East Champaran District: An Overview
East Champaran District, is one of the largest among 38-districts, located in northern part of Bihar state, India, holds immense historical, cultural, and agricultural significance. Spanning an area of 3,968 square kilometers (1,532 square miles), East Champaran lies at 26° 16′ to 27° 1′ N latitude and 84° 30′ to 85° 16′ E longitude, and shares borders with Nepal to the north, Sitamarhi district and Sheohar district to the east, Muzaffarpur district to the south, and Gopalganj district to the west. The district’s administrative headquarters is located at Motihari town. The region is part of the Tirhut Division.
The British administration formally established Champaran as an independent unit in 1866. However, in 1972, Champaran was divided into Purbi Champaran (East Champaran) and Paschim Champaran (West Champaran). It is famous for Mahatma Gandhi’s Champaran Satyagraha (1917), which was India’s first major movement against British rule. The district is also a major agricultural hub, known for its sugarcane production, and shares an international border with Nepal. As per the 2011 Census, district has a population of 5,099,371, making it the second most populous district in Bihar after Patna District.
Champaran: A Land of Historical and Revolutionary Significance
Champaran holds a glorious and historically significant place in Indian history, spanning from epic times to the modern era. According to the Puranas, Dhruv, the devoted son of King Uttanapada, performed intense penance at Tapovan in Champaran to attain divine knowledge. The district is also sacred to Hindus as it is associated with Goddess Sita.
During the time of King Janaka, Champaran was part of the Tirhut kingdom. It is believed that Jankigharh (also known as Chanchigarh) was the capital of King Janaka’s Videha state, which later became part of the Vaishali Empire in the 6th century BC. Champaran was also visited by Lord Buddha, who delivered sermons here, and in memory of his presence, Emperor Ashoka built pillars and stupas in the 3rd century BC. It was ruled by different kingdoms as Videha, Sunga and Kanvas. After the decline of the Gupta and Pala dynasties, the entire Champaran region, including Mithila, came under the rule of the Karnat dynasty, followed by local satraps under Muslim rule.
Champaran Satyagraha (1917)
A turning point in modern Indian history occurred in April 1917 when Mahatma Gandhi arrived in Motihari at the invitation of Raj Kumar Shukla, a local farmer and freedom fighter. Mahatma Gandhi’s Champaran Satyagraha became a landmark movement in India’s struggle for independence. Gandhi’s visit marked the first successful experiment of Satyagraha, where he protested against the forced cultivation of indigo (Nil crop) by British landlords. This movement ignited a new phase in India’s fight for independence, and Gandhi visited the region multiple times thereafter.
Origin of Name
The name Champaran originates from the Sanskrit words “Champa-aranya” or “Champkatanys,” where “Champa” (or Champaka) refers to the Magnolia tree, and “aranya” means forest. Thus, Champaranya translates to “Forest of Magnolia trees.” It is believed that the name was derived from the vast forests that once covered the region, which were inhabited by solitary ascetics. Purbi Champaran (Eastern Champaran) derives its name from its geographical location as the eastern part of the original Champaran district.
Champaran has a rich legacy, encompassing spiritual significance, political evolution, and revolutionary movements. From its association with King Janaka and Lord Buddha to being the birthplace of Gandhi’s Satyagraha, Champaran continues to be an important cultural, religious, and historical landmark in Bihar.
Key Dates of Historical Events Leading to Gandhi Ji’s Champaran Visit
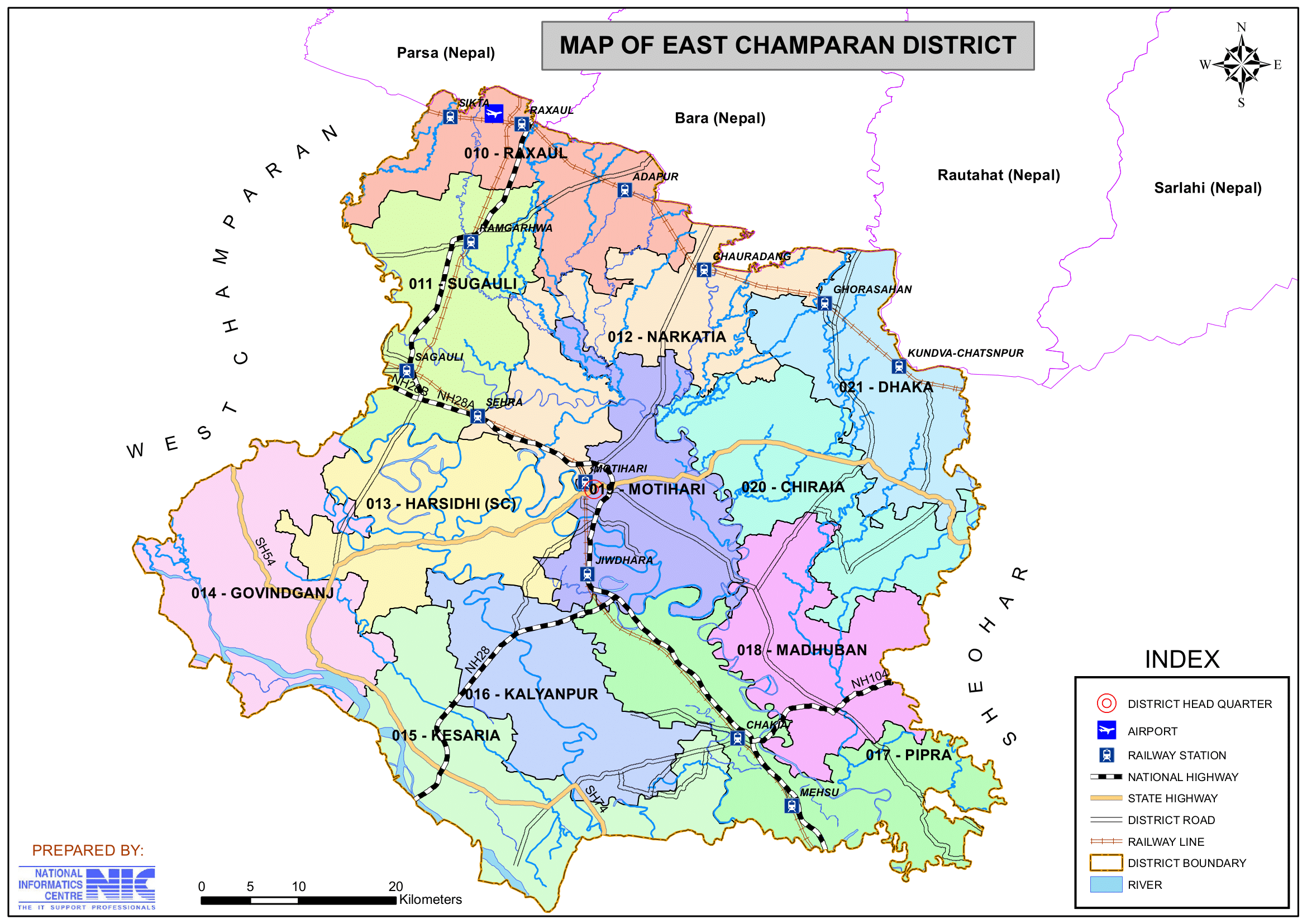
Key Facts About East Champaran District
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Region: Mithila
- Division: Tirhut
- Established: 2 November 1972
- Area: 3,968 km2 (1,532 sq mi)
- Coordinates: 26.6500°N 84.9167°E
- District Headquarters: Motihari Town
- District Magistrate: Shri Saurabh Jorwal, IAS
- Superintendent of Police: Sri Kantesh Kumar Mishra, IPS
- Population (2011):
- Total: 5,099,371
- Density: 1,300/km2 (3,300/sq mi)
- Literacy Rate: 55.79%
- Sex Ratio: 901/1000
- Gram Panchayats: 405
- Villages: 1344
- No. of Subdivision (Tehsil): 6 (Areraj, Chakia, Motihari, Pakaridayal, Raxaul, Sikarahana)
- No. of Blocks: 27
- Sangrampur, Harsidhi, Areraj, Paharpur, Chakia, Mehsi, Kesaria, Kalyanpur, Banjaria, Motihari, Piprakothi, Kotowa, Sugauli, Turkaulia, Madhuban, Tetaria, Patahi, Phenhara, Pakaridayal, Raxaul, Ramgarhwa, Adapur, Chauradano, Bankatwa, Chiraiya, Ghorasahan, Dhaka
- Police Station: 50
- Govindganj, Areraj, Malahi, Harsidhi, Paharpur, Sangrampur, Chhatauni, Turkauliya, Piprakothi, Kotwa, Banjariya, Lakhaura, Bhopatpur, Sagauli, Kesariya, Kalyanpur, Dumariya Ghat, Chakia, Mehsi, Pipra, Madhuban, Pakaridyal, Rajepur, Phenhara, Patahi, Dhaka, Chiraiya, Shikarganj, Kundwa Chainpur, Ghorasahan, Jharokhar, Jitna, Panchpakari, Raxaul, Chhauradano, Adapur, Darpa, Mahuawa, Nakardei, Ramgarwa, Palanwa, Hapur, Haraiya, Town P.S, Muphasil P.S, SC/ST P.S, Mahila P.S, Police Centre Motihari, Police Control Room, Bhelahi O.P.
- Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad): 2 (Motihari, Raxaul)
- Nagar Panchayats: 7 (Areraj Nagar, Dhaka, Chakiya, Kesariya, Mehsi, Pakaridayal, Sugauli
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 12
- Raxaul, Sugauli, Narkatiya, Harsidhi, Govindganj, Kesaria, Kalyanpur, Pipra, Madhuban, Motihari, Chiraia, Dhaka.
- Lok Sabha constituency: 3(Purvi Champaran, Paschim Champaran, Sheohar)
- Key Features:
- The site of Champaran Satyagraha, Mahatma Gandhi’s first movement in India.
- Tourist attractions: Gandhi Memorial, Kesariya Stupa (largest Buddhist stupa in the world).
- Fertile land producing sugarcane, maize, and pulses.
- Significance: A historical and agricultural hub of Bihar.
- Major Rivers: Gandak, Burhi Gandak and Baghmati
- Time Zone: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- PIN Code: 845401 (East Champaran)
- Vehicle Registration: BR-05
- Major Highways: NH-28A, NH-104
- Average annual precipitation: 1241 mm
- Official Website: eastchamparan.nic.in
Geography
- Location: East Champaran is situated in northern Bihar and shares its borders with:
- Nepal (north)
- West Champaran (west)
- Sitamarhi & Sheohar (east)
- Muzaffarpur & Gopalganj (south)
- Area: 3,969 square kilometers, making it one of Bihar’s largest districts.
- Topography:
- Alluvial plains, with highly fertile land suitable for agriculture.
- Flat terrain, with small river basins and wetlands.
- Climate:
- Humid subtropical climate with hot summers, monsoon rains (June-September), and mild winters.
- Rivers:
- Gandak River
- Buri Gandak River
- Lalbakeya River
History
Ancient Period
- The region was part of the Mithila Kingdom and later the Magadha Empire.
- Mentioned in Hindu epics like the Ramayana.
Medieval Period
- East Champaran was ruled by Mauryas, Guptas, and Mughals.
- It was an important trading and administrative center.
Modern Era
- Champaran Satyagraha (1917):
- Mahatma Gandhi launched his first major movement against British rule from this region.
- Farmers protested against forced indigo cultivation, marking the beginning of India’s independence movement.
- Formation of District:
- Champaran district was split into East and West Champaran in 1972 for better administration.
Demographics (As per the 2011 Census)
- Population:
- Total Population: East Champaran district has a population of approximately 5,099,371.
- Population Male: 2,681,209
- Population Female: 2,418,162
- Ranking: 21st in India (out of 640 districts).
- Density: 1,285 persons per square kilometer (3,320/sq mi).
- Population Growth (2001–2011): 29.01% reflecting significant population increase.
- Sex Ratio: 901 females per 1,000 males, indicating a gender disparity.
- Literacy Rate: 55.79%, which is below the national and state average but with significant efforts being made to improve education access and quality.
- Male Literacy Rate: 65.34%
- Female Literacy Rate: 45.12%
- Urban Population: 7.87% of the total population lives in urban areas.
- Total Population: East Champaran district has a population of approximately 5,099,371.
- Religious Composition (2011 Census): The majority of the population follows Hinduism, with a significant Muslim community.
- Hinduism: 80.14%
- Scheduled Castes: 12.74%
- Scheduled Tribes: 0.24%
- Islam: 19.42%
- Other or not stated: 0.44%
- Languages: Hindi, Bhojpuri, Maithili, and Urdu are widely spoken.
- Bhojpuri: 82.67%
- Urdu: 7.33%
- Hindi: 7.06%
- ‘Other’ Hindi: 2.58%
- Bengali: 0.26%
- Others: 0.1%
Administration
- Headquarters: Motihari
- Subdivisions:
- The district has 6 subdivisions: Motihari Sadar, Areraj, Pakridayal, Raxaul, Chakia and Dhaka.
- Each subdivision is led by a subdivisional magistrate who is in charge of development, revenue-related tasks, and maintaining law and order.
- Blocks and Circles:
- East Champaran district comprises 27 administrative Blocks and Circles such as Sangrampur, Harsidhi, Areraj, Paharpur, Chakia, Mehsi, Kesaria, Kalyanpur, Banjaria, Motihari, Piprakothi, Kotowa, Sugauli, Turkaulia, Madhuban, Tetaria, Patahi, Phenhara, Pakaridayal, Raxaul, Ramgarhwa, Adapur, Chauradano, Bankatwa, Chiraiya, Ghorasahan and Dhaka, each responsible for local governance and development.
- A Circle officer (CO) leads each circle, while a Block Development Officer (BDO) leads each block.
- Lok Sabha Constituencies:
- Purvi Champaran Lok Sabha seat represents the district.
- Vidhan Sabha Constituencies:
- The district has 12 assembly constituencies are: Raxaul, Sugauli, Narkatiya, Harsidhi, Govindganj, Kesaria, Kalyanpur, Pipra, Madhuban, Motihari, Chiraia and Dhaka.
Organization Chart

Economy
Agriculture: The Backbone of East Champaran
East Champaran has a strong agricultural economy, with farming being the primary source of income for most of its residents. The district is among the top producers of rice and wheat in Bihar.
Key Crops Grown in East Champaran
- Agriculture is the backbone of the economy, with major crops including:
- Paddy, wheat, maize, pulses, and mustard
- Vegetables like potatoes, onions, and tomatoes.
- Rice & Paddy: East Champaran accounts for 5.7% of Bihar’s total rice production, making it one of the top rice-producing districts.
- Wheat: The district is the second-largest wheat producer in Bihar, contributing 5.2% of the state’s wheat yield.
- Sugarcane: A major cash crop, supporting the sugar industry in the region (largest producer in Bihar).
- Jute & Lentils: Important crops that contribute to the district’s agrarian economy.
(Data Source: Government of Bihar Economic Survey 2014-15)
Animal Husbandry: A Key Rural Livelihood
- Animal husbandry plays a crucial role in rural income and employment.
- The sector contributes about 20% of the total rural income.
- Women from marginalized communities are extensively involved in this sector.
- Goat farming is particularly prominent, with East Champaran, Araria, and Katihar having the largest concentration of goats in Bihar.
(Data Source: Government of Bihar Economic Survey 2014-15)
Small-Scale Industries & Emerging Sectors
Apart from agriculture, small-scale industries are developing in East Champaran, including:
- Pearl Button Industry: A growing sector producing buttons from mother-of-pearl shells.
- Fisheries Development: Increasing focus on fish farming as an alternative livelihood.
- Sugar Industry: Several sugar mills, including in Motihari, Raxaul, and Chakia.
- Dairy Farming: Milk production is a growing sector.
- Handicrafts & Cottage Industries: Local artisans produce bamboo crafts, jute products, and handloom textiles.
- Trade & Commerce: Raxaul serves as a major trade hub with Nepal, handling cross-border goods transportation.
Fisheries Industry in East Champaran
East Champaran has great potential for fisheries development due to its abundant water bodies, including rivers, lakes, marshes, ponds, and tanks. Despite these natural resources, integrated efforts for modern fish farming have been limited.
Existing Fishery Resources
- 823 Government tanks & 161 private tanks, covering a total water area of 1,920 acres.
- 28 lakes (mans) with a water area of 7,486 acres.
- Proposed development: About 282 acres of government and private tanks (from 151 identified tanks) have been planned for fisheries development.
Fish Production & Economic Impact
- Annual fish production: 2,500 metric tonnes (MT).
- Estimated market value: ₹25 crores per year.
- Limited export: Currently, fish production is mostly consumed within the district, with little to no exports beyond East Champaran.
Common Fish Species in East Champaran
- Carps: Rohu, Catla, Naini, Calbasu.
- Catfish: Boari, Tengra, Silonal, Bachawa.
- Others: Hilsa, Gorarah, Sawra, Pothiya, Bangas, Murels, Garai, Chenga, Chitla, Chelwa, Bami, Gaineha, Changari, etc.
Development Initiatives & World Bank Funding
- The World Bank has financed ₹19 crore for fisheries development projects in Motijheel and Kararia Jheel (Motihari town and nearby areas).
- The project aims to enhance fish production and modernize fish farming techniques.
- Key development activities include:
- Lake restoration for modern fish farming.
- Construction of sluice gates for better water management.
- Strengthening and protecting the bandh (embankments).
- Deepening inlet and outlet channels.
- Clearing weeds and improving water quality.
Future Potential & Industry Growth
- Fisheries is an emerging industry in East Champaran with significant scope for expansion.
- Adopting composite fish culture techniques can further boost productivity.
- Encouraging private investment and cooperative fish farming can create employment and economic growth.
- Improving infrastructure for fish export can enhance the district’s contribution to Bihar’s fishery sector.
East Champaran’s fisheries industry is poised for rapid growth, making it a key sector for economic development.
Economic Outlook & Opportunities
- Strengthening agricultural infrastructure (irrigation, storage, and processing units) can enhance productivity.
- Expanding small-scale industries and promoting agro-based industries can create employment.
- Improving rural entrepreneurship (like dairy farming and fishery development) can diversify income sources.
Challanges: Flooding from rivers often damages crops, requiring better irrigation and flood control measures.
East Champaran’s agriculture-driven economy is gradually expanding into animal husbandry and small-scale industries, creating new employment and business opportunities.
Education
Higher Educational Institutions
- Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University (RPCAU) – A premier agricultural university.
- Munshi Singh College, Motihari – One of the oldest colleges in Bihar.
- Sri Krishna Jubilee Law College, Motihari – A reputed law college.
- Mahatma Gandhi Central University, Motihari, East Champaran
- Motihari College Of Engineering, NH-28A, Furshatpur Bariyarpur, Motihari
- Government Polytechnic, Near Gandhi Maidan, Behind ITI Motihari, East Champaran
- Several government and private schools, but higher education opportunities remain limited.
- High School Adapur, East Champaran (Motihari)
- Someshwar High School Areraj, East Champaran (Motihari)
Challenges
- Low literacy rate compared to other districts.
- Many students migrate to Patna or other cities for higher education.
Culture
East Champaran is a culturally rich region in Bihar, known for its folk traditions, vibrant festivals, and delicious cuisine. The district’s art, music, dance, and culinary heritage reflect its deep-rooted traditions and historical significance.
Festivals & Celebrations 🎊🙏
East Champaran celebrates several festivals with great enthusiasm, uniting people from different communities.
Chhath Puja ☀️🌊
- The most significant festival of East Champaran, dedicated to Surya Dev (Sun God).
- The only Hindu festival where the setting sun is worshipped.
- Celebrated twice a year:
- Chaitra Chhath (March-April).
- Kartik Chhath (October-November).
- A four-day festival with strict rituals:
- Holy bathing, fasting, and standing in water for long hours.
- Offering ‘Arghya’ (water offerings) to the rising and setting sun.
- Singing folk songs in honor of Chhathi Maiya and Surya Dev.
- Women (Parvaitins) fast for the well-being of their families.
- Men also actively participate in the festival.
Other Important Festivals
- Makar Sankranti – Celebrated with kite flying and feasting on sesame sweets.
- Holi – The festival of colors, marking the arrival of spring.
- Durga Puja – A grand festival dedicated to Goddess Durga, celebrated with processions and cultural programs.
- Diwali and Eid are also celebrated.
- Champaran Mahotsav – An annual festival celebrating the region’s cultural heritage.
Famous Cuisine & Sweets 🍛🍬
- Delicious Traditional dishes include:
- Litti Chokha, Sattu Paratha, Dal Pitha
- Champaran Meat (Ahuna Mutton) is a famous delicacy from the region.
- Most famous sweets and snacks include:
- Chhena Murki – A sweet made from paneer (chhena) and sugar syrup.
- Kesaria Peda – A saffron-flavored milk-based sweet.
- Khaja – A crispy, layered, deep-fried sweet.
- Malpua – A traditional Indian pancake made with flour, milk, and sugar.
- Khurma – A sweet snack made from flour and sugar syrup.
- Thekua – A crispy and flavorful snack, often made during Chhath Puja.
- Tilkut – A winter delicacy made with sesame seeds and jaggery.
- Murabba – A sweet fruit preserve.
Folk Music & Dance 🎶💃
- Traditional folk songs are an integral part of East Champaran’s cultural identity.
- These songs are performed on various occasions, including weddings, festivals, and religious ceremonies.
- Jhumari Dance:
- A widely loved dance form performed by married women.
- This dance expresses joy, devotion, and celebration.
Tourism
East Champaran, is a blend of historical significance, natural beauty, cultural heritage and religious destination. It is famous for its role in India’s freedom struggle, Buddhist heritage sites, and picturesque landscapes. Major Attractions are:
1. Gandhi Sangrahalaya, Motihari: A Tribute to Champaran Satyagraha
Gandhi Sangrahalaya (Gandhi Museum) in Motihari, East Champaran, is a historical landmark dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi’s first Satyagraha movement in India. The museum commemorates the Champaran Satyagraha of 1917, which was a turning point in India’s independence movement against British colonial rule.
Historical Significance
- Champaran Satyagraha (1917): Mahatma Gandhi first raised his voice against the atrocities of British indigo planters on poor peasants in Champaran, marking the beginning of India’s non-violent struggle for independence.
- Site of Gandhi’s Court Appearance: The museum is located exactly at the spot where Mahatma Gandhi was produced before the court of the then S.D.M. of Motihari on April 18, 1917, for violating Section 144 Cr. P.C..
- Foundation & Dedication:
- The foundation stone was laid on June 10, 1972, by the then Governor, Mr. D.K. Barooch.
- The memorial was inaugurated on April 18, 1978, by Gandhian leader Vidyakar Kavi.
Key Attractions
- Gandhi Memorial Pillar (Smarak Stambh)
- Designed by famous artist Nandalal Bose of Santiniketan.
- 48-feet tall stone pillar made of Chunar stone.
- Built at the exact spot where Gandhi was presented in court in 1917.
- Gandhi Museum & Exhibits
- Photographs and relics related to the Champaran Satyagraha.
- Writings, letters, and personal belongings of Mahatma Gandhi.
- Artifacts showcasing the lives of indigo farmers and their struggle.
- Educational & Cultural Center
- A leading center for research, education, and cultural activities related to India’s freedom movement.
- Workshops, lectures, and discussions on Gandhi’s philosophy of non-violence and truth.
Why Visit Gandhi Sangrahalaya?
- Experience the birthplace of India’s first Satyagraha movement.
- See rare photographs, documents, and relics from the Champaran Satyagraha.
- Learn about Gandhi’s role in India’s independence struggle.
- A must-visit for history enthusiasts, researchers, and students.
Gandhi Sangrahalaya is not just a museum—it is a symbol of India’s fight for justice and self-rule.
2. Gandhi Memorial, Chandrahiya: A Historic Landmark of Champaran Satyagraha
Gandhi Memorial in Chandrahiya, located in East Champaran, Bihar, is a historic site where Mahatma Gandhi was stopped by British officials on April 16, 1917, while on his way to Jasauli Patti to hear the grievances of oppressed indigo farmers. This incident became a turning point in the Champaran Satyagraha, India’s first major civil disobedience movement against British rule.
Historical Significance
- April 16, 1917: Gandhi was traveling to Jasauli Patti village to meet farmers forced to cultivate indigo.
- Stopped by British Authorities: A police official, riding a horse-driven buggy, handed Gandhi a notice from then-Champaran Collector W.B. Heycock, ordering him to leave the district immediately.
- Gandhi’s Response:
- He obeyed the order temporarily, returning to Motihari on a bullock cart.
- However, he refused to leave Champaran and, on April 18, 1917, appeared before the court of the sub-divisional magistrate.
- Gandhi’s defiance and reasoning in court led to the launch of Champaran Satyagraha, marking the beginning of India’s freedom struggle under his leadership.
Key Attractions
- Gandhi Memorial at Chandrahiya
- A monument commemorating Gandhi’s historic confrontation with British authorities.
- Symbolizes the courage and resistance of Champaran farmers.
- Historic Location
- Chandrahiya is just 8 km from Motihari, making it easily accessible for visitors.
- The village holds deep historical and cultural significance in India’s freedom movement.
Why Visit Gandhi Memorial, Chandrahiya?
- Stand at the exact location where Gandhi was stopped, marking the beginning of Satyagraha.
- Learn about the Champaran movement and its impact on India’s independence struggle.
- A must-visit for history enthusiasts, researchers, and students.
- Explore nearby places of historical importance, including Gandhi Sangrahalaya in Motihari.
Gandhi Memorial in Chandrahiya is a symbol of resistance, justice, and the power of non-violence.
3. George Orwell’s Birthplace, Motihari
Motihari, a small town in East Champaran, Bihar, is known for being the birthplace of George Orwell, one of the most influential writers of the 20th century. Orwell, born Eric Arthur Blair on June 25, 1903, is best known for his novels “Nineteen Eighty-Four” and “Animal Farm”, both of which remain classics in world literature.
Historical Significance
- Birthplace: Orwell was born near Gopal Sah High School in Motihari, where his father served as a British civil servant in the Opium Department.
- Family Background:
- His father, Richard Walmesley Blair, was a minor British official in the Indian Civil Service.
- His mother, Ida Mabel Blair, had French lineage and came from a family involved in the Burmese teak trade.
- Early Life: Although Orwell lived in India only for a year, his colonial upbringing and experiences shaped his critical views on imperialism, which later influenced his writings.
Key Attractions at George Orwell’s Birthplace
- George Orwell Memorial
- A simple yet significant monument marking the house where Orwell was born.
- The building has been preserved to honor his literary legacy.
- Restoration & Recognition
- The site was recognized by the Bihar government, with efforts to restore and develop it as a heritage site.
- Literary enthusiasts and tourists visit to explore the birthplace of a writer whose works continue to shape political and social discourse.
Famous Works of George Orwell
- Nineteen Eighty-Four (1949) – A dystopian novel about totalitarianism, surveillance, and state control, introducing concepts like Big Brother and Thought Police.
- Animal Farm (1945) – An allegorical novella critiquing power, corruption, and political tyranny, inspired by Orwell’s anti-totalitarian beliefs.
- Homage to Catalonia (1938) – A memoir of his experiences in the Spanish Civil War.
- Burmese Days (1934) – A novel inspired by his time in colonial Burma, reflecting on the evils of imperialism.
Why Visit George Orwell’s Birthplace?
- Explore the origins of one of the greatest literary figures of the 20th century.
- Understand Orwell’s early connection with colonial India and its influence on his works.
- A must-visit for literature lovers, history enthusiasts, and Orwellian scholars.
George Orwell’s birthplace in Motihari is a hidden literary landmark that connects India’s colonial past with modern political thought.
4. Someshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir, Areraj
Someshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir, located in Areraj, East Champaran, Bihar, is one of the most revered Shiva temples in North Bihar. The temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva, attracts thousands of devotees from across India and Nepal, especially during the Shravani Mela (July-August).
Areraj is 28 km southwest of Motihari, well connected by pucca roads. Over time, Areraj has developed from a village into a town and now serves as the headquarters of the Areraj Subdivision.
Religious Significance
- The temple is considered ancient and sacred, making it an important pilgrimage site.
- Devotees from Bihar, neighboring states, and Nepal visit the temple to seek blessings.
- Shrawani Mela is the biggest annual festival celebrated here, during which thousands of Kanwariyas (Shiva devotees) carry holy water from the Ganges to offer to Lord Shiva.
Key Attractions at Someshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir
- Someshwar Nath Mahadev Temple
- The main temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva and is a significant spiritual and cultural landmark in the region.
- Shiva devotees visit throughout the year, but the temple sees massive crowds during the month of Shravan.
- Shrawani Mela (July-August)
- A grand fair organized during the holy month of Shravan (Sawan).
- Thousands of pilgrims, including Kanwariyas, visit the temple to perform the Jalabhishek (holy water offering) to Lord Shiva.
- The festival includes devotional songs, bhajans, and religious processions, making it a vibrant and spiritual event.
Why Visit Someshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir, Areraj?
- One of the most famous Shiva temples in Bihar.
- Experience the grand Shrawani Mela celebrations.
- Visit the historic Ashokan Pillar nearby.
- A must-visit for devotees, history enthusiasts, and cultural travelers.
5. Ashokan Pillar, Lauriya Areraj: A Monument of Emperor Ashoka
The Ashokan Pillar in Lauriya Areraj, located in East Champaran, Bihar, is a majestic stone column erected by Emperor Ashoka in 249 BC. This pillar, known as “Stambh Dharma Lekh,” contains six well-preserved edicts of Ashoka, reflecting his principles of Dhamma (righteousness and moral conduct).
Situated on the left side of the Areraj–Bettiah road, the pillar stands as a testament to India’s rich history and Ashoka’s message of peace.
Architectural & Historical Significance
- Height: 36.5 feet above ground.
- Base Diameter: 41.8 inches, tapering to 37.6 inches at the top.
- Estimated Weight: Nearly 40 tons, including the buried portion.
- Material: A single block of polished sandstone, showcasing the superior craftsmanship of the Mauryan period.
- The Edicts of Ashoka
- The pillar inscriptions are divided into two sections:
- Western side: 18 lines of inscriptions.
- Southern side: 23 lines of inscriptions.
- These edicts emphasize moral conduct, non-violence, religious tolerance, and governance based on Dharma (righteousness).
- The engravings remain clear but have suffered some weathering over time.
- The pillar inscriptions are divided into two sections:
- Missing Capital & Historical Relocation
- Unlike other Ashokan pillars, this pillar lacks its capital (the topmost decorative structure).
- Originally crowned with an animal statue, the capital was later removed and transferred to the Kolkata Museum.
- Local Beliefs & Naming of Lauriya
- The pillar is locally known as “Laur,” meaning phallus, giving the nearby village its name, Lauriya.
- The Lauriya Nandangarh region is believed to have been a center of Buddhist and Mauryan civilization.
Ashokan Pillar: A Protected Monument
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has classified this pillar as a protected monument, ensuring its preservation and maintenance.
- The site is a popular attraction for historians, archaeologists, and tourists interested in ancient Indian history.
Location & Accessibility
- Lauriya Areraj is 28 km from Bettiah and 14 km from Narkatiaganj in West Champaran, Bihar.
- The site is near the banks of the Budhi Gandak River, adding to its scenic beauty.
Why Visit Ashokan Pillar in Lauriya Areraj?
- One of the best-preserved Ashokan pillars in India.
- A historical site showcasing Emperor Ashoka’s teachings of Dharma.
- A must-visit for history buffs, scholars, and travelers interested in India’s ancient heritage.
- A serene and historically rich destination near Motihari and Bettiah.
6. Kesaria Buddhist Stupa: The Tallest Stupa in the World
The Kesaria Buddhist Stupa, located in Kesaria, East Champaran, Bihar, is the tallest and one of the largest Buddhist Stupas in the world. Discovered in 1998 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), this ancient structure stands at 104 feet, surpassing even the famous Borobudur Stupa in Java, Indonesia.
Situated about 120 km from Patna and 30 miles from Vaishali, near the Indo-Nepal border, Kesaria holds immense historical and religious significance in Buddhism.
Historical Significance
- Connection with Lord Buddha
- Buddha’s Last Journey: Kesaria is believed to be the place where Lord Buddha spent one of his last days before attaining Mahaparinirvana (final liberation).
- The Begging Bowl Incident: Before his passing, Buddha asked the Licchavis of Vaishali to return home and gifted them his begging bowl as a symbol of detachment.
- Mention in Jataka Tales: Buddhist scriptures record Buddha’s past life as a Chakravarti Raja (Universal Monarch) at Kesaria.
- A Monument Built by the Licchavis
- Kesaria Stupa was built by the Licchavis of Vaishali before Buddha attained Nirvana.
- Chinese traveler Hiuen Tsang visited the Stupa in the 7th century and documented its significance.
Architectural & Archaeological Importance
- Tallest Buddhist Stupa in the World
- Original height: 150 feet (before decline over centuries).
- Present height: 104 feet, slightly taller than Borobudur Stupa (103 feet).
- Comparison:
- Kesaria Stupa: 104 feet.
- Borobudur Stupa (Java, Indonesia): 103 feet.
- Sanchi Stupa (Madhya Pradesh, India): 77.5 feet.
- Archaeological Discoveries by ASI
- Terraces with Pradakshina Path (circumambulatory path for devotees).
- Numerous Buddha statues in Bhoomi Sparsh Mudra (earth-touching posture).
- Earthen lamps, decorated bricks, and ancient pottery.
- Locally known as “Raja Ben ka Deora”, the site was hidden under debris until excavated by ASI.
Location & Accessibility
- Situated on the eastern banks of River Gandak.
- 120 km from Patna.
- 30 miles from Vaishali, near the Indo-Nepal border.
- Accessible via Motihari and other major towns in Bihar.
Why Visit Kesaria Stupa?
- World’s tallest and largest Buddhist Stupa.
- A sacred site associated with Lord Buddha’s final days.
- Archaeological marvel with ancient relics and Buddha statues.
- A must-visit for history buffs, spiritual seekers, and travelers on the Buddhist circuit.
The Kesaria Stupa stands as a grand testament to India’s Buddhist heritage.
Motihari, the district headquarters of East Champaran, Bihar, is a blend of historical significance, natural beauty, and cultural heritage. The city is famous for its role in India’s freedom struggle, Buddhist heritage sites, and picturesque landscapes.
7. Moti Jheel – The Heart of Motihari
- A stunning lake that divides the city into two parts.
- Offers breathtaking views and is an ideal place for relaxation and photography.
- A popular attraction for locals and tourists.
8. Champaran Satyagraha Park – A Tribute to India’s Freedom Struggle
- Built to commemorate the 100th anniversary of Champaran Satyagraha.
- Located at the district headquarters of East Champaran.
- Constructed by the Urban Development and Housing Department at a cost of ₹2 crore.
- A beautiful and peaceful place where people enjoy quality time with family and friends.
9. NREGA Park – A Serene Recreational Spot
- A well-maintained park, perfect for relaxation and leisure activities.
- Ideal for family outings and picnics.
- A refreshing spot for people of all age groups.
10. Raxaul – The Gateway to Nepal
- One of the most important towns in East Champaran due to its strategic location.
- Known as the “Gateway to Nepal”, as it connects India with Nepal via Birgunj.
- A major trade and transport hub between the two countries.
11. Sitakund – A Sacred Hindu Site
- Located 16 km from Pipra Railway Station.
- A legendary site where Goddess Sita is believed to have taken a holy dip.
- A significant pilgrimage destination for Hindus.
Other Must-Visit Places in and Around Motihari
- Gayatri Mandir – A famous temple attracting devotees throughout the year.
- Navyuvak Pustakalay (Youth Library) – A haven for book lovers.
- Urdu Library – A cultural and literary hub.
Why Visit Motihari?
- A mix of history, spirituality, and natural beauty.
- Perfect for weekend getaways with family and friends.
- Ideal for history buffs, nature lovers, and pilgrims.
Transportation
Motihari, the district headquarters of East Champaran, is well connected by road, rail, and air, making it easily accessible from major cities in Bihar and across India.
Railways 🚆
The town has its own railway station, Bapudham Motihari (BMKI), with regular train services to major destinations.
Key Train Routes:
- Motihari Railway Station – A major railway hub.
- Raxaul Junction – Connects Bihar to Nepal and North India.
- Other stations include Chakia, Dhaka, and Areraj.
- New Delhi – Motihari
- Anand Vihar – Motihari
- Howrah – Motihari
- Raxaul – Motihari
Advantages of Train Travel:
✅ Well-connected to major Indian cities.
✅ Affordable fares compared to buses or flights and you can Book tickets in advance for a comfortable journey.
🔹 For train schedules and bookings, visit: Indian Railways
Roadways 🚌
Motihari is well connected by state highways and national highways. Regular buses operate to and from the city, making it a convenient travel option.
Bus Routes:
- National Highways NH-27 and NH-28 connect East Champaran to Patna, Muzaffarpur, and Nepal.
- Bus services operate between Motihari, Raxaul, and major cities.
- Patna – Motihari (160 km)
- Fare: ₹210 – ₹250 per person
- Frequent buses by state transport and private operators.
- Bodh Gaya – Patna – Muzaffarpur – Motihari – Birgunj – Kathmandu
- Betia – Motihari – Muzaffarpur – Hajipur – Patna
- Chapra – Siwan – Gopalganj – Motihari
✅ Comfortable and budget-friendly travel.
✅ Multiple bus operators available.
Airways ✈️
The nearest airport to Motihari is Patna Airport (Lok Nayak Jayprakash Airport), which is about 160 km away.
Nearest Airports:
- Darbhanga Airport (110 km away) for domestic flights.
- Patna Airport (PAT) – 160 km
- Daily flights to major Indian cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Ranchi, and Bhopal.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport, Lucknow – 473 km
- International flights for overseas travelers.
- A proposal for a Raxaul Airport is under consideration.
✅ Taxi and bus services available from Patna Airport to Motihari.
Challenges
- Flooding – The district faces severe annual floods from the Gandak River.
- Unemployment & Migration – Lack of industries leads to outmigration for jobs.
- Infrastructure Development – Many rural roads and healthcare facilities need improvement.
- Education – The low literacy rate requires better educational facilities.
Conclusion
East Champaran is a historically and agriculturally significant district in Bihar. Its association with Champaran Satyagraha, Kesariya Stupa, and sugarcane production makes it unique. While agriculture and trade with Nepal are key economic drivers, flooding, unemployment, and lack of industries remain major challenges. With better infrastructure, education, and industrial growth, East Champaran can emerge as a leading district in Bihar.
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below or Checkout these topics
पूर्वी चंपारण जिला: क्रांति की एक विशेष भूमि
अवलोकन
पूर्वी चंपारण जिला, भारत के बिहार राज्य के उत्तरी-भाग में स्थित 38-जिलों में से सबसे बड़ा है, जो ऐतिहासिक, सांस्कृतिक और कृषि संबंधी महत्व रखता है। 3,968 वर्ग किलोमीटर (1,532 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र में फैला पूर्वी चंपारण 26° 16′ से 27° 1′ उत्तरी अक्षांश और 84° 30′ से 85° 16′ पूर्वी देशांतर पर स्थित है, और उत्तर में नेपाल, पूर्व में सीतामढ़ी जिला और शिवहर जिला, दक्षिण में मुजफ्फरपुर जिला और पश्चिम में गोपालगंज जिला के साथ सीमा साझा करता है। जिले का प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय मोतिहारी शहर में स्थित है। यह क्षेत्र तिरहुत प्रमंडल का हिस्सा है।
ब्रिटिश प्रशासन ने औपचारिक रूप से 1866 में चंपारण को एक स्वतंत्र इकाई के रूप में स्थापित किया। हालाँकि, 1972 में चंपारण को पूर्वी चंपारण और पश्चिम चंपारण में विभाजित कर दिया गया। यह महात्मा गांधी के चंपारण सत्याग्रह (1917) के लिए प्रसिद्ध है, जो ब्रिटिश शासन के खिलाफ भारत का पहला बड़ा आंदोलन था। यह जिला एक प्रमुख कृषि केंद्र भी है, जो अपने गन्ना उत्पादन के लिए जाना जाता है, और नेपाल के साथ एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय सीमा साझा करता है। 2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार, जिले की जनसंख्या 5,099,371 है, जो इसे पटना जिले के बाद बिहार का दूसरा सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला जिला बनाता है।
चंपारण: ऐतिहासिक और क्रांतिकारी महत्व की भूमि
चंपारण भारतीय इतिहास में एक गौरवशाली और ऐतिहासिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण स्थान रखता है, जो महाकाव्य काल से लेकर आधुनिक युग तक फैला हुआ है। पुराणों के अनुसार, राजा उत्तानपाद के समर्पित पुत्र ध्रुव ने दिव्य ज्ञान प्राप्त करने के लिए चंपारण के तपोवन में गहन तपस्या की थी। यह जिला हिंदुओं के लिए भी पवित्र है क्योंकि यह देवी सीता से जुड़ा हुआ है।
राजा जनक के समय में चंपारण तिरहुत साम्राज्य का हिस्सा था। ऐसा माना जाता है कि जानकीगढ़ (जिसे चंचीगढ़ के नाम से भी जाना जाता है) राजा जनक के विदेह राज्य की राजधानी थी, जो बाद में छठी-शताब्दी ईसा पूर्व में वैशाली साम्राज्य का हिस्सा बन गया। चंपारण में भगवान बुद्ध भी आए थे, जिन्होंने यहाँ उपदेश दिए थे और उनकी उपस्थिति की याद में सम्राट-अशोक ने तीसरी-शताब्दी ईसा पूर्व में स्तंभ और स्तूप बनवाए थे। इस पर विदेह, शुंग और कण्व जैसे अलग-अलग राज्यों का शासन था। गुप्त और पाल राजवंशों के पतन के बाद, मिथिला सहित पूरा चंपारण क्षेत्र कर्नाट राजवंश के शासन में आ गया, उसके बाद स्थानीय क्षत्रप मुस्लिम शासन के अधीन आ गए।
चंपारण सत्याग्रह (1917)
आधुनिक भारतीय इतिहास में एक महत्वपूर्ण मोड़ अप्रैल 1917 में आया जब महात्मा गांधी स्थानीय किसान और स्वतंत्रता सेनानी राज कुमार शुक्ला के निमंत्रण पर मोतिहारी पहुंचे। महात्मा गांधी का चंपारण सत्याग्रह भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में एक ऐतिहासिक आंदोलन बन गया। गांधी की यात्रा सत्याग्रह के पहले सफल प्रयोग को चिह्नित करती है, जहाँ उन्होंने ब्रिटिश जमींदारों द्वारा नील (नील की फसल) की जबरन खेती का विरोध किया। इस आंदोलन ने भारत की स्वतंत्रता की लड़ाई में एक नए चरण को प्रज्वलित किया, और उसके बाद गांधी ने कई बार इस क्षेत्र का दौरा किया।
नाम की उत्पत्ति
चंपारण नाम संस्कृत के शब्द “चम्पा-अरण्य” या “चंपकटनीस” से उत्पन्न हुआ है, जहाँ “चम्पा” (या चंपक) मैगनोलिया के पेड़ को संदर्भित करता है, और “अरण्य” का अर्थ है जंगल। इस प्रकार, चंपारण्य का अनुवाद “मैगनोलिया के पेड़ों का जंगल” होता है। ऐसा माना जाता है कि यह नाम उन विशाल जंगलों से लिया गया था जो कभी इस क्षेत्र को कवर करते थे, जहाँ एकांत तपस्वी रहते थे। पूर्वी चंपारण का नाम मूल चंपारण जिले के पूर्वी भाग के रूप में अपनी भौगोलिक स्थिति से लिया गया है।
चंपारण की एक समृद्ध विरासत है, जिसमें आध्यात्मिक महत्व, राजनीतिक विकास और क्रांतिकारी आंदोलन शामिल हैं। राजा जनक और भगवान बुद्ध से जुड़े होने से लेकर गांधी के सत्याग्रह की जन्मस्थली होने तक, चंपारण बिहार में एक महत्वपूर्ण सांस्कृतिक, धार्मिक और ऐतिहासिक स्थल बना हुआ है।
पूर्वी चंपारण जिले के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - क्षेत्र: मिथिला
- प्रमंडल: तिरहुत
- स्थापना: 2 नवंबर 1972
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,968 km2 (1,532 sq mi)
- निर्देशांक: 26.6500°N 84.9167°E
- जिला मुख्यालय: मोतिहारी शहर
- जिला मजिस्ट्रेट: श्री सौरभ जोरवाल, IAS
- पुलिस अधीक्षक: श्री कांतेश कुमार मिश्रा, IPS
- जनसंख्या (2011):
- कुल: 5,099,371
- घनत्व: 1,300/km2 (3,300/sq mi)
- साक्षरता दर: 55.79%
- लिंग अनुपात: 901/1000
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 405
- गांव: 1344
- अनुमण्डल (तहसील) की संख्या: 6 (अरेराज, चकिया, मोतिहारी, पकड़ीदयाल, रक्सौल, सिकरहना)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 27
- संग्रामपुर, हरसिद्धि, अरेराज, पहाड़पुर, चकिया, मेहसी, केसरिया, कल्याणपुर, बंजरिया, मोतिहारी, पीपराकोठी, कोटोवा, सुगौली, तुरकौलिया, मधुबन, तेतरिया, पताही, फेनहारा, पकड़ीदयाल, रक्सौल, रामगढ़वा, आदापुर, छौड़ादानो, बनकटवा, चिरैया, घोड़ासहन, ढाका
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 50
- गोविंदगंज, अरेराज, मलाही, हरसिद्धि, पहाड़पुर, संग्रामपुर, छतौनी, तुरकौलिया, पीपराकोठी, कोटवा, बंजरिया, लखौरा, भोपतपुर, सगौली, केसरिया, कल्याणपुर, डुमरिया घाट, चकिया, मेहसी, पिपरा, मधुबन, पकड़ीदयाल, राजेपुर, फेनहारा, पताही, ढाका, चिरैया, शिकारगंज, कुंडवा चैनपुर, घोड़ासहन, झरोखर, जितना, पंचपकड़ी, रक्सौल, छौड़ादानो, आदापुर, दरपा, महुआवा, नकरदेई, रामगढ़वा, पलनवा, हापुड, हरैया, टाउन थाना, मुफसिल पी.एस., एससी/एसटी पी.एस., महिला पी.एस., पुलिस केंद्र मोतिहारी, पुलिस नियंत्रण कक्ष, भेलाही ओ.पी.
- नगर परिषद: 2 (मोतिहारी, रक्सौल)
- नगर पंचायत: 7 (अरेराज नगर, ढाका, चकिया, केसरिया, मेहसी, पकड़ीदयाल, सुगौली
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 12
- रक्सौल, सुगौली, नरकटिया, हरसिद्धि, गोविंदगंज, केसरिया, कल्याणपुर, पिपरा, मधुबन, मोतिहारी, चिरैया, ढाका।
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: 3(पूर्वी चंपारण, पश्चिम चंपारण, शिवहर)
- प्रमुख विशेषताऐं:
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह का स्थल, भारत में महात्मा गांधी का पहला आंदोलन।
- पर्यटक आकर्षण: गांधी स्मारक, केसरिया स्तूप (दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा बौद्ध स्तूप)।
- गन्ना, मक्का और दालें पैदा करने वाली उपजाऊ भूमि।
- महत्व: बिहार का एक ऐतिहासिक और कृषि केंद्र।
- प्रमुख नदियाँ: गंडक, बूढ़ी गंडक और बागमती
- समय क्षेत्र: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- पिन कोड: 845401 (पूर्वी चंपारण)
- वाहन पंजीकरण: BR-05
- प्रमुख राजमार्ग: NH-28A, NH-104
- औसत वार्षिक वर्षा: 1241 mm
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: eastchamparan.nic.in
भूगोल
- स्थान: पूर्वी चंपारण उत्तरी बिहार में स्थित है और इसकी सीमाएँ निम्नलिखित से मिलती हैं:
- नेपाल (उत्तर)
- पश्चिमी चंपारण (पश्चिम)
- सीतामढ़ी और शिवहर (पूर्व)
- मुजफ्फरपुर और गोपालगंज (दक्षिण)
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,969 वर्ग किलोमीटर, जो इसे बिहार के सबसे बड़े जिलों में से एक बनाता है।
- स्थलाकृति:
- जलोढ़ मैदान, कृषि के लिए उपयुक्त अत्यधिक उपजाऊ भूमि।
- छोटी नदी घाटियों और आर्द्रभूमि के साथ समतल भूभाग।
- जलवायु:
- गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल, मानसूनी वर्षा (जून-सितंबर), और हल्की सर्दियाँ वाली आर्द्र उपोष्णकटिबंधीय जलवायु।
- नदियाँ:
- गंडक नदी
- बुरी गंडक नदी
- लालबकेया नदी
इतिहास
- प्राचीन काल
- यह क्षेत्र मिथिला साम्राज्य और बाद में मगध साम्राज्य का हिस्सा था।
- रामायण जैसे हिंदू महाकाव्यों में इसका उल्लेख है।
- मध्यकालीन काल
- पूर्वी चंपारण पर मौर्य, गुप्त और मुगलों का शासन था।
- यह एक महत्वपूर्ण व्यापारिक और प्रशासनिक केंद्र था।
- आधुनिक युग
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह (1917):
- महात्मा गांधी ने ब्रिटिश शासन के खिलाफ अपना पहला बड़ा आंदोलन इसी क्षेत्र से शुरू किया था।
- किसानों ने जबरन नील की खेती के खिलाफ विरोध प्रदर्शन किया, जिससे भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन की शुरुआत हुई।
- जिले का गठन:
- बेहतर प्रशासन के लिए चंपारण जिले को 1972 में पूर्वी और पश्चिमी चंपारण में विभाजित किया गया था।
जनसांख्यिकी (2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार)
- जनसंख्या:
- कुल जनसंख्या: पूर्वी चंपारण जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 5,099,371 है।
- पुरुषों की जनसंख्या: 2,681,209
- महिलाओं की जनसंख्या: 2,418,162
- रैंकिंग: भारत में 21वीं (640 जिलों में से)।
- घनत्व: 1,285 व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर (3,320/वर्ग मील)।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि (2001-2011): 29.01%, जो महत्वपूर्ण जनसंख्या वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- लिंग अनुपात: प्रति 1,000 पुरुषों पर 901 महिलाएँ, जो लैंगिक असमानता को दर्शाता है।
- साक्षरता दर: 55.79%, जो राष्ट्रीय और राज्य औसत से कम है, लेकिन शिक्षा की पहुँच और गुणवत्ता में सुधार के लिए महत्वपूर्ण प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं।
- पुरुष साक्षरता दर: 65.34%
- महिला साक्षरता दर: 45.12%
- शहरी जनसंख्या: कुल जनसंख्या का 7.87% शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- कुल जनसंख्या: पूर्वी चंपारण जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 5,099,371 है।
- धार्मिक संरचना (2011 की जनगणना): अधिकांश आबादी हिंदू धर्म का पालन करती है, जिसमें एक महत्वपूर्ण मुस्लिम समुदाय है।
- हिंदू धर्म: 80.14%
- अनुसूचित जाति: 12.74%
- अनुसूचित जनजातियाँ: 0.24%
- इस्लाम: 19.42%
- अन्य या नहीं बताया गया: 0.44%
- भाषाएँ: हिंदी, भोजपुरी, मैथिली और उर्दू व्यापक रूप से बोली जाती हैं।
- भोजपुरी: 82.67%
- उर्दू: 7.33%
- हिंदी: 7.06%
- ‘अन्य’ हिंदी: 2.58%
- बंगाली: 0.26%
- अन्य: 0.1%
प्रशासन
- मुख्यालय: मोतिहारी
- उपखंड:
- जिले में 6 उपमंडल हैं: मोतिहारी सदर, अरेराज, पकड़ीदयाल, रक्सौल, चकिया और ढाका।
- प्रत्येक उपविभाग का नेतृत्व एक उपविभागीय मजिस्ट्रेट द्वारा किया जाता है जो विकास, राजस्व संबंधी कार्यों और कानून एवं व्यवस्था बनाए रखने का प्रभारी होता है।
- ब्लॉक और सर्कल:
- पूर्वी चंपारण जिले में 27 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और मंडल शामिल हैं जैसे संग्रामपुर, हरसिद्धि, अरेराज, पहाड़पुर, चकिया, मेहसी, केसरिया, कल्याणपुर, बंजरिया, मोतिहारी, पिपराकोठी, कोटोवा, सुगौली, तुरकौलिया, मधुबन, तेतरिया, पताही, फेनहारा, पकड़ीदयाल, रक्सौल ,रामगढ़वा, आदापुर, छौड़ादानो, बनकटवा, चिरैया, घोड़ासहन और ढाका, एक-एक जिम्मेदार स्थानीय शासन और विकास के लिए.
- प्रत्येक सर्किल का नेतृत्व एक सर्किल अधिकारी (सीओ) करता है, जबकि प्रत्येक ब्लॉक का नेतृत्व एक ब्लॉक विकास अधिकारी (बीडीओ) करता है।
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र:
- पूर्वी चंपारण लोकसभा सीट जिले का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है।
- विधानसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र:
- जिले में 12 विधानसभा क्षेत्र हैं: रक्सौल, सुगौली , नरकटिया, हरसिद्धि, गोविंदगंज, केसरिया, कल्याणपुर, पिपरा, मधुबन, मोतिहारी, चिरैया और ढाका।
अर्थव्यवस्था
कृषि: पूर्वी चंपारण की रीढ़
पूर्वी चंपारण की अर्थव्यवस्था मजबूत कृषि है, यहाँ के अधिकांश निवासियों की आय का प्राथमिक स्रोत खेती है यह जिला बिहार में चावल और गेहूं के शीर्ष उत्पादकों में से एक है।
पूर्वी चंपारण में उगाई जाने वाली प्रमुख फसलें
- कृषि अर्थव्यवस्था की रीढ़ है, जिसमें प्रमुख फसलें शामिल हैं:
- धान, गेहूं, मक्का, दालें और सरसों
- आलू, प्याज जैसी सब्जियाँ, और टमाटर
- चावल और धान: पूर्वी चंपारण बिहार के कुल चावल उत्पादन का 5.7% हिस्सा है, जो इसे शीर्ष चावल उत्पादक जिलों में से एक बनाता है।
- गेहूँ: यह जिला बिहार में दूसरा सबसे बड़ा गेहूँ उत्पादक है, जो राज्य की गेहूँ उपज का 5.2% योगदान देता है।
- गन्ना: एक प्रमुख नकदी फसल, जो इस क्षेत्र में चीनी उद्योग को सहायता प्रदान करती है (बिहार में सबसे बड़ा उत्पादक)।
- जूट और दाल: महत्वपूर्ण फसलें जो जिले की कृषि अर्थव्यवस्था में योगदान देती हैं।
(डेटा स्रोत: बिहार सरकार का आर्थिक सर्वेक्षण 2014-15)
पशुपालन: एक प्रमुख ग्रामीण आजीविका
- पशुपालन ग्रामीण आय और रोजगार में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
- यह क्षेत्र कुल ग्रामीण आय का लगभग 20% योगदान देता है।
- हाशिये पर पड़े समुदायों की महिलाएँ इस क्षेत्र में बड़े पैमाने पर शामिल हैं।
- बकरी पालन विशेष रूप से प्रमुख है, जिसमें पूर्वी चंपारण, बिहार में अररिया और कटिहार में बकरियों की सबसे अधिक संख्या है।
(डेटा स्रोत: बिहार सरकार का आर्थिक सर्वेक्षण 2014-15)
लघु उद्योग और उभरते क्षेत्र
कृषि के अलावा, पूर्वी चंपारण में लघु उद्योग विकसित हो रहे हैं, जिनमें शामिल हैं:
- मोती बटन उद्योग: एक उभरता हुआ क्षेत्र जो मदर-ऑफ-पर्ल से बटन बनाता है। मोती के गोले।
- मत्स्य विकास: वैकल्पिक आजीविका के रूप में मछली पालन पर अधिक ध्यान दिया जा रहा है।
- चीनी उद्योग: मोतिहारी, रक्सौल और चकिया सहित कई चीनी मिलें।
- डेयरी फार्मिंग: दूध उत्पादन एक बढ़ता हुआ क्षेत्र है।
- हस्तशिल्प और कुटीर उद्योग: स्थानीय कारीगर उत्पादन करते हैं बांस शिल्प, जूट उत्पाद और हथकरघा वस्त्र।
- व्यापार और वाणिज्य: रक्सौल नेपाल के साथ एक प्रमुख व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता है, जो सीमा पार माल परिवहन को संभालता है।
पूर्वी चंपारण में मत्स्य उद्योग
पूर्वी चंपारण में प्रचुर जल निकायों के कारण मत्स्य पालन विकास की बहुत संभावना है जिसमें नदियाँ, झीलें, दलदल, तालाब और टैंक शामिल हैं। इन प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के बावजूद, आधुनिक मछली पालन के लिए एकीकृत प्रयास सीमित रहे हैं।
मौजूदा मत्स्य संसाधन
- 823 सरकारी तालाब और 161 निजी तालाब, जो कुल 1,920 एकड़ जल क्षेत्र को कवर करते हैं।
- 28 झीलें (मनस) जिनका जल क्षेत्र 7,486 एकड़ है।
- प्रस्तावित विकास मत्स्य पालन विकास के लिए लगभग 282 एकड़ सरकारी और निजी टैंक (151 चिन्हित टैंकों में से) की योजना बनाई गई है।
मछली उत्पादन और आर्थिक प्रभाव
- वार्षिक मछली उत्पादन: 2,500 मीट्रिक टन (एमटी)।
- अनुमानित बाजार मूल्य: ₹25 करोड़ प्रति वर्ष।
- सीमित निर्यात: वर्तमान में, मछली उत्पादन का अधिकांश हिस्सा जिले के भीतर ही खपत होता है, तथा पूर्वी चंपारण से बाहर इसका निर्यात बहुत कम या बिलकुल नहीं होता।
पूर्वी चंपारण में सामान्य मछली प्रजातियाँ
- कार्प्स: रोहू, कैटला, नैनी, कैलबासु।
- कैटफ़िश: बोरी, टेंगरा, सिलोनल, बचावा।
- अन्य: हिलसा, गोरारा, सावरा, पोथिया, बंगास, मुरेल्स, गरई, चेंगा, चितला, चेलवा, बामी, गेनेहा, चंगारी, आदि।
विकास पहल और विश्व बैंक से वित्तपोषण
- विश्व बैंक ने मोतीझील में मत्स्य पालन विकास परियोजनाओं के लिए ₹19 करोड़ का वित्तपोषण किया है और कररिया झील (मोतिहारी शहर और आस-पास के क्षेत्र)।
- इस परियोजना का उद्देश्य मछली उत्पादन को बढ़ाना और मछली पालन तकनीकों को आधुनिक बनाना है।
- प्रमुख विकास गतिविधियों में शामिल हैं:
- आधुनिक मछली पालन के लिए झील का जीर्णोद्धार।
- बेहतर जल प्रबंधन के लिए स्लुइस गेट का निर्माण।
- बांध को मजबूत करना और उसकी सुरक्षा करना (तटबंध)
- इनलेट और आउटलेट चैनलों को गहरा करना।
- खरपतवारों को साफ करना और पानी की गुणवत्ता में सुधार करना।
भविष्य की संभावनाएँ और उद्योग वृद्धि
- पूर्वी चंपारण में मत्स्य पालन एक उभरता हुआ उद्योग है, जिसमें विस्तार की काफी गुंजाइश है।
- मिश्रित मछली पालन तकनीक अपनाने से उत्पादकता में और वृद्धि हो सकती है।
- निजी निवेश और सहकारी मछली पालन को प्रोत्साहित करने से रोजगार और आर्थिक विकास हो सकता है।
- मछली निर्यात के लिए बुनियादी ढाँचे में सुधार से बिहार के मत्स्य पालन क्षेत्र में जिले का योगदान बढ़ सकता है।
पूर्वी चंपारण का मत्स्य पालन उद्योग तेजी से विकास के लिए तैयार है, जिससे यह आर्थिक विकास के लिए एक प्रमुख क्षेत्र बन गया है।
आर्थिक दृष्टिकोण और अवसर
- कृषि बुनियादी ढाँचे (सिंचाई, भंडारण और प्रसंस्करण इकाइयाँ) को मजबूत करने से उत्पादकता बढ़ सकती है।
- लघु उद्योगों का विस्तार और कृषि आधारित उद्योगों को बढ़ावा देने से रोजगार पैदा हो सकता है।
- ग्रामीण उद्यमिता (जैसे डेयरी फार्मिंग और मत्स्य पालन विकास) में सुधार से आय के स्रोतों में विविधता आ सकती है।
चुनौतियाँ: नदियों में बाढ़ से अक्सर फसलें खराब हो जाती हैं, जिसके लिए बेहतर सिंचाई और बाढ़ नियंत्रण उपायों की आवश्यकता होती है।
पूर्वी चंपारण की कृषि-संचालित अर्थव्यवस्था धीरे-धीरे पशुपालन और लघु उद्योगों में फैल रही है, जिससे नए रोजगार और व्यवसाय के अवसर पैदा हो रहे हैं।
शिक्षा
उच्च शैक्षणिक संस्थान
- डॉ. राजेंद्र प्रसाद केंद्रीय कृषि विश्वविद्यालय (RPCAU) – एक प्रमुख कृषि विश्वविद्यालय।
- मुंशी सिंह कॉलेज, मोतिहारी – बिहार के सबसे पुराने कॉलेजों में से एक।
- श्री कृष्ण जुबली लॉ कॉलेज, मोतिहारी – एक प्रतिष्ठित लॉ कॉलेज।
- महात्मा गांधी केंद्रीय विश्वविद्यालय, मोतिहारी, पूर्वी चंपारण
- मोतिहारी कॉलेज ऑफ इंजीनियरिंग, NH-28A, फुरशतपुर बरियारपुर, मोतिहारी
- सरकारी पॉलिटेक्निक, गांधी मैदान के पास, ITI मोतिहारी के पीछे, पूर्वी चंपारण
- कई सरकारी और निजी स्कूल हैं, लेकिन उच्च शिक्षा के अवसर सीमित हैं।
- हाई स्कूल आदापुर, पूर्वी चंपारण (मोतिहारी)
- सोमेश्वर हाई स्कूल अरेराज, पूर्वी चंपारण (मोतिहारी)
चुनौतियाँ
- अन्य जिलों की तुलना में साक्षरता दर कम है।
- कई छात्र उच्च शिक्षा के लिए पटना या अन्य शहरों में जाते हैं।
संस्कृति
पूर्वी चंपारण बिहार का एक सांस्कृतिक रूप से समृद्ध क्षेत्र है, जो अपनी लोक परंपराओं, जीवंत त्योहारों और स्वादिष्ट व्यंजनों के लिए जाना जाता है। जिले की कला, संगीत, नृत्य और पाक विरासत इसकी गहरी जड़ों वाली परंपराओं और ऐतिहासिक महत्व को दर्शाती है।
त्यौहार और उत्सव 🎊🙏
पूर्वी चंपारण कई त्योहारों को बड़े उत्साह के साथ मनाता है, जो विभिन्न समुदायों के लोगों को एकजुट करता है।
छठ पूजा ☀️🌊
- पूर्वी चंपारण का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण त्योहार, सूर्य देव (सूर्य देव) को समर्पित है।
- एकमात्र हिंदू त्योहार जिसमें डूबते सूर्य की पूजा की जाती है।
- वर्ष में दो बार मनाया जाता है:
- चैत्र छठ (मार्च-अप्रैल)।
- कार्तिक छठ (अक्टूबर-नवंबर)।
- कठोर अनुष्ठानों वाला चार दिवसीय त्योहार:
- पवित्र स्नान, उपवास और लंबे समय तक पानी में खड़े रहना।
- उगते और डूबते सूर्य को अर्घ्य (जल का प्रसाद) देना।
- छठी मैया और सूर्य देव के सम्मान में लोकगीत गाना।
- महिलाएं (परवैतिन) अपने परिवार की खुशहाली के लिए व्रत रखती हैं।
- पुरुष भी इस त्यौहार में सक्रिय रूप से भाग लेते हैं।
अन्य महत्वपूर्ण त्यौहार
- मकर संक्रांति – पतंग उड़ाने और तिल की मिठाई खाने के साथ मनाया जाता है।
- होली – रंगों का त्यौहार, जो वसंत के आगमन का प्रतीक है।
- दुर्गा पूजा – देवी दुर्गा को समर्पित एक भव्य त्यौहार, जिसे जुलूस और सांस्कृतिक कार्यक्रमों के साथ मनाया जाता है।
- दिवाली और ईद भी मनाई जाती है।
- चम्पारण महोत्सव – क्षेत्र की सांस्कृतिक विरासत का जश्न मनाने वाला एक वार्षिक त्यौहार।
प्रसिद्ध व्यंजन और मिठाइयाँ 🍛🍬
- स्वादिष्ट पारंपरिक व्यंजनों में शामिल हैं:
- लिट्टी चोखा, सत्तू पराठा, दाल पीठा
- चम्पारण मीट (अहुना मटन) इस क्षेत्र का एक प्रसिद्ध व्यंजन है।
- सबसे प्रसिद्ध मिठाइयों और स्नैक्स में शामिल हैं:
- छेना मुरकी – पनीर (छेना) और चीनी की चाशनी से बनी मिठाई।
- केसरिया पेड़ा – केसर के स्वाद वाली दूध से बनी मिठाई।
- खाजा – एक कुरकुरी, परतदार, तली हुई मिठाई।
- मालपुआ – आटा, दूध और चीनी से बना एक पारंपरिक भारतीय पैनकेक।
- खुरमा – आटे और चीनी की चाशनी से बना एक मीठा नाश्ता।
- ठेकुआ – एक कुरकुरा और स्वादिष्ट नाश्ता, जो अक्सर छठ पूजा के दौरान बनाया जाता है।
- तिलकुट – तिल और गुड़ से बना एक सर्दियों का व्यंजन।
- मुरब्बा – एक मीठा फल संरक्षित।
लोक संगीत और नृत्य 🎶💃
- पारंपरिक लोक गीत पूर्वी चंपारण की सांस्कृतिक पहचान का एक अभिन्न अंग हैं।
- ये गीत विभिन्न अवसरों पर गाए जाते हैं, जिनमें विवाह, त्यौहार और धार्मिक समारोह शामिल हैं।
- झुमरी नृत्य:
- विवाहित महिलाओं द्वारा किया जाने वाला एक व्यापक रूप से पसंद किया जाने वाला नृत्य रूप।
- यह नृत्य खुशी, भक्ति और उत्सव को व्यक्त करता है।
पर्यटन
पूर्वी चंपारण, ऐतिहासिक महत्व, प्राकृतिक सुंदरता, सांस्कृतिक विरासत और धार्मिक स्थल का मिश्रण है। यह भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में अपनी भूमिका, बौद्ध विरासत स्थलों और सुरम्य परिदृश्यों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। प्रमुख आकर्षण हैं:
1. गांधी संग्रहालय, मोतिहारी: चंपारण सत्याग्रह को श्रद्धांजलि
पूर्वी चंपारण के मोतिहारी में गांधी संग्रहालय (गांधी संग्रहालय), भारत में महात्मा गांधी के पहले सत्याग्रह आंदोलन को समर्पित एक ऐतिहासिक स्थल है। यह संग्रहालय 1917 के चंपारण सत्याग्रह की याद दिलाता है, जो ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक शासन के खिलाफ भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन में एक महत्वपूर्ण मोड़ था।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह (1917): महात्मा गांधी ने पहली बार चंपारण में गरीब किसानों पर ब्रिटिश नील बागान मालिकों के अत्याचारों के खिलाफ आवाज उठाई, जिसने भारत के स्वतंत्रता के लिए अहिंसक संघर्ष की शुरुआत की।
- गांधी जी की अदालत में उपस्थिति का स्थान: यह संग्रहालय ठीक उसी स्थान पर स्थित है, जहाँ महात्मा गांधी को 18 अप्रैल, 1917 को धारा 144 सीआरपीसी का उल्लंघन करने के लिए मोतिहारी के तत्कालीन एस.डी.एम. की अदालत में पेश किया गया था।
- नींव और समर्पण:
- इसकी आधारशिला 10 जून, 1972 को तत्कालीन राज्यपाल श्री डी.के. बरूच ने रखी थी।
- इस स्मारक का उद्घाटन 18 अप्रैल, 1978 को गांधीवादी नेता विद्याकर कवि ने किया था।
मुख्य आकर्षण
- गांधी स्मारक स्तंभ (स्मारक स्तंभ)
- शांतिनिकेतन के प्रसिद्ध कलाकार नंदलाल बोस द्वारा डिजाइन किया गया।
- चुनार पत्थर से बना 48 फीट ऊंचा पत्थर का स्तंभ।
- यह ठीक उसी स्थान पर बनाया गया है, जहाँ 1917 में गांधी जी को अदालत में पेश किया गया था।
- गांधी संग्रहालय और प्रदर्शनी
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह से संबंधित तस्वीरें और अवशेष।
- महात्मा गांधी के लेख, पत्र और निजी सामान।
- नील किसानों के जीवन और उनके संघर्ष को दर्शाती कलाकृतियाँ।
- शैक्षणिक और सांस्कृतिक केंद्र
- भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन से संबंधित शोध, शिक्षा और सांस्कृतिक गतिविधियों के लिए एक प्रमुख केंद्र।
- गांधी के अहिंसा और सत्य के दर्शन पर कार्यशालाएँ, व्याख्यान और चर्चाएँ।
गांधी संग्रहालय क्यों जाएँ?
- भारत के पहले सत्याग्रह आंदोलन के जन्मस्थान का अनुभव करें।
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह की दुर्लभ तस्वीरें, दस्तावेज़ और अवशेष देखें।
- भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में गांधी की भूमिका के बारे में जानें।
- इतिहास के प्रति उत्साही, शोधकर्ताओं और छात्रों के लिए ज़रूर जाएँ।
गांधी संग्रहालय सिर्फ़ एक संग्रहालय नहीं है – यह न्याय और स्वशासन के लिए भारत की लड़ाई का प्रतीक है।
2. गांधी स्मारक, चंद्रहिया: चंपारण सत्याग्रह का एक ऐतिहासिक स्थल
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण में स्थित चंद्रहिया में गांधी स्मारक एक ऐतिहासिक स्थल है, जहां महात्मा गांधी को 16 अप्रैल, 1917 को ब्रिटिश अधिकारियों ने रोका था, जब वे नील की खेती करने वाले किसानों की शिकायतें सुनने के लिए जसौली पट्टी जा रहे थे। यह घटना चंपारण सत्याग्रह में एक महत्वपूर्ण मोड़ बन गई, जो ब्रिटिश शासन के खिलाफ भारत का पहला बड़ा सविनय अवज्ञा आंदोलन था।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- 16 अप्रैल, 1917: गांधी नील की खेती करने के लिए मजबूर किसानों से मिलने के लिए जसौली पट्टी गांव जा रहे थे।
- ब्रिटिश अधिकारियों द्वारा रोका जाना: एक पुलिस अधिकारी ने घोड़े से चलने वाली बग्गी पर सवार होकर गांधी को तत्कालीन चंपारण कलेक्टर डब्ल्यू.बी. हेकॉक का एक नोटिस दिया, जिसमें उन्हें तुरंत जिला छोड़ने का आदेश दिया गया था।
- गांधी की प्रतिक्रिया:
- उन्होंने अस्थायी रूप से आदेश का पालन किया और बैलगाड़ी पर सवार होकर मोतिहारी लौट आए।
- हालांकि, उन्होंने चंपारण छोड़ने से इनकार कर दिया और 18 अप्रैल, 1917 को उप-विभागीय मजिस्ट्रेट की अदालत में पेश हुए।
- अदालत में गांधी की अवज्ञा और तर्क ने चंपारण सत्याग्रह की शुरुआत की, जो उनके नेतृत्व में भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम की शुरुआत थी।
मुख्य आकर्षण
- चंद्रहिया में गांधी स्मारक
- ब्रिटिश अधिकारियों के साथ गांधी के ऐतिहासिक टकराव की याद में एक स्मारक।
- चंपारण के किसानों के साहस और प्रतिरोध का प्रतीक है।
- ऐतिहासिक स्थान
- चंद्रहिया मोतिहारी से सिर्फ 8 किमी दूर है, जिससे आगंतुकों के लिए यह आसानी से सुलभ है।
- यह गांव भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन में गहरा ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व रखता है।
गांधी स्मारक, चंद्रहिया क्यों जाएँ?
- उस सटीक स्थान पर खड़े हों जहाँ गांधी को रोका गया था, जो सत्याग्रह की शुरुआत को चिह्नित करता है।
- चंपारण आंदोलन और भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम पर इसके प्रभाव के बारे में जानें।
- इतिहास के प्रति उत्साही, शोधकर्ताओं और छात्रों के लिए यह एक ज़रूरी जगह है।
- मोतिहारी में गांधी संग्रहालय सहित ऐतिहासिक महत्व के आस-पास के स्थानों का भ्रमण करें।
चंद्रहिया में गांधी स्मारक प्रतिरोध, न्याय और अहिंसा की शक्ति का प्रतीक है।
3. जॉर्ज ऑरवेल का जन्मस्थान, मोतिहारी
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण का एक छोटा सा शहर मोतिहारी, 20वीं सदी के सबसे प्रभावशाली लेखकों में से एक जॉर्ज ऑरवेल का जन्मस्थान होने के लिए जाना जाता है। ऑरवेल, जिनका जन्म 25 जून, 1903 को एरिक आर्थर ब्लेयर के रूप में हुआ था, अपने उपन्यासों “नाइनटीन एटी-फोर” और “एनिमल फ़ार्म” के लिए सबसे ज़्यादा जाने जाते हैं, जो दोनों ही विश्व साहित्य में क्लासिक हैं।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- जन्मस्थान: ऑरवेल का जन्म मोतिहारी में गोपाल साह हाई स्कूल के पास हुआ था, जहाँ उनके पिता अफीम विभाग में एक ब्रिटिश सिविल सेवक के रूप में कार्यरत थे।
- पारिवारिक पृष्ठभूमि:
- उनके पिता, रिचर्ड वाल्मेस्ले ब्लेयर, भारतीय सिविल सेवा में एक छोटे ब्रिटिश अधिकारी थे।
- उनकी माँ, इडा मेबेल ब्लेयर, फ्रांसीसी वंश की थीं और बर्मी सागौन के व्यापार से जुड़े एक परिवार से थीं।
- प्रारंभिक जीवन: हालाँकि ऑरवेल भारत में केवल एक वर्ष ही रहे, लेकिन उनके औपनिवेशिक पालन-पोषण और अनुभवों ने साम्राज्यवाद पर उनके आलोचनात्मक विचारों को आकार दिया, जिसने बाद में उनके लेखन को प्रभावित किया।
जॉर्ज ऑरवेल के जन्मस्थान पर मुख्य आकर्षण
- जॉर्ज ऑरवेल स्मारक
- एक साधारण लेकिन महत्वपूर्ण स्मारक, जिस घर में ऑरवेल का जन्म हुआ था।
- इस इमारत को उनकी साहित्यिक विरासत का सम्मान करने के लिए संरक्षित किया गया है।
- पुनर्स्थापना और मान्यता
- इस स्थल को बिहार सरकार द्वारा मान्यता दी गई थी, तथा इसे एक विरासत स्थल के रूप में पुनर्स्थापित करने और विकसित करने के प्रयास किए गए थे।
- साहित्यिक उत्साही और पर्यटक एक ऐसे लेखक के जन्मस्थान को देखने आते हैं, जिनकी रचनाएँ राजनीतिक और सामाजिक विमर्श को आकार देती रहती हैं।
जॉर्ज ऑरवेल की प्रसिद्ध रचनाएँ
- नाइनटीन एटी-फोर (1949) – अधिनायकवाद, निगरानी और राज्य नियंत्रण के बारे में एक डायस्टोपियन उपन्यास, जिसमें बिग ब्रदर और थॉट पुलिस जैसी अवधारणाएँ शामिल हैं।
- एनिमल फ़ार्म (1945) – ऑरवेल की अधिनायकवाद-विरोधी मान्यताओं से प्रेरित, शक्ति, भ्रष्टाचार और राजनीतिक अत्याचार की आलोचना करने वाला एक रूपक उपन्यास।
- होमेज टू कैटालोनिया (1938) – स्पेनिश गृहयुद्ध में उनके अनुभवों का संस्मरण।
- बर्मीज़ डेज़ (1934) – औपनिवेशिक बर्मा में बिताए गए समय से प्रेरित एक उपन्यास, जो साम्राज्यवाद की बुराइयों को दर्शाता है।
जॉर्ज ऑरवेल के जन्मस्थान पर क्यों जाएँ?
- 20वीं सदी के सबसे महान साहित्यिक हस्तियों में से एक की उत्पत्ति का पता लगाएँ।
- औपनिवेशिक भारत के साथ ऑरवेल के शुरुआती संबंध और उनके कार्यों पर इसके प्रभाव को समझें।
- साहित्य प्रेमियों, इतिहास के प्रति उत्साही और ऑरवेलियन विद्वानों के लिए यह एक ज़रूरी जगह है।
मोतिहारी में जॉर्ज ऑरवेल का जन्मस्थान एक छिपा हुआ साहित्यिक स्थल है जो भारत के औपनिवेशिक अतीत को आधुनिक राजनीतिक विचारों से जोड़ता है।
4. सोमेश्वर नाथ महादेव मंदिर, अरेराज
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण के अरेराज में स्थित सोमेश्वर नाथ महादेव मंदिर, उत्तर बिहार के सबसे प्रतिष्ठित शिव मंदिरों में से एक है। भगवान शिव को समर्पित यह मंदिर, विशेष रूप से श्रावणी मेले (जुलाई-अगस्त) के दौरान, पूरे भारत और नेपाल से हज़ारों भक्तों को आकर्षित करता है।
अरेराज मोतिहारी से 28 किमी दक्षिण-पश्चिम में है, जो पक्की सड़कों से अच्छी तरह जुड़ा हुआ है। समय के साथ, अरेराज एक गाँव से एक कस्बे में विकसित हुआ और अब अरेराज उपखंड का मुख्यालय है।
धार्मिक महत्व
- मंदिर को प्राचीन और पवित्र माना जाता है, जो इसे एक महत्वपूर्ण तीर्थ स्थल बनाता है।
- बिहार, पड़ोसी राज्यों और नेपाल से भक्त आशीर्वाद लेने के लिए मंदिर आते हैं।
- श्रावणी मेला यहाँ मनाया जाने वाला सबसे बड़ा वार्षिक उत्सव है, जिसके दौरान हज़ारों कांवड़िए (शिव भक्त) भगवान शिव को चढ़ाने के लिए गंगा से पवित्र जल लेकर आते हैं।
सोमेश्वर नाथ महादेव मंदिर में मुख्य आकर्षण
- सोमेश्वर नाथ महादेव मंदिर
- मुख्य मंदिर भगवान शिव को समर्पित है और इस क्षेत्र में एक महत्वपूर्ण आध्यात्मिक और सांस्कृतिक स्थल है।
- शिव भक्त साल भर आते हैं, लेकिन श्रावण के महीने में मंदिर में भारी भीड़ होती है।
- श्रावणी मेला (जुलाई-अगस्त)
- श्रावण (सावन) के पवित्र महीने के दौरान आयोजित एक भव्य मेला।
- कांवरियों सहित हजारों तीर्थयात्री भगवान शिव को जलाभिषेक (पवित्र जल चढ़ाने) के लिए मंदिर आते हैं।
- इस त्यौहार में भक्ति गीत, भजन और धार्मिक जुलूस शामिल होते हैं, जो इसे एक जीवंत और आध्यात्मिक आयोजन बनाते हैं।
अरेराज में सोमेश्वर नाथ महादेव मंदिर क्यों जाएँ?
- बिहार के सबसे प्रसिद्ध शिव मंदिरों में से एक।
- भव्य श्रावणी मेला समारोह का अनुभव करें।
- पास में स्थित ऐतिहासिक अशोक स्तंभ पर जाएँ।
- भक्तों, इतिहास के प्रति उत्साही और सांस्कृतिक यात्रियों के लिए यह एक ज़रूरी जगह है।
5. अशोक स्तंभ, लौरिया अरेराज: सम्राट अशोक का एक स्मारक
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण में स्थित लौरिया अरेराज में अशोक स्तंभ, सम्राट अशोक द्वारा 249 ईसा पूर्व में बनवाया गया एक भव्य पत्थर का स्तंभ है। “स्तंभ धर्म लेख” के नाम से प्रसिद्ध इस स्तंभ में अशोक के छह अच्छी तरह से संरक्षित शिलालेख हैं, जो उनके धम्म (धार्मिकता और नैतिक आचरण) के सिद्धांतों को दर्शाते हैं।
अरेराज-बेतिया मार्ग के बाईं ओर स्थित यह स्तंभ भारत के समृद्ध इतिहास और अशोक के शांति के संदेश का प्रमाण है।
वास्तुकला और ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- ऊंचाई: जमीन से 36.5 फीट ऊपर।
- आधार व्यास: 41.8 इंच, जो शीर्ष पर 37.6 इंच तक पतला होता है।
- अनुमानित वजन: दफन हिस्से सहित लगभग 40 टन।
- सामग्री: पॉलिश किए गए बलुआ पत्थर का एक एकल खंड, मौर्य काल की बेहतरीन शिल्पकला को दर्शाता है।
- अशोक के शिलालेख
- स्तंभ शिलालेख दो खंडों में विभाजित हैं:
- पश्चिमी भाग: शिलालेखों की 18 पंक्तियाँ।
- दक्षिणी भाग: शिलालेखों की 23 पंक्तियाँ।
- ये शिलालेख नैतिक आचरण, अहिंसा, धार्मिक सहिष्णुता और धर्म (धार्मिकता) पर आधारित शासन पर जोर देते हैं।
- उत्कीर्णन स्पष्ट हैं, लेकिन समय के साथ कुछ खराब हो गए हैं।
- स्तंभ शिलालेख दो खंडों में विभाजित हैं:
- राजधानी का अभाव और ऐतिहासिक स्थानांतरण
- अन्य अशोक स्तंभों के विपरीत, इस स्तंभ में इसकी राजधानी (सबसे ऊपरी सजावटी संरचना) का अभाव है।
- मूल रूप से एक पशु मूर्ति के साथ ताज पहनाया गया, बाद में राजधानी को हटा दिया गया और कोलकाता संग्रहालय में स्थानांतरित कर दिया गया।
- लौरिया की स्थानीय मान्यताएँ और नामकरण
- स्तंभ को स्थानीय रूप से “लौर” के रूप में जाना जाता है, जिसका अर्थ है लिंग, जिससे पास के गाँव का नाम लौरिया पड़ा।
- माना जाता है कि लौरिया नंदनगढ़ क्षेत्र बौद्ध और मौर्य सभ्यता का केंद्र था।
अशोक स्तंभ: एक संरक्षित स्मारक
- भारतीय पुरातत्व सर्वेक्षण (एएसआई) ने इस स्तंभ को संरक्षित स्मारक के रूप में वर्गीकृत किया है, ताकि इसका संरक्षण और रखरखाव सुनिश्चित किया जा सके।
- यह स्थल इतिहासकारों, पुरातत्वविदों और प्राचीन भारतीय इतिहास में रुचि रखने वाले पर्यटकों के लिए एक लोकप्रिय आकर्षण है।
स्थान और पहुँच
- लौरिया अरेराज, बेतिया से 28 किमी और बिहार के पश्चिमी चंपारण में नरकटियागंज से 14 किमी दूर है।
- यह स्थल बूढ़ी गंडक नदी के तट के पास है, जो इसकी प्राकृतिक सुंदरता को और भी बढ़ा देता है।
लौरिया अरेराज में अशोक स्तंभ क्यों देखें?
- भारत में सबसे अच्छी तरह से संरक्षित अशोक स्तंभों में से एक।
- सम्राट अशोक की धर्म की शिक्षाओं को प्रदर्शित करने वाला एक ऐतिहासिक स्थल।
- इतिहास के शौकीनों, विद्वानों और भारत की प्राचीन विरासत में रुचि रखने वाले यात्रियों के लिए यह एक ज़रूरी जगह है।
- मोतिहारी और बेतिया के पास एक शांत और ऐतिहासिक रूप से समृद्ध गंतव्य।
6. केसरिया बौद्ध स्तूप: दुनिया का सबसे ऊंचा स्तूप
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण के केसरिया में स्थित केसरिया बौद्ध स्तूप दुनिया का सबसे ऊंचा और सबसे बड़ा बौद्ध स्तूप है। भारतीय पुरातत्व सर्वेक्षण (एएसआई) द्वारा 1998 में खोजा गया यह प्राचीन ढांचा 104 फीट ऊंचा है, जो इंडोनेशिया के जावा में स्थित प्रसिद्ध बोरोबुदुर स्तूप से भी ऊंचा है।
भारत-नेपाल सीमा के पास पटना से लगभग 120 किमी और वैशाली से 30 मील की दूरी पर स्थित केसरिया बौद्ध धर्म में ऐतिहासिक और धार्मिक दृष्टि से बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है।
ऐतिहासिक महत्व
- भगवान बुद्ध से संबंध
- बुद्ध की अंतिम यात्रा: माना जाता है कि केसरिया वह स्थान है जहां भगवान बुद्ध ने महापरिनिर्वाण (अंतिम मुक्ति) प्राप्त करने से पहले अपने अंतिम दिनों में से एक दिन बिताया था।
- भिक्षापात्र घटना: अपने देहावसान से पहले बुद्ध ने वैशाली के लिच्छवियों से घर लौटने को कहा और उन्हें वैराग्य के प्रतीक के रूप में अपना भिक्षापात्र भेंट किया।
- जातक कथाओं में उल्लेख: बौद्ध धर्मग्रंथों में बुद्ध के केसरिया में चक्रवर्ती राजा (सार्वभौमिक सम्राट) के रूप में पिछले जीवन का उल्लेख है।
- लिच्छवियों द्वारा निर्मित एक स्मारक
- केसरिया स्तूप का निर्माण बुद्ध के निर्वाण प्राप्त करने से पहले वैशाली के लिच्छवियों द्वारा किया गया था।
- चीनी यात्री ह्वेन त्सांग ने 7वीं शताब्दी में स्तूप का दौरा किया और इसके महत्व का दस्तावेजीकरण किया।
वास्तुकला और पुरातात्विक महत्व
- दुनिया का सबसे ऊंचा बौद्ध स्तूप
- मूल ऊंचाई: 150 फीट (सदियों से गिरावट से पहले)।
- वर्तमान ऊंचाई: 104 फीट, बोरोबुदुर स्तूप (103 फीट) से थोड़ा ऊंचा।
- तुलना:
- केसरिया स्तूप: 104 फीट।
- बोरोबुदुर स्तूप (जावा, इंडोनेशिया): 103 फीट।
- सांची स्तूप (मध्य प्रदेश, भारत): 77.5 फीट।
- एएसआई द्वारा पुरातात्विक खोजें
- प्रदक्षिणा पथ (भक्तों के लिए परिक्रमा पथ) के साथ छतें।
- भूमि स्पर्श मुद्रा (धरती को छूने वाली मुद्रा) में बुद्ध की कई मूर्तियाँ।
- मिट्टी के दीपक, सजी हुई ईंटें और प्राचीन मिट्टी के बर्तन।
- स्थानीय रूप से “राजा बेन का देवरा” के रूप में जाना जाने वाला यह स्थल एएसआई द्वारा खुदाई किए जाने तक मलबे के नीचे छिपा हुआ था।
स्थान और पहुँच
- गंडक नदी के पूर्वी तट पर स्थित है।
- पटना से 120 किमी।
- वैशाली से 30 मील दूर, भारत-नेपाल सीमा के पास।
- मोतिहारी और बिहार के अन्य प्रमुख शहरों से पहुँचा जा सकता है।
केसरिया स्तूप क्यों जाएँ?
- दुनिया का सबसे ऊँचा और सबसे बड़ा बौद्ध स्तूप।
- भगवान बुद्ध के अंतिम दिनों से जुड़ा एक पवित्र स्थल।
- प्राचीन अवशेषों और बुद्ध की मूर्तियों के साथ पुरातात्विक चमत्कार।
- इतिहास प्रेमियों, आध्यात्मिक साधकों और बौद्ध सर्किट पर यात्रियों के लिए एक ज़रूरी जगह।
केसरिया स्तूप भारत की बौद्ध विरासत का एक शानदार प्रमाण है।
बिहार के पूर्वी चंपारण का जिला मुख्यालय मोतिहारी ऐतिहासिक महत्व, प्राकृतिक सुंदरता और सांस्कृतिक विरासत का मिश्रण है। यह शहर भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में अपनी भूमिका, बौद्ध विरासत स्थलों और सुरम्य परिदृश्यों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है।
7. मोती झील – मोतिहारी का दिल
- एक शानदार झील जो शहर को दो भागों में विभाजित करती है।
- लुभावने दृश्य प्रस्तुत करता है और विश्राम तथा फोटोग्राफी के लिए एक आदर्श स्थान है।
- स्थानीय लोगों और पर्यटकों के लिए एक लोकप्रिय आकर्षण।
8. चंपारण सत्याग्रह पार्क – भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम को श्रद्धांजलि
- चंपारण सत्याग्रह की 100वीं वर्षगांठ मनाने के लिए बनाया गया।
- पूर्वी चंपारण के जिला मुख्यालय में स्थित है।
- ₹2 करोड़ की लागत से शहरी विकास और आवास विभाग द्वारा निर्मित।
- एक सुंदर और शांतिपूर्ण जगह जहाँ लोग परिवार और दोस्तों के साथ क्वालिटी टाइम बिताते हैं।
9. नरेगा पार्क – एक शांत मनोरंजन स्थल
- एक अच्छी तरह से बनाए रखा गया पार्क, विश्राम और अवकाश गतिविधियों के लिए एकदम सही।
- पारिवारिक सैर और पिकनिक के लिए आदर्श।
- सभी आयु वर्ग के लोगों के लिए एक ताज़ा जगह।
10. रक्सौल – नेपाल का प्रवेश द्वार
- अपनी रणनीतिक स्थिति के कारण पूर्वी चंपारण के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण शहरों में से एक।
- “नेपाल का प्रवेश द्वार” के रूप में जाना जाता है, क्योंकि यह भारत को बीरगंज के माध्यम से नेपाल से जोड़ता है।
- दोनों देशों के बीच एक प्रमुख व्यापार और परिवहन केंद्र।
11. सीताकुंड – एक पवित्र हिंदू स्थल
- पिपरा रेलवे स्टेशन से 16 किमी दूर स्थित है।
- एक पौराणिक स्थल जहाँ माना जाता है कि देवी सीता ने पवित्र स्नान किया था।
- हिंदुओं के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण तीर्थ स्थल।
मोतिहारी और उसके आस-पास के अन्य दर्शनीय स्थल
- गायत्री मंदिर – एक प्रसिद्ध मंदिर जो पूरे साल भक्तों को आकर्षित करता है।
- नवयुवक पुस्तकालय (युवा पुस्तकालय) – पुस्तक प्रेमियों के लिए एक आश्रय।
- उर्दू पुस्तकालय – एक सांस्कृतिक और साहित्यिक केंद्र।
मोतिहारी क्यों जाएँ?
- इतिहास, आध्यात्मिकता और प्राकृतिक सुंदरता का मिश्रण।
- परिवार और दोस्तों के साथ सप्ताहांत की छुट्टियों के लिए एकदम सही।
- इतिहास प्रेमियों, प्रकृति प्रेमियों और तीर्थयात्रियों के लिए आदर्श।
परिवहन
पूर्वी चंपारण का जिला मुख्यालय मोतिहारी सड़क, रेल और हवाई मार्ग से अच्छी तरह जुड़ा हुआ है, जिससे बिहार और पूरे भारत के प्रमुख शहरों से यहाँ आसानी से पहुँचा जा सकता है।
रेलवे 🚆
शहर का अपना रेलवे स्टेशन, बापूधाम मोतिहारी (BMKI) है, जहाँ से प्रमुख गंतव्यों के लिए नियमित ट्रेन सेवाएँ उपलब्ध हैं।
मुख्य रेल मार्ग:
- मोतिहारी रेलवे स्टेशन – एक प्रमुख रेलवे हब।
- रक्सौल जंक्शन – बिहार को नेपाल और उत्तर भारत से जोड़ता है।
- अन्य स्टेशनों में चकिया, ढाका और अरेराज शामिल हैं।
- नई दिल्ली – मोतिहारी
- आनंद विहार – मोतिहारी
- हावड़ा – मोतिहारी
- रक्सौल – मोतिहारी
ट्रेन यात्रा के लाभ:
✅ प्रमुख भारतीय शहरों से अच्छी तरह जुड़ा हुआ है।
✅ बसों या उड़ानों की तुलना में किफ़ायती किराया और आप आरामदायक यात्रा के लिए पहले से टिकट बुक कर सकते हैं।
🔹 ट्रेन शेड्यूल और बुकिंग के लिए, यहाँ जाएँ: भारतीय रेलवे
रोडवेज 🚌
मोतिहारी राज्य राजमार्गों और राष्ट्रीय राजमार्गों से अच्छी तरह जुड़ा हुआ है। शहर से आने-जाने के लिए नियमित बसें चलती हैं, जो इसे एक सुविधाजनक यात्रा विकल्प बनाती हैं।
बस मार्ग:
- राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग NH-27 और NH-28 पूर्वी चंपारण को पटना, मुजफ्फरपुर और नेपाल से जोड़ते हैं।
- मोतिहारी, रक्सौल और प्रमुख शहरों के बीच बस सेवाएँ चलती हैं।
- पटना – मोतिहारी (160 किमी)
- किराया: ₹210 – ₹250 प्रति व्यक्ति
- राज्य परिवहन और निजी ऑपरेटरों द्वारा लगातार बसें।
- बोधगया – पटना – मुजफ्फरपुर – मोतिहारी – बीरगंज – काठमांडू
- बेतिया – मोतिहारी – मुजफ्फरपुर – हाजीपुर – पटना
- छपरा – सीवान – गोपालगंज – मोतिहारी
✅ आरामदायक और बजट के अनुकूल यात्रा।
✅ कई बस ऑपरेटर उपलब्ध हैं।
हवाई मार्ग ✈️
मोतिहारी का सबसे नजदीकी हवाई अड्डा पटना हवाई अड्डा (लोक नायक जयप्रकाश हवाई अड्डा) है, जो लगभग 160 किमी दूर है।
निकटतम हवाई अड्डे:
- घरेलू उड़ानों के लिए दरभंगा हवाई अड्डा (110 किमी दूर)।
- पटना हवाई अड्डा (पीएटी) – 160 किमी
- दिल्ली, मुंबई, कोलकाता, चेन्नई, रांची और भोपाल जैसे प्रमुख भारतीय शहरों के लिए दैनिक उड़ानें।
- चौधरी चरण सिंह अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डा, लखनऊ – 473 किमी
- विदेशी यात्रियों के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय उड़ानें।
- रक्सौल हवाई अड्डे के लिए एक प्रस्ताव पर विचार किया जा रहा है।
✅ पटना हवाई अड्डे से मोतिहारी के लिए टैक्सी और बस सेवाएँ उपलब्ध हैं।
चुनौतियाँ
- बाढ़ – जिले में गंडक नदी से हर साल भयंकर बाढ़ आती है।
- बेरोज़गारी और पलायन – उद्योगों की कमी के कारण नौकरियों के लिए लोगों का पलायन होता है।
- बुनियादी ढांचे का विकास – कई ग्रामीण सड़कों और स्वास्थ्य सुविधाओं में सुधार की आवश्यकता है।
- शिक्षा – कम साक्षरता दर के कारण बेहतर शैक्षिक सुविधाओं की आवश्यकता है।
निष्कर्ष
पूर्वी चंपारण बिहार का ऐतिहासिक और कृषि संबंधी दृष्टि से महत्वपूर्ण जिला है। चंपारण सत्याग्रह, केसरिया स्तूप और गन्ना उत्पादन से इसका जुड़ाव इसे अद्वितीय बनाता है। जबकि कृषि और नेपाल के साथ व्यापार प्रमुख आर्थिक चालक हैं, बाढ़, बेरोजगारी और उद्योगों की कमी प्रमुख चुनौतियां बनी हुई हैं। बेहतर बुनियादी ढांचे, शिक्षा और औद्योगिक विकास के साथ, पूर्वी चंपारण बिहार में एक अग्रणी जिले के रूप में उभर सकता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

3 thoughts on “East Champaran District: A Special Land of Revolution”