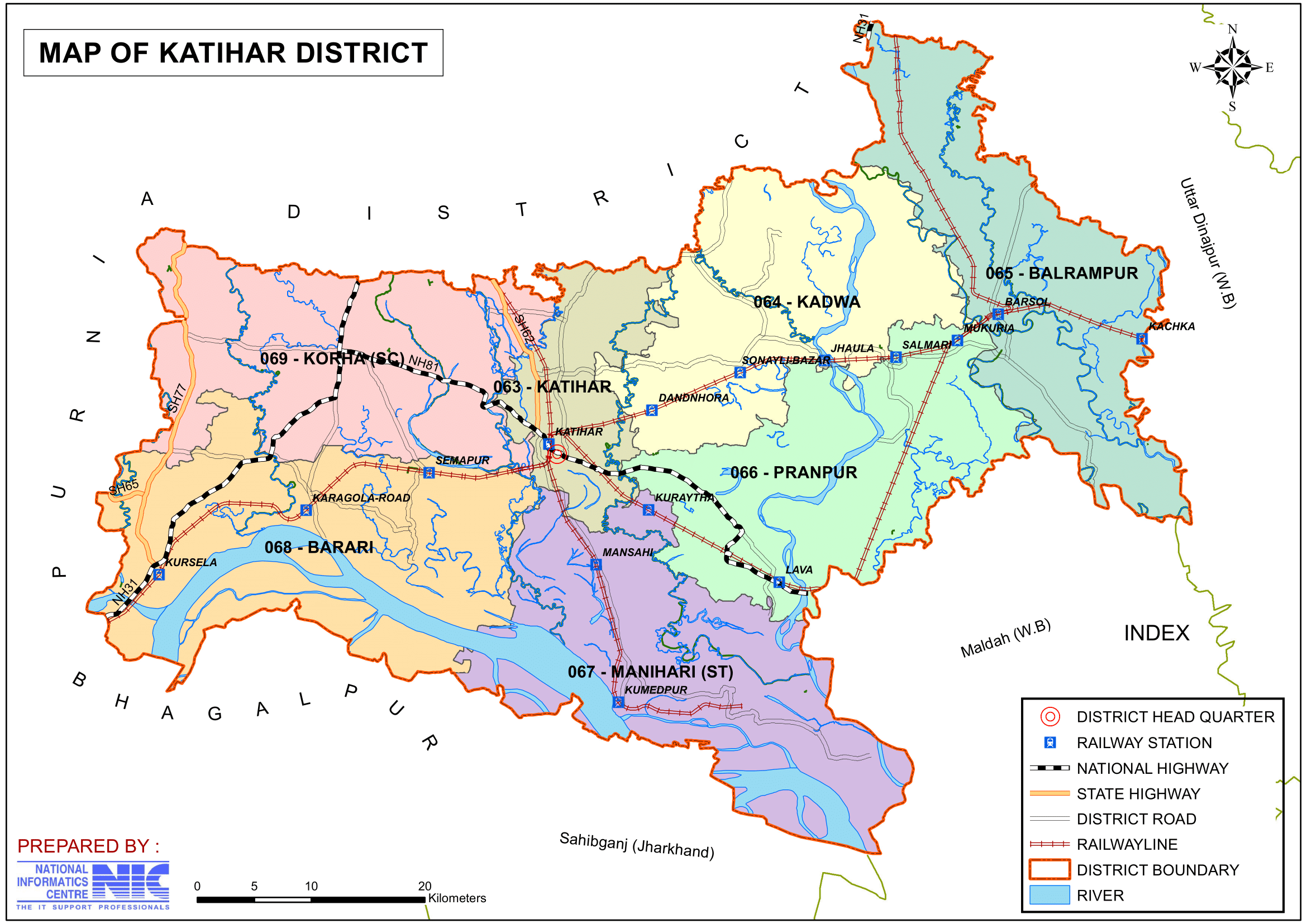
Katihar District: An Overview
Katihar district, is one of the 38th-districts located in the northeastern part of Bihar, India with rich in agricultural, historical, and cultural significance. Known as an important rail and trade hub, Katihar plays a crucial role in connecting Bihar to other parts of India, particularly the northeastern states. The district’s lush agricultural lands and cultural diversity add to its importance in the state.
Katihar became a full-fledged district when it was separated from Purnia district on 2nd October 1973. The district covers an area of 3,056 km2 (1,180 sq mi), which bordering Purnia district to the north and the west, Bhagalpur district of Bihar and Sahebganj district of Jharkhand to the south, and Malda district and Uttar Dinajpur district of west Bengal to the east. The district’s administrative center is located at Katihar town. It is one of the district under the Purnia division (Seemanchal).
Katihar is a historical location that has significance in Indian history. It is stated that Hindu Lord Shri Krishna visited here and lost mani in Manihari (a sacred site in Katihar district).
Previously, the Choudhary family ruled Katihar district, being the largest landlords in the Koshi zone. Khan Bahadur Mohammad Baksh, the founder of the Choudhary dynasty, owns around 15,000 acres in Katihar district and 8,500 acres in Purnea.
Key Facts About Katihar District
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Region: Mithila
- Division: Purnia
- Coordinates: 25°33′00″N 87°34′12″E
- Established: 2nd October 1973
- Area: 3,056 km2 (1,180 sq mi)
- District Headquarters: Katihar
- District Magistrate (DM): Manesh Kumar Meena, IAS
- Superintendent of Police (SP): Vaibhav Sharma, IPS
- Population (2011):
- Total: 3,071,029
- Density: 1,000/km2 (2,600/sq mi)
- Literacy Rate: 52.24%
- Sex Ratio: 916 females for every 1000 males
- Official Language: Hindi
- Regional Languages: Maithili, Surjapuri, Bengali
- Gram Panchayats: 238
- Villages: 1547 (approx)
- No. of Subdivision: 3 (Katihar, Manihari, Barsoi)
- No. of Blocks: 16
- Katihar- Katihar, Dandkhora, Hasanganj, Korha, Sameli, Falka, Kursela, Barari, Mansahi and Pranpur.
- Barsoi- Barsoi, Balrampur, Azamnagar and Kadwa.
- Manihari- Manihari and Amdabad.
- Police Station: 25
- Town PS, Sahayak, Mufasil, Mansahi, Pranpur, Dandkhora, Manihari, Amdabad, Korha, Kursela, Barari, Falka, Pothiya, Barsoi, Sudhani, Kachana, Aabadpur, Kadwa, Baliya Belon, Azamnagar, Rautara, Balrampur (O.P- Telta, Roshna, Salmari)
- Municipal Corporation (Nagar Nigam): 1 (Katihar)
- Nagar Panchayat: 1 (Manihari)
- Lok Sabha constituency: 1 (Katihar)
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 6
- 63- Katihar, 64- Kadwa, 65- Balrampur, 66- Pranpur, 67- Manihari, 68- Barari, 69- Korha
- Key Features:
- A major railway hub in eastern India, connecting various parts of Bihar and neighboring states.
- Known for its production of jute and agricultural goods.
- Culturally significant for its diverse population and heritage sites.
- Significance: A center of transportation, agriculture, and trade.
- Major Rivers: Ganga, Koshi, Mahananda and Righa.
- Major Highways: NH-31, NH-81, NH-131A
- Time Zone: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- Vehicle Registration: BR-39
- PIN Code: 854105 (Katihar)
- STD Code: 06452 (Katihar)
- Official Website: katihar.nic.in
Geography
- Location: Katihar is situated in the northeastern region of Bihar, sharing its borders with Purnia to the north, Bhagalpur to the west, Sahebganj (Jharkhand) to the south, and Malda and Uttar Dinajpur (West Bengal) to the east.
- The district latitude and longitude is 25.5422194 , 87.5645687.
- Area: The district spans approximately 3,057 square kilometers.
- Rivers: The Ganga, Kosi, and Mahananda rivers flow through Katihar, providing fertile land for agriculture but also making the district prone to floods.
- Climate: Katihar experiences a humid subtropical climate with hot summers, heavy monsoons, and cool winters.
History
Ancient History:
- Katihar has historical connections to the ancient Mithila and Anga regions and has witnessed the influence of Hindu, Buddhist, and Islamic cultures over centuries.
- During the time of Mahajanpada, the region was ruled by Anga and Magadh Kings. Raja Birat of Morang is also said to have visited the area.
- Katihar was a part of the Purnia district, which was constituted in approximately 1813, along with Malda district.
Medieval Period:
The province of Bihar came under Muslim rule after Bakhtiyar Khilji conquered Bihar town, then the capital of Bihar, towards the close of the 12th century. His successor, Ghiasuddin Iwaz, extended the limits of the territory to include virtually the whole of Bihar, and Katihar must have come under Mohammedan rule in the early 13th century.
Mughal Rule:
Under the Mughal rule, the district was constituted of Sarkar Tajpur (east of the Mahananda River) and Sarkar Purnia (west of the river). This area remained under indirect Mughal control until the advent of British rule.
British Era:
- The district passed into British hands in 1770 when Mohammad Ali Khan was the Governor of Purnia. He was replaced by Ducarrel, the first English Supervisor or Collector of the district.
- In 1872, the district was transferred from the control of the Bihar and Banaras Board of Commissioners to the Calcutta Board of Revenue.
- Early British rule was focused on establishing law and order and setting up revenue administration.
- During British rule, Katihar served as a prominent railway and trade center due to its strategic location near Bengal and Jharkhand.
Partition of Bengal:
Before the partition of Bengal, Katihar was part of Bengal. However, after the division of Bengal into Bihar, Bengal, and Orissa, today’s Katihar district came under Bihar. During British rule, Katihar came under the control of Zamindars and Nawabs who collaborated with the British to exploit farmers and laborers.
Freedom Movement:
The people of Katihar actively participated in the freedom movement, challenging British rule. With India’s independence, the people of Katihar, like all Indians, gained freedom.
Formation of Katihar District:
Katihar was initially a sub-divisional town of Purnia district. However, on 2nd October 1973, Katihar was granted the status of an independent district. It has a rich heritage and close historical connections with the parent district of Purnia.
Etymology of Katihar:
The district derives its name from its chief town, which likely got its name from a small village on the northeast called Dighi-Katihar. The village had a large tank (dighi) excavated for the troops when the soldiers of the Nawab of Purnea fought with the troops of the Nawab of Murshidabad.
Political History of Katihar
- Role in the Freedom Struggle:
- Katihar was a significant center of activity during India’s independence movement.
- Notable freedom fighters:
- Alhaj Azhar Ali: Honored with a village named Ajhrail after him.
- Dhrub Kundu and his father, Dr. Kishori Lal Kundu.
- Nakshtra Malakar: Known as the “Robin Hood of the Kosi belt.”
- The busy Shaheed Chowk market square is named in memory of the martyrs of the 1942 Quit India Movement.
- Katihar Lok Sabha Constituency:
- Represented by several prominent politicians over the years:
- Sitaram Kesri: Former Treasurer and President of the All India Congress Committee (AICC).
- Tariq Anwar: Veteran leader and significant political figure.
- Nikhil Choudhary and Mohammad Yunus Saleem: Other notable representatives.
- Mufti Mohammad Sayeed, a renowned Kashmiri politician, contested the 1996 Lok Sabha elections from Katihar but was unsuccessful.
- Represented by several prominent politicians over the years:
Katihar’s political history reflects its active participation in the freedom struggle and its importance as a constituency represented by several notable leaders in India’s political landscape.
Demographics (According to the 2011 Census)
- Population:
- Total Population: Katihar district has a population of 3,071,029 (approximately 3.07 million), comparable to the nation of Oman or the US state of Iowa.
- Ranking: 117th in India (out of 640 districts).
- Population Density: 1,004 inhabitants per square kilometer (2,600/sq mi).
- Population Growth (2001–2011): 28.23% reflecting significant population increase.
- Sex Ratio: 916 females per 1,000 males, indicating a gender disparity.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate is 53.56%, with significant disparities between urban and rural areas, and efforts ongoing to improve educational access in rural areas.
- Urban Population: 8.92% of the total population lives in urban areas.
- Religious Composition (2011 Census): Although there are equal proportions of Muslims and Hindus in rural regions, Hinduism is the majority religion. The primary population in the district’s eastern region is Muslim.
- Hinduism: 54.85%
- Scheduled Castes: 8.57%
- Scheduled Tribes: 5.86%
- Islam: 44.47%
- Other or not stated: 0.68%
- Hinduism: 54.85%
- Languages: The primary languages spoken are Hindi, Maithili, Bengali, Angika, and Urdu, reflecting the district’s cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Surjapuri: 25.86%, Surjapuri speakers are predominantly concentrated in the Kadwa, Azamnagar, Barsoi, and Balrampur blocks, which border West Bengal.
- ‘Other’ Hindi: 25.46%
- Hindi: 19.73%
- Bengali: 12.04%, Bengali speakers form nearly a majority in the Amdabad block.
- Urdu: 9.11%
- Santali: 2.97%
- Bhojpuri: 2.29%
- Others: 2.54%
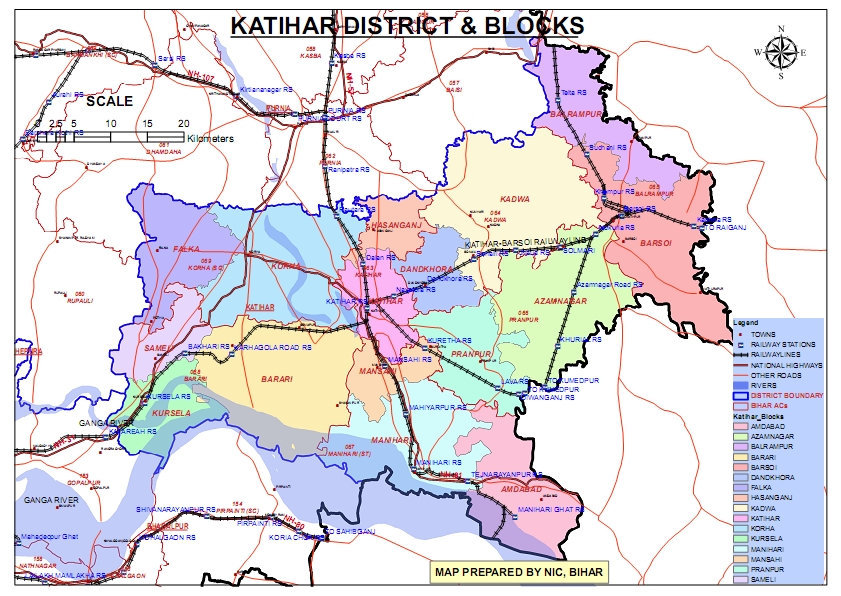
Administration
- Headquarters: Katihar town serves as the district headquarters.
- Subdivisions:
- The district is divided into three subdivisions: Katihar Sadar, Barsoi, and Manihari, further subdivided into 16 administrative blocks.
- Each subdivision is led by a subdivisional magistrate who is in charge of development, revenue-related tasks, and maintaining law and order.
- Blocks and Circles:
- Katihar district is divided into 16 Blocks and Circles such as Katihar, Dandkhora, Hasanganj, Korha, Sameli, Falka, Kursela, Barari, Mansahi, Pranpur, Barsoi, Balrampur, Ajamnagar, Kadwa, Manihari and Amdabad.
- Katihar- Katihar, Dandkhora, Hasanganj, Korha, Sameli, Falka, Kursela, Barari, Mansahi and Pranpur.
- Barsoi- Barsoi, Balrampur, Azamnagar and Kadwa.
- Manihari- Manihari and Amdabad.
- A circle officer (CO) leads each circle, while a Block Development Officer (BDO) leads each block.
- Hasanganj Block:
- Largest block in Katihar district, historically under Zamindari rule.
- The vast land was under the possession of Late Shri Jogendranarayan Roy Choudhury.
- Contributions to the Community:
- Land, schools, temples, and markets were donated to the people by the Zamindar’s predecessors.
- Present-day descendants, notably from the Paul Choudhury family, retain minimal possession of the land.
- Other Prominent Zamindari Estates:
- Mansahi: Known for its influential Zamindari estate, comparable to the prominence of Kursela and Falka.
- Hasanganj Block:
- This rich Zamindari heritage highlights the historical significance and community contributions of Katihar’s prominent estates.
- Katihar district is divided into 16 Blocks and Circles such as Katihar, Dandkhora, Hasanganj, Korha, Sameli, Falka, Kursela, Barari, Mansahi, Pranpur, Barsoi, Balrampur, Ajamnagar, Kadwa, Manihari and Amdabad.
- Governance: Katihar is part of the Purnia division and is represented in both the Bihar Legislative Assembly and the Indian Parliament.
- Lok Sabha constituency: Katihar
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies: 6
- 63- Katihar, 64- Kadwa, 65- Balrampur, 66- Pranpur, 67- Manihari, 68- Barari, 69- Korha
Economy
- Backward District Status:
- Named one of India’s 250 most backward districts by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj in 2006.
- Receives support under the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).
- Included in the Aspirational Districts Program since 2018 to improve socio-economic conditions.
- Agriculture: Agriculture is the backbone of Katihar’s economy.
- Major crops cultivated in the district include cash crops (Banana, Jute, Maize), Paddy, Makhana, Wheat, Rice (staple crop), Sugarcane, and pulses.
- The fertile alluvial soil, coupled with an abundant water supply, makes the district one of Bihar’s major agricultural hubs.
- The district is also good producer of Green Vegetables which is dominated by Potato, onion and Cauliflowers.
- Since 2018, it has been part of the Government of India’s Aspirational Districts Program, which aims to improve its socio-economic metrics.
- Katihar is Bihar’s largest maize-producing district in 2022.
- Emerging industry: Makhana Phodi (processing of raw foxnuts into edible makhana).
- Cash Crops: Banana, Jute, Maize, and Makhana are the main cash crops grown by farmers.
- Trade and Commerce: Katihar is a key trading center for jute, grains, and other agricultural products. Its proximity to West Bengal and Jharkhand enhances its commercial significance.
- The cloth market, known for cotton and sarees, is vibrant and caters to nearby districts and even countries like Nepal and Bangladesh.
- Cycle Trading Companies: A couple of old cycle trading companies have significant turnovers.
- Pharmaceuticals: The pharmaceuticals business is thriving, contributing to the local economy with high turnover.
- Railway Economy: Katihar is an important railway hub for the northeastern region, contributing significantly to the district’s economy.
Emerging Industries:
Jute-based industries and agro-processing units are growing, though large-scale industrialization is still limited.
Jute Mills: Katihar was historically known as the “jute capital” of Bihar. Katihar once had two prominent jute mills, known as Purana Mill and Naya Mill, which shaped the town’s identity. Unfortunately, these mills have been non-operational for a long time.
- Old Jute Mill (Sunbio Manufacturing Private Limited):
- Spread over 35 acres.
- Operated by Govind Sharda’s Sunbio Manufacturing since 2001.
- Peak production: 100 tonnes/day; current capacity (2020): 10 tonnes/day with 200 workers.
- New Jute Mill (RBHM Jute Mill):
- Established in 1935, covering 53.39 acres.
- Closed in 1977, reopened in 1980 under NJMC, and shut again in 2004.
- Briefly reopened in 2014 under the PPP model but ceased operations in 2016 following NJMC’s closure based on NITI Aayog’s recommendation.
- Flour Mills: Two flour mills operate in the region.
- Agro-Based Industries:
- Tingachhiya has units producing agricultural products.
- The rice industry is flourishing in this area.
- Makhana Production: The Makhana Phodi, where raw makhana is processed into edible makhana, is growing rapidly.
Katihar’s economy primarily relies on its agricultural base, with limited industrial activity largely concentrated in agro-processing and the once-thriving jute sector. The district remains a focal point for developmental programs aimed at uplifting its socio-economic profile.
Education
Katihar has made significant progress in education, though rural areas still face challenges in access and infrastructure:
- Katihar Medical College: A renowned medical institution offering quality education and healthcare services.
- Schools and Colleges: Katihar district has several government and private schools and colleges affiliated with BN Mandal University.
- Vocational Training: Institutions providing skill development and vocational training are emerging to meet the needs of the local population.
Culture
- Festivals: Festivals such as Chhath Puja, Durga Puja, Eid, and Holi are celebrated with great enthusiasm, reflecting the district’s religious and cultural harmony.
- Cuisine: Katihar’s cuisine includes traditional Bihari and Bengali dishes, such as litti chokha, panta bhat, and sweets like rosogolla and sandesh.
- Art and Music: The district contributes to Mithila culture through folk music, Maithili art, and traditional dances.
Tourism
Katihar offers a mix of natural, historical, and religious attractions:
- Manihari Ghat:
- Manihari, a town close to Katihar, is well-known for its role as a commercial hub during the British colonial era. This Ghat is a popular location for Ganges River boat rides.
- A scenic spot on the banks of the Ganga River, known for its picturesque views and as a transit point to Sahibganj (Jharkhand).
- Madhuban Temple: A popular religious site dedicated to Lord Shiva, attracting devotees from nearby regions.
- Railway Heritage: Katihar Railway Junction, one of the oldest and busiest railway stations, holds historical significance for the Indian Railways.
- Gandhi Ghar: A historical site of local importance.
- Bari Durga Mandir: A revered Hindu temple dedicated to Goddess Durga.
- Bhairav Nath Mandir: A temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, significant for devotees.
- Peer Mazar: A prominent religious site for spiritual seekers.
- Gorkhanath Temple: A temple dedicated to Lord Gorkhanath, significant for worship and rituals.
- Gauri Shankar Temple: A temple dedicated to Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati.
- Trimohini Sangam: The confluence of three rivers, offering a tranquil and picturesque spot.
Gogabil Lake:
- Location:
Gogabil Lake is situated in Amdabad block of Katihar district, Bihar. - Area:
The lake covers an area of 217.99 acres, of which 143.84 acres is purely lake area belonging to the Government of Bihar under thana no. 252 and mouza Jangalatal. - Connectivity:
- Nearest Airport: Bagdogra, 85 km from Katihar District Headquarters.
- Distance to Patna: Approximately 350 km.
- Nearest Railway Stations:
- Manihari (closer)
- Katihar Junction, 25 km away.
- The lake is connected to the district town by a state highway.
- National Highway No. 31 is located about 40 km towards the northeast of the lake.
Guru Teg Bahadur Sahib Historical Gurudwara:
- Location:
Situated in Lakshmipur Panchayat of Barari Block, Katihar District, Bihar. - Distance:
Approximately 40 km from Katihar District Headquarters. - Historical Significance:
- The Gurudwara is associated with Guru Tegh Bahadur Sahib, the Ninth Guru of the Sikhs.
- Guru Tegh Bahadur stayed here in 1670 AD (earlier known as Kant Nagar) on his return journey from Assam to Patna.
- The villagers became followers of the Sikh faith due to his influence.
- Religious Importance:
- The Gurudwara houses ancient scripts and documents of religious significance.
- An old volume of Guru Granth Sahib is preserved here.
- Tourism and Pilgrimage:
Many devotees and tourists visit the Gurudwara due to its association with Guru Tegh Bahadur Sahib and its historical relics.
Transportation
- Railways: Katihar Junction Railway Station, a Category A1 station on the Barauni–Guwahati route, is one of the most important railway hubs in Bihar, connecting the district to major cities like Kolkata, Delhi, Guwahati, and Patna.
- Roadways: National Highways such as NH-31 and NH-81 pass through Katihar, ensuring connectivity to other districts and states.
- Waterways: The Ganga River provides opportunities for inland water transport, particularly at Manihari Ghat.
- Airways: The nearest airport is Bagdogra Airport in West Bengal (about 160 km away), with plans for improved air connectivity in the future.
Challenges
- Flooding: Frequent flooding due to rivers like the Kosi and Mahananda disrupts agriculture, transportation, and livelihoods.
- Infrastructure: Rural areas face challenges in healthcare, education, and road connectivity.
- Unemployment: Limited industrial development leads to migration to other states for employment.
Conclusion
Katihar is a district of immense economic, cultural, and historical importance in Bihar. Its strategic location as a railway and trade hub, coupled with fertile agricultural lands, makes it a vital part of the state. Despite challenges such as flooding and underdeveloped infrastructure, Katihar has significant potential for growth in agriculture, trade, and industrial development. With focused investments and disaster management efforts, Katihar can emerge as a key economic and cultural hub in the region.
Post Office & PIN Codes
| SL. NO. | Head Offices (H.O) | Sub Offices (S.O) | Branch Offices (B.O) | Pin Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ayodhyaganj Bazar | Balthi Maheshpur, Chandpur, Chapahari, Goriar, Khaira, M.T.Devipur, Moula Nagar, Nandgola, Sameli, Simra, Tikapatti. | 854101 | |
| 2 | Daharia Molls | Kumaripur, Mansahi, Sirnia, Tingahhia. | 854103 | |
| 3 | Bhaisdiara, Bhandartal, Bishanpur, Bokia, Dhenuabishanpur, Dumar, Hasimpur, Jarlahi, Jot Ram Roy, K.N. Guru Mela, Kant Nagar, Karha Gola Road, Laxmipur, Maraghia, Marwa, Pakahara, Pawai, Rounia, Samda. | 854104 | ||
| 4 | Katihar | Katihar Bara Bazar, Katihar Colony, Katihar Rs, Durgapur | 854105 | |
| 5 | Katihar Bmp Camp | B.Simaria, Dalan, Dighri, Sandalpur | 854106 | |
| 6 | Belwa, Budhnagar, Kuretha’, Madhura, Sahja, Sauriya, Sukhasan. | 854107 | ||
| 7 | Bhatwara, Dhanetha, Jhagruchak, Kheria, Morsanda, Musapur, Sisia. | 854108 | ||
| 8 | Katihar Court | 854109 | ||
| 9 | Amdabad | 854112 | ||
| 10 | Manihari | B.Deora, Bakharganj, Dilarpur, Gopalpur Diara, Hemkunj, Mahinagar, Manihari Nawabganj, Narayanpur, Pani Kamla, Pardiara, R.N.Baulia, T.M. Baghar. | 854113 | |
| 11 | Pothia | Arihiana, Bareta, Basantpur, Bhangaha, Chhohar, Falka, Pirmokam, Salepur. | 854114 | |
| 12 | Semapur Factory | Bansgarha, Binjee, Bishanpurhariabhir, Jagdishpur, Sikat, Sujapur | 854115 | |
| 13 | Mahadevpur (Katihar) | Baina, Bastaul, Dharhan, Dhena Bagchhata, Gauripur, Kehunia, Mahaur, Mainanagar, Palsa, Pranpur, Tangore. | 854116 | |
| 14 | Rosna | Dilli Diwanganj, Neema | 854117 | |
| 15 | Fatehpur | 854335 | ||
| 16 | Barsoi | Awadpur, Chhoghra, Dasgram, Gaualtoli, Hat Balrampur, Jalki, Khirdirpur, Mathurapur, Porla, Sankola, Sitalmani, Shivananpur. | 855102 | |
| 17 | Durgaganj | Babhani, Bharri, Chandpur, Chouki Hajipur, Dwasi, Parveli, Sagrath. | 855105 | |
| 18 | Salmari | Azamnagar, Balia Belon, Baltor, Belbari, Dhumnagar, Kantakosh, Kharsouta, Nimoul, Sadapur, Shipur, Siktia, Teghra. | 855113 | |
| 19 | Sonali | Bijaili, Dumaria, Dandkhora, Kadwa, Millik Palagarh, Regheli | 855114 |
Helpline
| Service | Contact Number |
|---|---|
| Health Control Room, Katihar | 06452-295350 |
| District Control Room And Dist Emergency Operation Centre, Katihar | 06452-239025 / 06452-239026 / 06452-242400 |
| JTO, BSNL, Katihar | 06452-222256 |
| Railway Enquiry, Katihar | 06452-131 / 133 / 135 / 139 / 06452-222551 |
| Railway Enquiry, Salmari | 06451-248238 |
| Railway Enquiry, Kursela | 06457-258226 |
| Railway Accidental Enquiry | 06452-1072 |
| Fire Brigade, Katihar | 06452-224200 |
| Fire Brigade, Barsoi | 06451-220645 |
| Ambulance | 06452-102 |
| Television Station, Katihar | 06452-249362 |
| Medical College, Katihar | 06452-249202 / 249203 |
| Police Station, Katihar | 06452-230414 |
| Women Help Line | 181 / 9771468016 |
| Jigyasa Help Line | 0612-2233333 |
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below or checkout these topics
कटिहार जिला: विशेष ऐतिहासिक महत्व वाली भूमि
अवलोकन
कटिहार जिला, भारत के बिहार के पूर्वोत्तर भाग में स्थित 38वें जिलों में से एक है, जो कृषि, ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व से समृद्ध है। एक महत्वपूर्ण रेल और व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में जाना जाने वाला कटिहार बिहार को भारत के अन्य हिस्सों, विशेष रूप से पूर्वोत्तर राज्यों से जोड़ने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है। जिले की हरी-भरी कृषि भूमि और सांस्कृतिक विविधता राज्य में इसके महत्व को बढ़ाती है।
2 अक्टूबर 1973 को पूर्णिया जिले से अलग होने पर कटिहार एक पूर्ण विकसित जिला बन गया। यह जिला 3,056 किमी2 (1,180 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र में फैला हुआ है, जो उत्तर और पश्चिम में पूर्णिया जिले, दक्षिण में बिहार के भागलपुर जिले और झारखंड के साहेबगंज जिले और पूर्व में पश्चिम बंगाल के मालदा जिले और उत्तर दिनाजपुर जिले की सीमा से लगा हुआ है। जिले का प्रशासनिक केंद्र कटिहार शहर में स्थित है। यह पूर्णिया डिवीजन (सीमांचल) के अंतर्गत आने वाले जिलों में से एक है।
कटिहार एक ऐतिहासिक स्थान है जिसका भारतीय इतिहास में महत्व है। ऐसा कहा जाता है कि हिंदू भगवान श्री कृष्ण यहाँ आए थे और मनिहारी (कटिहार जिले में एक पवित्र स्थल) में मणि खो दी थी।
पहले, चौधरी परिवार कटिहार जिले पर शासन करता था, जो कोशी क्षेत्र का सबसे बड़ा जमींदार था। चौधरी वंश के संस्थापक खान बहादुर मोहम्मद बख्श के पास कटिहार जिले में लगभग 15,000 एकड़ और पूर्णिया में 8,500 एकड़ जमीन है।
कटिहार जिले के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - क्षेत्र: मिथिला
- प्रमंडल: पूर्णिया
- निर्देशांक: 25°33′00″N 87°34′12″E
- स्थापना: 2 अक्टूबर 1973
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,056 km2 (1,180 वर्ग मील)
- जिला मुख्यालय: कटिहार
- जिला मजिस्ट्रेट (DM): मनेश कुमार मीना, IAS
- पुलिस अधीक्षक (SP): वैभव शर्मा, IPS
- जनसंख्या (2011):
- कुल: 3,071,029
- घनत्व: 1,000/km2 (2,600/वर्ग मील)
- साक्षरता दर: 52.24%
- लिंगानुपात: प्रति 1000 पुरुषों पर 916 महिलाएँ
- राजभाषा: हिंदी
- क्षेत्रीय भाषाएँ: मैथिली, सुरजापुरी, बंगाली
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 238
- गांव: 1547 (लगभग)
- अनुमंडल की संख्या: 3 (कटिहार, मनिहारी, बारसोई)
- ब्लॉकों की संख्या: 16
- कटिहार-कटिहार, डंडखोरा, हसनगंज, कोरहा, समेली, फलका, कुर्सेला, बरारी, मनसाही और प्राणपुर
- बारसोई- बारसोई, बलरामपुर, आजमनगर और कदवा
- मनिहारी- मनिहारी और अमदाबाद
- पुलिस स्टेशन: 25
- टाउन थाना, सहायक, मुफ्फसिल, मनसाही, प्राणपुर, डंडखोरा, मनिहारी, अमदाबाद, कोरहा, कुरसेला, बरारी, फलका, पोठिया, बारसोई, सुधानी, कचना, आबादपुर, कदवा, बलिया बेलोन, आजमनगर, रौतारा, बलरामपुर (ओ.पी.) तेल्टा, रोशना, सालमारी)
- नगर निगम: 1 (कटिहार)
- नगर पंचायत: 1 (मनिहारी)
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र: 1 (कटिहार)
- विधानसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र: 6
- 63-कटिहार, 64-कदवा, 65-बलरामपुर, 66-प्राणपुर, 67-मनिहारी, 68-बरारी, 69-कोरहा
- मुख्य विशेषताएं:
- पूर्वी भारत में एक प्रमुख रेलवे हब, जो विभिन्न बिहार और पड़ोसी राज्यों के कुछ हिस्से।
- जूट और कृषि उत्पादों के उत्पादन के लिए जाना जाता है।
- अपनी विविध आबादी और विरासत स्थलों के लिए सांस्कृतिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण है।
- महत्व: परिवहन, कृषि और व्यापार का केंद्र।
- प्रमुख नदियाँ: गंगा, कोशी, महानंदा और रिघा।
- प्रमुख राजमार्ग: NH-31, NH-81, NH-131A
- समय क्षेत्र: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- वाहन पंजीकरण: BR-39
- पिन कोड: 854105 (कटिहार)
- एसटीडी कोड: 06452 (कटिहार)
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: katihar.nic.in
भूगोल
- स्थान: कटिहार बिहार के पूर्वोत्तर क्षेत्र में स्थित है, जिसकी सीमा उत्तर में पूर्णिया, पश्चिम में भागलपुर, दक्षिण में साहेबगंज (झारखंड) और पूर्व में मालदा और उत्तर दिनाजपुर (पश्चिम बंगाल) से मिलती है।
- जिले का अक्षांश और देशांतर 25.5422194, 87.5645687 है।
- क्षेत्रफल: जिले का क्षेत्रफल लगभग 3,057 वर्ग किलोमीटर है।
- नदियाँ: गंगा, कोसी और महानंदा नदियाँ कटिहार से होकर बहती हैं, जो कृषि के लिए उपजाऊ भूमि प्रदान करती हैं, लेकिन जिले को बाढ़ का खतरा भी देती हैं।
- जलवायु: कटिहार में गर्म ग्रीष्मकाल, भारी मानसून और ठंडी सर्दियाँ के साथ आर्द्र उपोष्णकटिबंधीय जलवायु होती है।
इतिहास
प्राचीन इतिहास:
- कटिहार का प्राचीन मिथिला और अंग क्षेत्रों से ऐतिहासिक संबंध है और सदियों से हिंदू, बौद्ध और इस्लामी संस्कृतियों का प्रभाव देखा गया है।
- महाजनपद के समय में, इस क्षेत्र पर अंग और मगध राजाओं का शासन था। कहा जाता है कि मोरंग के राजा बीरट ने भी इस क्षेत्र का दौरा किया था।
- कटिहार पूर्णिया जिले का एक हिस्सा था, जिसका गठन लगभग 1813 में मालदा जिले के साथ किया गया था।
मध्यकालीन काल:
12वीं शताब्दी के अंत में बख्तियार खिलजी द्वारा बिहार शहर, जो उस समय बिहार की राजधानी थी, पर विजय प्राप्त करने के बाद बिहार प्रांत मुस्लिम शासन के अधीन आ गया। उनके उत्तराधिकारी, गयासुद्दीन इवाज ने क्षेत्र की सीमाओं का विस्तार करके लगभग पूरे बिहार को शामिल कर लिया, और कटिहार 13वीं शताब्दी की शुरुआत में मुस्लिम शासन के अधीन आ गया होगा।
मुगल शासन:
मुगल शासन के तहत, जिले में सरकार ताजपुर (महानंदा नदी के पूर्व में) और सरकार पूर्णिया (नदी के पश्चिम में) शामिल थे। यह क्षेत्र ब्रिटिश शासन के आगमन तक अप्रत्यक्ष रूप से मुगल नियंत्रण में रहा।
ब्रिटिश काल:
- 1770 में जब मोहम्मद अली खान पूर्णिया के गवर्नर थे, तब यह जिला ब्रिटिश हाथों में चला गया था। उनकी जगह डुकारेल ने ली, जो जिले के पहले अंग्रेज पर्यवेक्षक या कलेक्टर थे।
- 1872 में, जिले को बिहार और बनारस बोर्ड ऑफ कमिश्नर्स के नियंत्रण से कलकत्ता बोर्ड ऑफ रेवेन्यू को सौंप दिया गया था।
- शुरुआती ब्रिटिश शासन कानून और व्यवस्था स्थापित करने और राजस्व प्रशासन स्थापित करने पर केंद्रित था।
- ब्रिटिश शासन के दौरान, बंगाल और झारखंड के निकट अपनी रणनीतिक स्थिति के कारण कटिहार एक प्रमुख रेलवे और व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में कार्य करता था।
बंगाल का विभाजन:
बंगाल के विभाजन से पहले, कटिहार बंगाल का हिस्सा था। हालाँकि, बंगाल के बिहार, बंगाल और उड़ीसा में विभाजन के बाद, आज का कटिहार जिला बिहार के अधीन आ गया। ब्रिटिश शासन के दौरान, कटिहार जमींदारों और नवाबों के नियंत्रण में आ गया, जिन्होंने किसानों और मजदूरों का शोषण करने के लिए अंग्रेजों के साथ मिलकर काम किया।
स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन:
कटिहार के लोगों ने ब्रिटिश शासन को चुनौती देते हुए स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन में सक्रिय रूप से भाग लिया। भारत की स्वतंत्रता के साथ, सभी भारतीयों की तरह कटिहार के लोगों को भी स्वतंत्रता मिली।
कटिहार जिले का गठन:
पहले कटिहार पूर्णिया जिले का एक अनुमंडल शहर था। हालाँकि, 2 अक्टूबर 1973 को कटिहार को एक स्वतंत्र जिले का दर्जा दिया गया था। इसकी एक समृद्ध विरासत है और मूल जिले पूर्णिया के साथ इसके घनिष्ठ ऐतिहासिक संबंध हैं।
कटिहार की व्युत्पत्ति:
इस जिले का नाम इसके मुख्य शहर से लिया गया है, जिसका नाम संभवतः उत्तर-पूर्व में स्थित एक छोटे से गाँव दिघी-कटिहार से पड़ा है। इस गाँव में एक बड़ा तालाब (दिघी) था जिसे सैनिकों के लिए खोदा गया था जब पूर्णिया के नवाब के सैनिकों ने मुर्शिदाबाद के नवाब की सेना के साथ युद्ध किया था।
कटिहार का राजनीतिक इतिहास
- स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में भूमिका:
- कटिहार भारत के स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन के दौरान गतिविधि का एक महत्वपूर्ण केंद्र था।
- उल्लेखनीय स्वतंत्रता सेनानी:
- अल्हाज अजहर अली: उनके नाम पर अजहरैल नामक एक गाँव का नाम दिया गया।
- ध्रुब कुंडू और उनके पिता डॉ. किशोरी लाल कुंडू।
- नक्षत्र मालाकार: “कोसी बेल्ट के रॉबिन हुड” के रूप में जाने जाते हैं।
- व्यस्त शहीद चौक बाजार चौक का नाम 1942 के भारत छोड़ो आंदोलन के शहीदों की याद में रखा गया है।
- कटिहार लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र:
- पिछले कई वर्षों में कई प्रमुख राजनेताओं द्वारा प्रतिनिधित्व किया गया:
- सीताराम केसरी: अखिल भारतीय कांग्रेस कमेटी (AICC) के पूर्व कोषाध्यक्ष और अध्यक्ष।
- तारिक अनवर: वरिष्ठ नेता और महत्वपूर्ण राजनीतिक व्यक्ति।
- निखिल चौधरी और मोहम्मद यूनुस सलीम: अन्य उल्लेखनीय प्रतिनिधि।
- प्रसिद्ध कश्मीरी राजनेता मुफ्ती मोहम्मद सईद ने 1996 में कटिहार से लोकसभा चुनाव लड़ा था, लेकिन असफल रहे।
- पिछले कई वर्षों में कई प्रमुख राजनेताओं द्वारा प्रतिनिधित्व किया गया:
कटिहार का राजनीतिक इतिहास स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में इसकी सक्रिय भागीदारी और भारत के राजनीतिक परिदृश्य में कई उल्लेखनीय नेताओं द्वारा प्रतिनिधित्व किए जाने वाले निर्वाचन क्षेत्र के रूप में इसके महत्व को दर्शाता है।
जनसांख्यिकी (2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार)
- जनसंख्या:
- कुल जनसंख्या: कटिहार जिले की जनसंख्या 3,071,029 (लगभग 3.07 मिलियन) है, जो ओमान राष्ट्र या यू.एस. राज्य आयोवा के बराबर है।
- रैंकिंग: भारत में 117वाँ स्थान (640 जिलों में से)।
- जनसंख्या घनत्व: 1,004 निवासी प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर (2,600/वर्ग मील)।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि (2001-2011): 28.23% जो महत्वपूर्ण जनसंख्या वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- लिंग अनुपात: प्रति 1,000 पुरुषों पर 916 महिलाएँ, जो लैंगिक असमानता को दर्शाता है।
- साक्षरता दर: साक्षरता दर 53.56% है, जिसमें शहरी और ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों के बीच महत्वपूर्ण असमानताएँ हैं, और ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में शिक्षा तक पहुँच को बेहतर बनाने के लिए प्रयास जारी हैं।
- शहरी जनसंख्या: कुल जनसंख्या का 8.92% शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- धार्मिक संरचना (2011 की जनगणना): यद्यपि ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में मुसलमानों और हिंदुओं का अनुपात बराबर है, लेकिन हिंदू धर्म बहुसंख्यक धर्म है। जिले के पूर्वी क्षेत्र में प्राथमिक आबादी मुस्लिम है।
- हिंदू धर्म: 54.85%
- अनुसूचित जाति: 8.57%
- अनुसूचित जनजाति: 5.86%
- इस्लाम: 44.47%
- अन्य या नहीं बताया गया: 0.68%
- हिंदू धर्म: 54.85%
- भाषाएँ: बोली जाने वाली मुख्य भाषाएँ हिंदी, मैथिली, बंगाली, अंगिका और उर्दू हैं, जो जिले की सांस्कृतिक और भाषाई विविधता को दर्शाती हैं।
- सूरजापुरी: 25.86%, सुरजापुरी बोलने वाले मुख्य रूप से कदवा, आज़मनगर, बरसोई और बलरामपुर ब्लॉक में केंद्रित हैं, जो पश्चिम बंगाल की सीमा से लगे हैं।
- ‘अन्य’ हिंदी: 25.46%
- हिंदी: 19.73%
- बंगाली: 12.04%, बंगाली भाषी अमदाबाद ब्लॉक में लगभग बहुमत में हैं।
- उर्दू: 9.11%
- संथाली: 2.97%
- भोजपुरी: 2.29%
- अन्य: 2.54%
प्रशासन
- मुख्यालय: कटिहार शहर जिला मुख्यालय के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- उपखंड:
- जिले को तीन उपखंडों में विभाजित किया गया है: कटिहार सदर, बारसोई और मनिहारी, जिन्हें आगे 16 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉकों में विभाजित किया गया है।
- प्रत्येक उपखंड का नेतृत्व एक उपखंड मजिस्ट्रेट करता है जो विकास, राजस्व संबंधी कार्यों और कानून व्यवस्था बनाए रखने का प्रभारी होता है।
- ब्लॉक और सर्किल:
- किशनगंज जिले को 16 ब्लॉक और सर्किल में बांटा गया है।
- कटिहार-कटिहार, डंडखोरा, हसनगंज, कोरहा, समेली, फलका, कुर्सेला, बरारी, मनसाही और प्राणपुर
- बारसोई- बारसोई, बलरामपुर, आजमनगर और कदवा
- मनिहारी- मनिहारी और अमदाबाद
- प्रत्येक सर्किल का नेतृत्व एक सर्किल अधिकारी (सीओ) करता है, जबकि प्रत्येक ब्लॉक का नेतृत्व एक ब्लॉक विकास अधिकारी (बीडीओ) करता है।
- हसनगंज ब्लॉक:
- कटिहार जिले का सबसे बड़ा ब्लॉक, ऐतिहासिक रूप से जमींदारी शासन के अधीन।
- यह विशाल भूमि स्वर्गीय श्री जोगेंद्रनारायण रॉय चौधरी के कब्जे में थी।
- समुदाय के लिए योगदान:
- ज़मींदार के पूर्ववर्तियों द्वारा लोगों को भूमि, स्कूल, मंदिर और बाज़ार दान में दिए गए थे।
- वर्तमान समय के वंशज, विशेष रूप से पॉल चौधरी परिवार के पास भूमि का न्यूनतम कब्ज़ा है।
- अन्य प्रमुख ज़मींदारी एस्टेट:
- मनसाही: अपनी प्रभावशाली ज़मींदारी एस्टेट के लिए जाना जाता है, जो कुरसेला और फलका की प्रमुखता के बराबर है।
- हसनगंज ब्लॉक:
- यह समृद्ध ज़मींदारी विरासत कटिहार की प्रमुख एस्टेट के ऐतिहासिक महत्व और सामुदायिक योगदान को उजागर करती है।
- किशनगंज जिले को 16 ब्लॉक और सर्किल में बांटा गया है।
- शासन: कटिहार पूर्णिया डिवीजन का हिस्सा है और बिहार विधान सभा और भारतीय संसद दोनों में इसका प्रतिनिधित्व है।
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: कटिहार
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र: 6
- 63-कटिहार, 64-कदवा, 65-बलरामपुर, 66-प्राणपुर, 67-मनिहारी, 68-बरारी, 69-कोरहा
अर्थव्यवस्था
- पिछड़े जिले की स्थिति:
- पंचायती राज मंत्रालय द्वारा 2006 में भारत के 250 सबसे पिछड़े जिलों में से एक नामित।
- पिछड़े क्षेत्र अनुदान निधि कार्यक्रम (BRGF) के तहत सहायता प्राप्त करता है।
- सामाजिक-आर्थिक स्थितियों में सुधार के लिए 2018 से आकांक्षी जिला कार्यक्रम में शामिल किया गया।
- कृषि: कृषि कटिहार की अर्थव्यवस्था की रीढ़ है।
- जिले में उगाई जाने वाली प्रमुख फसलों में नकदी फसलें (केला, जूट, मक्का), धान, मखाना, गेहूं, चावल (मुख्य फसल), गन्ना और दालें शामिल हैं।
- उपजाऊ जलोढ़ मिट्टी, प्रचुर जल आपूर्ति के साथ मिलकर जिले को बिहार के प्रमुख कृषि केंद्रों में से एक बनाती है।
- जिला हरी सब्जियों का भी अच्छा उत्पादक है, जिसमें आलू, प्याज और फूलगोभी प्रमुख हैं।
- 2018 से, यह भारत सरकार के आकांक्षी जिला कार्यक्रम का हिस्सा रहा है, जिसका उद्देश्य इसके सामाजिक-आर्थिक मापदंडों में सुधार करना है।
- कटिहार 2022 में बिहार का सबसे बड़ा मक्का उत्पादक जिला है।
- उभरता हुआ उद्योग: मखाना फोड़ी (कच्चे फॉक्सनट्स को खाद्य मखाना में संसाधित करना)।
- नकदी फसलें: केला, जूट, मक्का और मखाना किसानों द्वारा उगाई जाने वाली मुख्य नकदी फसलें हैं।
- व्यापार और वाणिज्य: कटिहार जूट, अनाज और अन्य कृषि उत्पादों के लिए एक प्रमुख व्यापारिक केंद्र है। पश्चिम बंगाल और झारखंड से इसकी निकटता इसके वाणिज्यिक महत्व को बढ़ाती है।
- कपास और साड़ियों के लिए जाना जाने वाला कपड़ा बाजार जीवंत है और आस-पास के जिलों और यहां तक कि नेपाल और बांग्लादेश जैसे देशों को भी आपूर्ति करता है।
- साइकिल ट्रेडिंग कंपनियाँ: कुछ पुरानी साइकिल ट्रेडिंग कंपनियों का टर्नओवर काफी है।
- फार्मास्यूटिकल्स: फार्मास्यूटिकल्स व्यवसाय फल-फूल रहा है, जो उच्च टर्नओवर के साथ स्थानीय अर्थव्यवस्था में योगदान दे रहा है।
- रेलवे अर्थव्यवस्था: कटिहार पूर्वोत्तर क्षेत्र के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण रेलवे केंद्र है, जो जिले की अर्थव्यवस्था में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान देता है।
उभरते उद्योग:
जूट आधारित उद्योग और कृषि प्रसंस्करण इकाइयाँ बढ़ रही हैं, हालाँकि बड़े पैमाने पर औद्योगीकरण अभी भी सीमित है।
जूट मिलें: कटिहार को ऐतिहासिक रूप से बिहार की “जूट राजधानी” के रूप में जाना जाता था। कटिहार में कभी दो प्रमुख जूट मिलें हुआ करती थीं, जिन्हें पुराना मिल और नया मिल के नाम से जाना जाता था, जिसने शहर की पहचान को आकार दिया। दुर्भाग्य से, ये मिलें लंबे समय से बंद हैं।
- पुरानी जूट मिल (सनबायो मैन्युफैक्चरिंग प्राइवेट लिमिटेड):
- 35 एकड़ में फैली हुई है।
- 2001 से गोविंद शारदा की सनबायो मैन्युफैक्चरिंग द्वारा संचालित।
- अधिकतम उत्पादन: 100 टन/दिन; वर्तमान क्षमता (2020): 200 श्रमिकों के साथ 10 टन/दिन।
- नई जूट मिल (आरबीएचएम जूट मिल):
- 1935 में स्थापित, 53.39 एकड़ में फैली हुई।
- 1977 में बंद, 1980 में एनजेएमसी के तहत फिर से खोली गई, और 2004 में फिर से बंद हो गई।
- 2014 में पीपीपी मॉडल के तहत कुछ समय के लिए फिर से खोली गई, लेकिन नीति आयोग की सिफारिश के आधार पर एनजेएमसी के बंद होने के बाद 2016 में परिचालन बंद कर दिया गया।
- आटा मिलें: इस क्षेत्र में दो आटा मिलें संचालित होती हैं।
- कृषि आधारित उद्योग:
- टिंगाछिया में कृषि उत्पाद बनाने वाली इकाइयाँ हैं।
- इस क्षेत्र में चावल उद्योग फल-फूल रहा है।
- मखाना उत्पादन: मखाना फोड़ी, जहाँ कच्चे मखाना को खाद्य मखाना में संसाधित किया जाता है, तेजी से बढ़ रहा है।
कटिहार की अर्थव्यवस्था मुख्य रूप से अपने कृषि आधार पर निर्भर करती है, जिसमें सीमित औद्योगिक गतिविधि मुख्य रूप से कृषि-प्रसंस्करण और एक बार संपन्न जूट क्षेत्र में केंद्रित है। जिला अपने सामाजिक-आर्थिक प्रोफ़ाइल को ऊपर उठाने के उद्देश्य से विकास कार्यक्रमों के लिए एक केंद्र बिंदु बना हुआ है।
शिक्षा
कटिहार ने शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में उल्लेखनीय प्रगति की है, हालांकि ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अभी भी पहुंच और बुनियादी ढांचे में चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है:
- कटिहार मेडिकल कॉलेज: गुणवत्तापूर्ण शिक्षा और स्वास्थ्य सेवाएं प्रदान करने वाला एक प्रसिद्ध चिकित्सा संस्थान।
- स्कूल और कॉलेज: जिले में बीएन मंडल विश्वविद्यालय से संबद्ध कई सरकारी और निजी स्कूल और कॉलेज हैं।
- व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण: स्थानीय आबादी की जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए कौशल विकास और व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करने वाले संस्थान उभर रहे हैं।
संस्कृति
- त्यौहार: छठ पूजा, दुर्गा पूजा, ईद और होली जैसे त्यौहार बहुत उत्साह के साथ मनाए जाते हैं, जो जिले की धार्मिक और सांस्कृतिक सद्भाव को दर्शाते हैं।
- व्यंजन: कटिहार के व्यंजनों में पारंपरिक बिहारी और बंगाली व्यंजन, जैसे लिट्टी चोखा, पंता भात और रसगुल्ला और संदेश जैसी मिठाइयाँ शामिल हैं।
- कला और संगीत: यह जिला लोक संगीत, मैथिली कला और पारंपरिक नृत्यों के माध्यम से मिथिला संस्कृति में योगदान देता है।
पर्यटन
कटिहार प्राकृतिक, ऐतिहासिक और धार्मिक आकर्षणों का मिश्रण प्रदान करता है:
- मनिहारी घाट:
- कटिहार के नज़दीक एक शहर, मनिहारी, ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक काल के दौरान एक वाणिज्यिक केंद्र के रूप में अपनी भूमिका के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। मनिहारी घाट गंगा नदी की नाव की सवारी के लिए एक लोकप्रिय स्थान है।
- गंगा नदी के तट पर एक सुंदर स्थान, जो अपने मनोरम दृश्यों और साहिबगंज (झारखंड) के लिए एक पारगमन बिंदु के रूप में जाना जाता है।
- मधुबन मंदिर: भगवान शिव को समर्पित एक लोकप्रिय धार्मिक स्थल, जो आस-पास के क्षेत्रों से भक्तों को आकर्षित करता है।
- रेलवे विरासत: कटिहार रेलवे जंक्शन, सबसे पुराने और व्यस्ततम रेलवे स्टेशनों में से एक, भारतीय रेलवे के लिए ऐतिहासिक महत्व रखता है।
- गांधी घर: स्थानीय महत्व का एक ऐतिहासिक स्थल।
- बारी दुर्गा मंदिर: देवी दुर्गा को समर्पित एक प्रतिष्ठित हिंदू मंदिर।
- भैरव नाथ मंदिर: भगवान शिव को समर्पित एक मंदिर, जो भक्तों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
- पीर मजार: आध्यात्मिक साधकों के लिए एक प्रमुख धार्मिक स्थल।
- गोरखानाथ मंदिर: भगवान गोरखानाथ को समर्पित एक मंदिर, जो पूजा और अनुष्ठानों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
- गौरी शंकर मंदिर: भगवान शिव और देवी पार्वती को समर्पित एक मंदिर।
- त्रिमोहिनी संगम: तीन नदियों का संगम, एक शांत और मनोरम स्थान प्रदान करता है।
गोगाबिल झील:
- स्थान: गोगाबिल झील बिहार के कटिहार जिले के अमदाबाद ब्लॉक में स्थित है।
- क्षेत्र: झील 217.99 एकड़ क्षेत्र में फैली हुई है, जिसमें से 143.84 एकड़ पूरी तरह से झील क्षेत्र है, जो बिहार सरकार के थाना संख्या 252 और मौजा जंगलताल के अंतर्गत आता है।
- संपर्क:
- निकटतम हवाई अड्डा: बागडोगरा, कटिहार जिला मुख्यालय से 85 किमी दूर।
- पटना से दूरी: लगभग 350 किमी।
- निकटतम रेलवे स्टेशन:
- मनिहारी (निकट)
- कटिहार जंक्शन, 25 किमी दूर।
- झील एक राज्य राजमार्ग द्वारा जिला शहर से जुड़ी हुई है।
- राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग संख्या 31 झील के उत्तर-पूर्व की ओर लगभग 40 किमी दूर स्थित है।
गुरु तेग बहादुर साहिब ऐतिहासिक गुरुद्वारा:
- स्थान: बिहार के कटिहार जिले के बरारी ब्लॉक के लक्ष्मीपुर पंचायत में स्थित है।
- दूरी: कटिहार जिला मुख्यालय से लगभग 40 किमी दूर।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- गुरुद्वारा सिखों के नौवें गुरु, गुरु तेग बहादुर साहिब से जुड़ा हुआ है।
- गुरु तेग बहादुर 1670 ई. में असम से पटना लौटते समय यहाँ रुके थे (पहले इसे कांत नगर के नाम से जाना जाता था)।
- उनके प्रभाव के कारण गाँव के लोग सिख धर्म के अनुयायी बन गए।
- धार्मिक महत्व:
- गुरुद्वारे में धार्मिक महत्व की प्राचीन लिपियाँ और दस्तावेज़ हैं।
- गुरु ग्रंथ साहिब की एक पुरानी पुस्तक यहाँ संरक्षित है।
- पर्यटन और तीर्थयात्रा: गुरु तेग बहादुर साहिब और इसके ऐतिहासिक अवशेषों से जुड़े होने के कारण कई श्रद्धालु और पर्यटक गुरुद्वारे में आते हैं।
परिवहन
- रेलवे: बरौनी-गुवाहाटी मार्ग पर श्रेणी A1 स्टेशन, कटिहार जंक्शन रेलवे स्टेशन, बिहार के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण रेलवे केंद्रों में से एक है, जो जिले को कोलकाता, दिल्ली, गुवाहाटी और पटना जैसे प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ता है।
- सड़क मार्ग: NH-31 और NH-81 जैसे राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग कटिहार से होकर गुजरते हैं, जो अन्य जिलों और राज्यों से संपर्क सुनिश्चित करते हैं।
- जलमार्ग: गंगा नदी अंतर्देशीय जल परिवहन के अवसर प्रदान करती है, विशेष रूप से मनिहारी घाट पर।
- वायुमार्ग: निकटतम हवाई अड्डा पश्चिम बंगाल में बागडोगरा हवाई अड्डा (लगभग 160 किमी दूर) है, भविष्य में बेहतर हवाई संपर्क की योजना है।
चुनौतियाँ
- बाढ़: कोसी और महानंदा जैसी नदियों के कारण बार-बार आने वाली बाढ़ से कृषि, परिवहन और आजीविका बाधित होती है।
- बुनियादी ढाँचा: ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में स्वास्थ्य सेवा, शिक्षा और सड़क संपर्क में चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है।
- बेरोज़गारी: सीमित औद्योगिक विकास रोजगार के लिए दूसरे राज्यों में पलायन की ओर ले जाता है।
निष्कर्ष
कटिहार बिहार में अत्यधिक आर्थिक, सांस्कृतिक और ऐतिहासिक महत्व का जिला है। रेलवे और व्यापार केंद्र के रूप में इसकी रणनीतिक स्थिति, उपजाऊ कृषि भूमि के साथ मिलकर इसे राज्य का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा बनाती है। बाढ़ और अविकसित बुनियादी ढांचे जैसी चुनौतियों के बावजूद, कटिहार में कृषि, व्यापार और औद्योगिक विकास में वृद्धि की महत्वपूर्ण संभावना है। केंद्रित निवेश और आपदा प्रबंधन प्रयासों के साथ, कटिहार इस क्षेत्र में एक प्रमुख आर्थिक और सांस्कृतिक केंद्र के रूप में उभर सकता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

2 thoughts on “Katihar District: A Land with Special Historical Importance”