पांडुलिपियों की एक महत्वपूर्ण संख्या को डिजिटल किया गया है और ऑनलाइन उपलब्ध कराया गया है।
- अनुसंधान और वैश्विक महत्व:
- दुनिया में दुर्लभ और अद्वितीय पांडुलिपियों के सबसे बड़े भंडारों में से एक के रूप में मान्यता प्राप्त है।
- दुनिया भर से शोधकर्ताओं और विद्वानों को आकर्षित करता है।
- उल्लेखनीय आगंतुक:
- पुस्तकालय ने कम से कम छह वायसराय का स्वागत किया है।
- महात्मा गांधी, जवाहरलाल नेहरू और रवींद्रनाथ टैगोर जैसी प्रमुख हस्तियाँ।
- भारत के चार राष्ट्रपति यहाँ आ चुके हैं, जिनमें एपीजे अब्दुल कलाम भी शामिल हैं।
खुदा बख्श ओरिएंटल लाइब्रेरी ऐतिहासिक दस्तावेजों और दुर्लभ पांडुलिपियों का खजाना है, जो दुनिया भर में सांस्कृतिक विरासत और विद्वत्ता को संरक्षित करने और बढ़ावा देने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभा रही है।
5. कुम्हरार पार्क:
- स्थान और ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- कुम्हरार पार्क शहर (पटना) के मध्य में स्थित है और इसे शहर का प्राचीन हृदय माना जाता है।
- पटना के आसपास की खुदाई में प्राचीन शहर पाटलिपुत्र के अवशेष मिले हैं।
- कुम्हरार में प्रमुख पुरातात्विक खोजें:
- 80-स्तंभों वाला हॉल:
- कुम्हरार में 80 स्तंभों और लकड़ी के मंच वाला एक प्रभावशाली हॉल खोजा गया था।
- शुरू में, इस हॉल को शाही दरबार (शाही दर्शकों के लिए एक हॉल) माना जाता था।
- बाद में खोजों से पता चला कि यह बौद्धों के लिए एक सभा भवन के रूप में कार्य करता था और सम्राट अशोक के समय में बनाया गया था।
- मठ-सह-अस्पताल (आरोग्य विहार):
- पार्क के भीतर, आरोग्य विहार के रूप में जानी जाने वाली एक संरचना का पता चला।
- यह इमारत मठ और अस्पताल दोनों के रूप में कार्य करती थी।
- यह चौथी-पांचवीं शताब्दी ई.पू. की है।
- 80-स्तंभों वाला हॉल:
- अतिरिक्त कलाकृति:
- इस स्थल पर ‘धरवंतरेह’ शब्द से अंकित एक छोटा सा बर्तन मिला, जो पार्क के ऐतिहासिक और पुरातात्विक महत्व को बढ़ाता है।
ये खोजें सामूहिक रूप से पाटलिपुत्र के प्राचीन इतिहास और क्षेत्र की बौद्ध विरासत को समझने में कुम्हरार के महत्व को उजागर करती हैं।
6. तख्त श्री हरिमंदिर जी पटना साहिब:
- तख्त के रूप में महत्व:
- सिख धर्म में दूसरा सबसे पवित्र तख्त (अस्थायी सत्ता की सीट) माना जाता है।
- सिख सत्ता की सर्वोच्च सीटों का प्रतिनिधित्व करने वाले पाँच तख्तों में से एक।
- ऐतिहासिक और धार्मिक महत्व:
- दसवें सिख गुरु, श्री गुरु गोबिंद सिंह जी महाराज के जन्मस्थान के रूप में प्रतिष्ठित।
- इस मंदिर को तीन सिख गुरुओं ने पवित्र किया है, जिससे इसकी पवित्र स्थिति और भी बढ़ गई है।
- वीरता और निडरता के प्रतीक के रूप में जाना जाता है, जो अपने भक्तों में महान धर्मपरायणता को प्रेरित करता है।
- सांस्कृतिक प्रभाव:
- पटना शहर की शानदार विरासत में एक प्रमुख स्थान रखता है।
- इसे पटना साहिब के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, जो इस क्षेत्र के सांस्कृतिक और आध्यात्मिक परिदृश्य में इसकी अभिन्न भूमिका को दर्शाता है।
7. पटना में गोल घर:
- ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि:
- ब्रिटिश सेना के लिए कैप्टन जॉन गार्स्टिन द्वारा 1786 में बनाया गया।
- क्षेत्र में 1770 के अकाल के विनाशकारी प्रभाव के जवाब में निर्मित।
- उद्देश्य और संरचना:
- अनाज को संग्रहीत करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया एक विशाल अन्न भंडार।
- स्तंभ रहित डिज़ाइन:
- संरचना आंतरिक स्तंभों के बिना बनाई गई है।
- इसमें एक विशाल दीवार है जो आधार पर 3.6 मीटर मोटी है।
- ऊँचाई: 29 मीटर ऊँची है।
- वास्तुकला की विशेषताएँ:
- सर्पिल सीढ़ी:
- अनाज भंडार के बाहरी भाग के चारों ओर 145 सीढ़ियाँ हैं।
- मूल रूप से अनाज के परिवहन को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया:
- मज़दूर ऊपर एक छेद के माध्यम से भार उठाते थे और फिर अलग-अलग सीढ़ियों से नीचे उतरते थे।
- सर्पिल सीढ़ी:
- आगंतुक अनुभव:
- सीढ़ियों पर चढ़ने से पटना शहर का मनोरम दृश्य दिखाई देता है।
- पास की गंगा नदी का शानदार दृश्य प्रदान करता है।
8. बिहार संग्रहालय:
- स्थान: पटना के बेली रोड पर स्थित है।
- ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व:
- ऐतिहासिक ज्ञान के केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता है और कलाकृतियों की एक बड़ी संख्या को प्रदर्शित करता है।
- भारत के समृद्ध इतिहास और संस्कृति को उजागर करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
- हर मूर्ति और प्रदर्शनी क्षेत्र के गौरवशाली अतीत को दर्शाती है।
- आगंतुक अनुभव:
- संग्रहालय परिसर अच्छी तरह से बनाए रखा और साफ है।
- यह विभिन्न रुचियों को पूरा करने वाले विभिन्न अनुभाग प्रदान करता है।
- बच्चों की पसंदीदा: एक कृत्रिम वन्यजीव अभयारण्य युवा आगंतुकों के बीच लोकप्रिय है।
- संचालन समय: आगंतुकों के लिए सुबह 10:30 बजे से शाम 5:00 बजे तक खुला रहता है।
- इसके लिए आदर्श: इतिहास और संस्कृति के बारे में सीखते हुए दोस्तों और परिवार के साथ घूमने के लिए एक आदर्श स्थान।
9. बुद्ध स्मृति पार्क:
- उद्देश्य और स्मरणोत्सव:
- भगवान बुद्ध के 2554वें जन्मदिन के उपलक्ष्य में बिहार सरकार द्वारा विकसित।
- बुद्ध स्मारक पार्क के रूप में भी जाना जाता है।
- स्थान और आकार:
- महावीर मंदिर के सामने, पटना जंक्शन के पास फ्रेज़र रोड पर स्थित है।
- 22 एकड़ में फैला एक शहरी नखलिस्तान।
- मुख्य विशेषताएँ और आकर्षण:
- दो बोधि वृक्ष:
- दलाई लामा द्वारा लगाए गए ये वृक्ष भगवान बुद्ध की प्रतिमा के दोनों ओर हैं, जो एक प्रमुख दृश्य आकर्षण के रूप में कार्य करते हैं।
- पाटलिपुत्र करुणा स्तूप:
- 200 फुट ऊँचा गोलाकार स्तूप जो पार्क की सबसे प्रमुख विशेषता है।
- इसमें भगवान बुद्ध का एक अवशेष है – वैशाली से उत्खनित आठ मूल अवशेषों में से एक – एक कांच के बाड़े में।
- स्तूप में कई प्रवेश द्वार हैं।
- ध्यान केंद्र:
- नालंदा विश्वविद्यालय के मठों की वास्तुकला योजनाओं पर आधारित।
- इसमें 60 कक्ष हैं, जहाँ से आगंतुक स्तूप को देख सकते हैं।
- पुस्तकालय और संग्रहालय:
- पुस्तकालय में बौद्ध धर्म पर कई पुस्तकें हैं।
- संग्रहालय में कलाकृतियाँ हैं और भगवान बुद्ध के जीवन और शिक्षाओं के बारे में ऑडियो-विजुअल और मल्टीमीडिया प्रस्तुतियाँ प्रदान की जाती हैं।
- स्मृतियों का पार्क: बुद्ध की विरासत को संरक्षित करने के लिए समर्पित एक अतिरिक्त खंड।
- दो बोधि वृक्ष:
- अतिरिक्त अवशेष:
- परम पावन दलाई लामा और थाईलैंड, म्यांमार, जापान, दक्षिण कोरिया और श्रीलंका जैसे देशों के भिक्षुओं द्वारा लाए गए कई अन्य अवशेष पार्क के भीतर अलग-अलग ताबूतों में रखे गए हैं।
ये विशेषताएं बुद्ध स्मृति पार्क को एक व्यापक सांस्कृतिक और शैक्षिक केंद्र बनाती हैं जो भगवान बुद्ध की समृद्ध विरासत और शिक्षाओं को उजागर करती है।
10. संजय गांधी बॉटनिकल गार्डन (पटना चिड़ियाघर):
- स्थान: पटना में प्रसिद्ध बेली रोड पर स्थित है।
- जैव विविधता:
- विविध प्रकार के पक्षियों और जानवरों का घर।
- भारत के विभिन्न भागों के साथ-साथ अन्य देशों के वनस्पतियों और जीवों की विशेषताएँ।
- ऑन-साइट चिड़ियाघर बच्चों के बीच विशेष रूप से लोकप्रिय है।
- आकर्षण और सुविधाएँ:
- कृत्रिम झील: आगंतुकों के लिए नौका विहार की सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
- अनोखा लकड़ी का घर: एक पेड़ पर बना लकड़ी का ढांचा जो अपनी नवीनता के कारण आगंतुकों को आकर्षित करता है।
- आगंतुक अनुभव:
- साल भर खुला रहता है।
- विशेष रूप से नए साल के दिन और अन्य छुट्टियों के दौरान व्यस्त।
- पार्क स्थानीय परिवारों और पड़ोसी शहरों से आने वाले पर्यटकों के लिए एक जीवंत केंद्र बन जाता है।
- लोकप्रिय गतिविधियों में पिकनिक और कुकआउट शामिल हैं, जहाँ आगंतुक अक्सर उत्सव के अवसरों को मनाने के लिए रंगीन पोशाक पहनते हैं।
11. पटना कलम (पटना पेंटिंग शैली):
- परिभाषा और उत्पत्ति:
- पटना कलम भारतीय चित्रकला की एक अनूठी शैली है जो 18वीं शताब्दी में उभरी।
- मुगल कलाकारों द्वारा विकसित, यह चित्रकला की पहली शैली थी जो आम लोगों की जीवनशैली को विशेष रूप से दर्शाती थी।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- लगभग 200 वर्षों से अस्तित्व में है और लोकप्रिय बनी हुई है।
- शुरू में, अंग्रेजों ने इन चित्रों को स्मृति चिन्ह के रूप में खरीदा था।
- कलात्मक तकनीक:
- इस प्रक्रिया को “काजी सीही” के रूप में जाना जाता है, जो पटना कलम की शैली और तकनीक को अलग करती है।
12. पुराना सचिवालय, पटना:
- वास्तुशिल्प महत्व:
- 1917 में अंग्रेजों द्वारा इंडो-सरसेनिक शैली में पूरा किया गया, जो इसे शहर की सबसे बड़ी सरकारी इमारतों में से एक बनाता है।
- हरे-भरे बगीचे के बीच एक विशाल घंटाघर है; घंटाघर लगभग 184 फीट ऊंचा है।
- उल्लेखनीय तत्व:
- बिहार के पहले मुख्यमंत्री श्री कृष्ण सिन्हा (बिहार केसरी) की कांस्य प्रतिमा है, जो एक प्रमुख आकर्षण है।
- प्रसिद्ध सिडनी वास्तुकार जोसेफ मुनिंग्स द्वारा डिजाइन किया गया और कलकत्ता के मार्टिन बर्न द्वारा निर्मित।
- प्रशासनिक भूमिका: बिहार राज्य सरकार के प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय के रूप में कार्य करता है।
13. सभ्यता द्वार:
- अवलोकन और उद्घाटन:
- 2018 में मुख्यमंत्री नीतीश कुमार द्वारा उद्घाटन किया गया एक आधुनिक स्मारक।
- वास्तुशिल्प विशेषताएँ:
- गांधी मैदान के उत्तरी भाग में स्थित है।
- शीर्ष पर एक छोटे स्तूप के साथ लाल बलुआ पत्थर का उपयोग करके निर्मित।
- सांस्कृतिक महत्व:
- ऐतिहासिक उपलब्धियों की याद दिलाता है और वास्तुकला की उत्कृष्ट कृति के रूप में डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
- स्थानीय लोगों और पर्यटकों के लिए शाम को एक लोकप्रिय सभा स्थल।
14. कालिदास रंगालय:
- सांस्कृतिक केंद्र:
- गांधी मैदान के दक्षिण-पूर्व कोने में स्थित बिहार के प्रसिद्ध थिएटरों में से एक।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय रंगमंच संस्थान के क्षेत्रीय केंद्र, बिहार आर्ट थिएटर द्वारा प्रबंधित।
- सुविधाएँ:
- इसमें एक मंच, सभागार और बिहार नाट्य संस्थान का कार्यालय शामिल है।
- इसमें “अन्नपूर्णा” नामक एक कैफेटेरिया भी है।
- इस परिसर में शकुंतला जनता थिएटर, प्रियंबदा चिल्ड्रन थिएटर, अनसूया आर्ट गैलरी और कलाकारों के लिए अभ्याथना गेस्ट हाउस भी शामिल हैं।
- शैक्षणिक कार्यक्रम: नृत्य, संगीत, चित्रकला और फोटोग्राफी की कक्षाएँ प्रदान करता है।
- भूमिका: पटना में सांस्कृतिक प्रदर्शन और कलात्मक अभिव्यक्ति के केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता है।
15. प्रेमचंद रंगशाला:
- ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि:
- बिहार सरकार द्वारा 1971 में स्थापित राजेंद्र नगर में स्थित।
- पूर्वी भारत के सबसे बड़े थिएटरों में से एक माना जाता है।
- प्रशासन और जीर्णोद्धार:
- सी.आर.पी.एफ. द्वारा निष्क्रियता और उपयोग की अवधि के बाद, सांस्कृतिक कार्यकर्ताओं के दबाव के बाद सभागार को नियमित नाटकों के लिए फिर से खोल दिया गया।
- 2011-2012 में ₹5.91 करोड़ की अनुमानित लागत से बड़े पैमाने पर जीर्णोद्धार किया गया, जिससे इसकी बैठने की क्षमता में वृद्धि हुई और इसकी संरचना में सुधार हुआ।
- उद्घाटन:
- फरवरी 2012 में मुख्यमंत्री नीतीश कुमार ने अत्याधुनिक पुनर्निर्मित थिएटर का उद्घाटन किया।
16. रवींद्र परिषद:
- बहुउद्देश्यीय सांस्कृतिक केंद्र: पटना में बीर चंद पटेल पथ पर स्थित है।
- नाम: रवींद्रनाथ टैगोर के नाम पर, जो कला और साहित्य पर उनके प्रभाव को दर्शाता है।
- केंद्र के घटक:
- एक संगीत विद्यालय (गीत भवन)।
- टैगोर पर और उनके द्वारा लिखी गई पुस्तकों वाला एक पुस्तकालय।
- एक सभागार (रवींद्र भवन), सांस्कृतिक और नाट्य कार्यक्रमों के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण स्थल।
- प्रोग्रामिंग:
- थिएटर, लाइव संगीत, नृत्य, कॉमेडी, दृश्य कला, बोले गए शब्द और बच्चों के कार्यक्रमों सहित कई तरह के प्रदर्शन आयोजित करता है।
- नवीनीकरण विवरण:
- 2008 से 2010 के बीच ₹1.5 करोड़ की लागत से पुनर्निर्मित।
- ऑडिटोरियम की सीटिंग क्षमता 655 से बढ़ाकर 1,000 कर दी गई।
- फरवरी 2011 में मुख्यमंत्री नीतीश कुमार ने इस अपडेटेड सुविधा का उद्घाटन किया।
17. भारतीय नृत्य कला मंदिर:
- संस्था अवलोकन:
- भारतीय शास्त्रीय नृत्य शैलियों के प्रचार और संरक्षण के लिए समर्पित एक प्रसिद्ध संस्थान।
- स्थापना:
- पद्मश्री पंडित हरि उप्पल जी द्वारा 1963 में स्थापित।
- बिहार सोसायटी पंजीकरण अधिनियम, 1860 के तहत पंजीकृत।
- कार्यक्रम और प्रशिक्षण:
- भरतनाट्यम, कथक, ओडिसी, कुचिपुड़ी और मणिपुरी सहित विभिन्न शास्त्रीय नृत्य शैलियों में व्यापक प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करता है।
- शास्त्रीय नृत्य और सांस्कृतिक विरासत को बढ़ावा देने के लिए कार्यशालाएँ, सेमिनार और प्रदर्शन आयोजित करता है।
- सांस्कृतिक प्रभाव:
- पटना और उसके बाहर कलात्मक प्रतिभा को बढ़ावा देने और भारतीय शास्त्रीय नृत्य की समृद्ध परंपरा को संरक्षित करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
कुछ अन्य प्रमुख आकर्षण:
- पटना का समग्र महत्व:
- बिहार आने वाले सभी पर्यटकों में से 41% पटना आते हैं।
- विदेशी पर्यटकों के बीच बोधगया सबसे लोकप्रिय है, जबकि पटना ऐतिहासिक, सांस्कृतिक और आधुनिक आकर्षणों का एक समृद्ध मिश्रण समेटे हुए है।
- पटना में अतिरिक्त गुरुद्वारे:
- पहिला बड़ा गुरुद्वारा
- गोबिंद घाट गुरुद्वारा
- गुरु का बाग गुरुद्वारा
- बाल लीला गुरुद्वारा
- हांडी साहिब गुरुद्वारा
- ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक वास्तुकला:
- पादरी की हवेली, उच्च न्यायालय, गोलघर और सचिवालय भवन: ब्रिटिश युग की वास्तुकला के बेहतरीन उदाहरण।
- गांधी मैदान: एक ऐतिहासिक मैदान जहाँ कई स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन रैलियाँ हुईं।
- प्राचीन विरासत और सांस्कृतिक स्मारक:
- कुम्हरार और अगम कुआँ:
- प्राचीन शहर पाटलिपुत्र के खंडहर।
- मौर्य युग का एक प्राचीन कुआँ।
- प्रमुख स्थल जहाँ अशोक की वास्तुकला और प्राचीन शहरी नियोजन स्पष्ट हैं।
- दीदारगंज यक्षी:
- मौर्य कला का एक उल्लेखनीय उदाहरण जो इस क्षेत्र की प्रारंभिक सांस्कृतिक विरासत को दर्शाता है।
- कुम्हरार और अगम कुआँ:
- पटना तारामंडल (इंदिरा गांधी तारामंडल):
- इंदिरा गांधी विज्ञान परिसर के भीतर स्थित है।
- एशिया के सबसे बड़े तारामंडलों में से एक, जो बड़ी संख्या में आगंतुकों को आकर्षित करता है।
- आगामी अत्याधुनिक कला स्थल संग्रहालय:
- बेली रोड पर 13.9 एकड़ की साइट पर लगभग 530 करोड़ रुपये की लागत से बनाया जा रहा है।
- आंशिक रूप से खोला गया, जल्द ही पूरा होने की उम्मीद है।
ये आकर्षण सामूहिक रूप से पटना की समृद्ध ऐतिहासिक विरासत, जीवंत धार्मिक परंपराओं और चल रहे आधुनिक विकास को प्रदर्शित करते हैं, जो इसे बिहार में एक ज़रूरी गंतव्य बनाते हैं।
परिवहन
सड़क मार्ग
- व्यापक सड़क नेटवर्क: पूरे जिले में सड़कों के नेटवर्क द्वारा अच्छी तरह से सेवा प्रदान की जाती है।
- एनएच-31, एनएच-30, एनएच-83 और एनएच-98 पटना को अन्य प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ते हैं।
- राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग 31:
- दानापुर, पटना और पटना शहर से होकर गुजरता है।
- एनएच-31 की एक शाखा बाढ़ के रास्ते बरौनी जाती है।
- एक और शाखा बिहार के रास्ते नवादा जाती है।
- लगभग सभी उप-मंडल मुख्यालय (मसौढ़ी को छोड़कर) इस राजमार्ग पर स्थित हैं।
- पटना मेट्रो (निर्माणाधीन) शहरी परिवहन में सुधार करेगी।
- अंतर-शहर संपर्क:
- उत्तर और दक्षिण बिहार के बीच एक महत्वपूर्ण संपर्क प्रदान करता है।
- बोधगया, राजगीर, रांची और सिलीगुड़ी जैसे प्रमुख स्थलों तक सुविधाजनक सड़क पहुँच।
- अंतर-शहर परिवहन: पटना के भीतर कुशल स्थानीय परिवहन विकल्प।
- लोकनायक गंगा पथ, महात्मा गांधी सेतु, दीघा-सोनपुर पुल
रेलवे
- मुख्य रेलवे लाइन:
- पूर्व मध्य रेलवे की मुख्य लाइन पूरे जिले में गंगा के समानांतर चलती है।
- पटना जंक्शन:
- पटना का प्रमुख रेलवे स्टेशन।
- यह पटना को एक्सप्रेस और सुपरफास्ट ट्रेनों के माध्यम से दिल्ली, मुंबई, कोलकाता, गुवाहाटी, वाराणसी, अमृतसर, बैंगलोर, लखनऊ और चेन्नई जैसे प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ता है।
- रेलवे लाइनें:
- उत्तर से दक्षिण तक चलने वाली तीन मुख्य रेलवे लाइनें:
- पटना-गया शाखा लाइन
- फतवा-इस्लामपुर लाइट रेलवे
- बख्तियारपुर-राजगीर शाखा लाइन
- उत्तर से दक्षिण तक चलने वाली तीन मुख्य रेलवे लाइनें:
- अन्य स्टेशन – राजेंद्र नगर टर्मिनल, पाटलिपुत्र जंक्शन, पटना साहेब, गुलजारबाग स्टेशन, फुलवारी शरीफ रेलवे स्टेशन, दानापुर स्टेशन, फतुहा जंक्शन रेलवे स्टेशन, पटना मेट्रो।
हवाई मार्ग
- पटना हवाई अड्डा – पूर्वी भारत के सबसे व्यस्त हवाई अड्डों में से एक।
- जयप्रकाश नारायण अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे के रूप में जाना जाता है।
- दिल्ली, मुंबई और कोलकाता जैसे महत्वपूर्ण शहरों के साथ बेहतरीन हवाई संपर्क प्रदान करता है।
- कई एयरलाइनें इस हवाई अड्डे से नियमित उड़ानें संचालित करती हैं।
- इसका नाम “लोक नायक” जयप्रकाश नारायण (1902-1979) के नाम पर रखा गया है, जो एक प्रमुख स्वतंत्रता कार्यकर्ता और राजनीतिक नेता थे।
- बिहटा एयर फोर्स स्टेशन
- अधिक हवाई यातायात को संभालने के लिए आगामी बिहटा हवाई अड्डा।
जलमार्ग (नदी द्वारा):
- गंगा की नौगम्यता:
- गंगा पूरे वर्ष नौगम्य है, जिससे माल परिवहन में सुविधा होती है।
- छोटी नदियाँ:
- पुनपुन और दरधा जैसी नदियाँ केवल बरसात के मौसम में ही नौगम्य हो जाती हैं।
- इन नदियों का उपयोग कृषि उपज को फ़तवा में अनाज बाज़ार तक ले जाने के लिए किया जाता है।
चुनौतियाँ और मुद्दे
- यातायात भीड़भाड़ और प्रदूषण।
- मानसून के दौरान शहरी बाढ़।
- बेरोज़गारी और कौशल की कमी।
- स्वास्थ्य सेवा सुविधाओं में सुधार की आवश्यकता है।
निष्कर्ष
पटना बिहार का सांस्कृतिक, आर्थिक और राजनीतिक केंद्र है। ऐतिहासिक स्थलों, मजबूत शिक्षा बुनियादी ढांचे और बढ़ते उद्योगों के साथ, यह तेजी से विकसित हो रहा है। हालाँकि, पटना को वास्तव में आधुनिक शहर बनाने के लिए बुनियादी ढाँचे, यातायात और नौकरी के अवसरों में सुधार की आवश्यकता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
| DEPARTMENT | TOLL FREE HELPLINE NUMBER |
| Police | 100 |
| Fire Service | 101 |
| Ambulance | 102 |
| Indian Railway General Enquiry | 139 |
| Election Commission Of India | 1950 |
| Women Helpline | 1091/ 9771468012 |
| Child HelpLine | 1098 |
| Control Room | 06156-224601 |
| HIV/AIDS Helpline Number | 1097 |
| Electricity | 1912 |
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

7 thoughts on “Patna District: A Special Land of Heritage, Culture & Growth”