Rohtas District: An Overview
Rohtas District is one of the most historically and geographically significant among 38-districts of Bihar state, India. It is known for its rich historical heritage, natural landscapes, and cultural diversity. The district is home to the famous Rohtas Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and is known for its contribution to Indian history, agriculture, and tourism.
Spanning an area of 3,847.82 square kilometers (1,485.65 square miles), Rohtas is accounting for 4.3% of Bihar’s total land area, making it the 4th largest district in the state. Rohtas lies at 24°30” to 25°20” North latitude and 83°14” to 83°20” East longitude, and shares borders with Bhojpur District and Buxar District to the North, Garhwa District of Jharkhand to the South, Aurangabad District to the East and Kaimur District (Bhabua) to the West. The district’s administrative headquarters is located at Sasaram Town. The district is part of the Patna Division.
With a population of 2,959,918 and a population density of 763 persons per km², Rohtas district has the highest literacy rate among all 38-districts in Bihar, standing at 73.37% as per the 2011 Census. It also has one of the largest forest covers among Bihar’s districts and is a part of the Red Corridor.
The district was created on 10th November, 1972 when the former Shahabad district was divided into Bhojpur and Rohtas. Rohtas district originally comprised Sasaram and Bhabua sub-divisions of the former Shahabad district. In 1991, Bhabua was separated to form Kaimur district, officially renamed in 1994. The major languages spoken here are Bhojpuri, Hindi, and English.
History of Rohtas
Rohtas has a rich and fascinating history, dating back to prehistoric times when the Bhars, Cheers, and Oraons were the primary inhabitants of the plateau region. According to legend, the Kherwars were the original settlers in the hilly tracts near Rohtas, while the Oraons claim to have ruled the area between Rohtas and Patna.
The district is also linked to several mythological and historical figures. Local folklore connects King Sahasrabahu with Sasaram, the district headquarters. It is believed that he fought a fierce battle against Saint Parashuram, the legendary Brahmin protector, in which Sahasrabahu was slain. The name Sasaram is said to have been derived from Sahasrabahu and Parashuram.
Another legend attributes the name Rohtas to Rohitashwa, son of King Harishchandra, who was renowned for his piety and truthfulness.
Ancient History
Sasaram, the district headquarters, has been an important historical and archaeological center since ancient times. Excavations and discoveries suggest that Sasaram has been a hub of developed culture since the Mesolithic Age. Several Neolithic settlements have been found in locations like Senuvargarh, Sakasgarh, Kotagarh, and Anant Tila, indicating early human activity in agriculture and animal husbandry.
The Balkand of Valmiki Ramayana mentions that Siddhashram, an ancient hermitage, was located in Sasaram at the foothills of Kaimur. It is believed that Lord Vishnu meditated here for a thousand years, and his Vamana avatar was born to Maharishi Kashyap’s wife, Mata Aditi, making this one of the oldest living cities in the world.
Rohtas was a part of the Magadh Empire from the 6th century BCE to the 5th century CE. The presence of the Mauryan Empire in the region is confirmed by Emperor Ashoka’s minor rock edict at Chandan Sahid, near Sasaram. In the 7th century CE, the district came under the rule of Harsha, the ruler of Kannauj.
Medieval History
During the Mauryan period, Emperor Ashoka inscribed his miniature rock edict in Sasaram, marking its significance in ancient Indian history.
The district is best known as the birthplace of Sher Shah Suri, the founder of the Suri dynasty and one of India’s most powerful rulers, played a significant role in Rohtas. His father, Hassan Khan Suri, an Afghan adventurer, received the jagir of Sasaram for his service to Jamal Khan, the governor of Jaunpur. However, the region remained difficult to govern due to loosely held allegiances and independent landlords. Sher Shah’s son, Jalal Khan, later ascended the throne of Delhi as Islam Shah. Other rulers of the Suri dynasty, such as Firoz Shah and Adil Shah, also hailed from this region.
In 1529, Babur invaded Bihar, facing resistance from Sher Shah. In his memoirs, Babur described the superstitions of Hindus regarding the Karmanasa River and mentioned how he swam across the Ganges at Buxar in 1528.
After Babur’s death, Sher Shah re-emerged as a powerful force. In 1537, Mughal emperor Humayun advanced against him, capturing Chunar and Rohtas Garh. However, Humayun later suffered a devastating defeat at Chausa, allowing Sher Shah to ascend the throne of Delhi. The Suri dynasty, which he founded, was short-lived, as the Mughals soon regained control.
Later, Akbar expanded and consolidated the Mughal Empire, bringing Rohtas under its administration.
The district was also home to Hemu (Hemchandra), a Rauniyar Vaishya trader, who became the only non-Muslim emperor of Delhi in medieval India, assuming the title of Vikramaditya.
Over time, the region has been referred to by different names—Siddhashram, Sahsaram, Sasraon, and finally, Sasaram.
British Era and the Freedom Struggle
During the 18th century, the district was shaken by the rebellion of Raja Chait Singh of Banaras, whose rule extended over large parts of Shahabad, including Rohtas and Buxar. Chait Singh revolted against the British, and his forces defeated British troops at Chunar and Ghazipur, briefly threatening British rule in India. However, he was eventually defeated.
In 1857, the district played a role in the Indian Rebellion (First War of Independence). Kunwar Singh, the revolutionary leader from Bhojpur, fought against the British with the support of local forces from Rohtas. The region’s hilly terrain provided a natural refuge for those resisting British rule.
During the Indian freedom movement, Rohtas made significant contributions, with many people participating in non-cooperation and civil disobedience movements.
After India’s independence, Rohtas remained a part of Shahabad district until it was separated and officially became a district on 10th November 1972.
Rohtas is a district of historical, cultural, and geographical significance. From its ancient connections with mythology and early civilizations to its role in medieval Indian history, the district remains an integral part of Bihar’s rich heritage. With its high literacy rate, large forest cover, and unique geography, Rohtas continues to play an important role in the state’s development.
Key Facts About Rohtas District
- Country:
 India
India - State:
 Bihar
Bihar - Division: Patna
- Established: 10th November 1972
- Area: 3,847.82 km2 (1,485.65 sq mi)
- District Headquarters: Sasaram
- District Magistrate: Udita Singh, IAS
- Superintendent of Police: Roshan Kumar, IPS
- Divisional Forest Officer: Manish Kumar Verma, IFS
- Population (2011):
- Total: 2,959,918
- Density: 770/km2 (2,000/sq mi)
- Literacy: 73.37%
- Sex Ratio: 914/1000
- Official Language: Hindi
- No. of Sub-divisions (Tehsils): 3 (Sasaram, Bikramganj, Dehri)
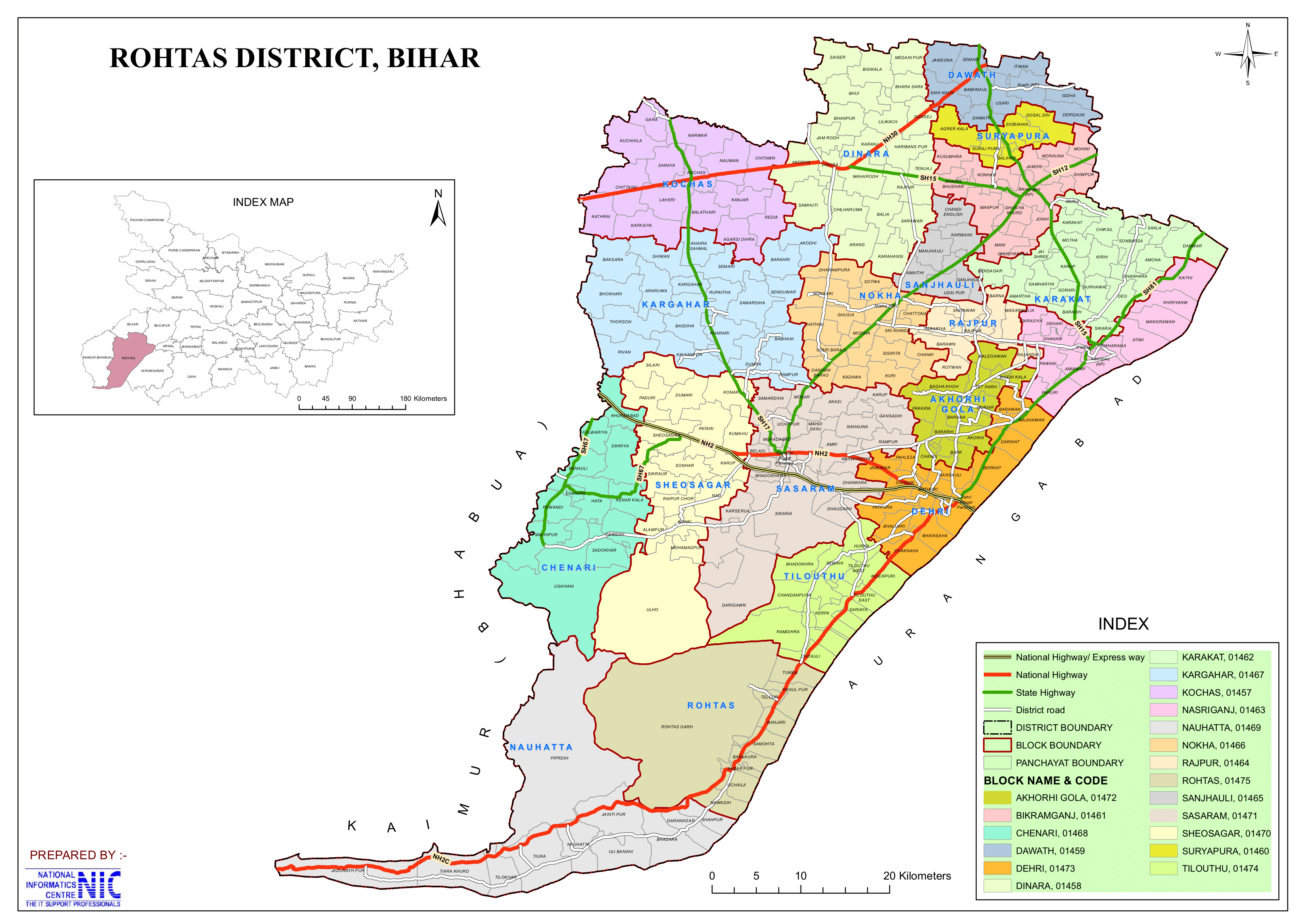
- No. of Blocks/Circles: 19
- Akodhi gola, Bikramganj, Chenari, Dawath, Dehri, Dinara, Karakat, Kargahar, Kochas, Nasriganj, Nauhatta, Nokha, Rajpur, Rohtas, Sanjhouli, Sasaram, Shivsagar, Suryapura, Tilouthu
- Number of Police Stations: 38
- Dehri Mufassil (Indrapuri), Dehri Town, Sasaram Mufassil, Sasaram Town, Sasaram Model Thana, SC/ST Thana (Dehri), Mahila Thana (Dehri), Agrer, Akorhigola, Ayar Kotha, Bikramganj, Chenari, Chutiya, Darihat, Dawath, Dinara, Kachhawan, Karakat, Karghar, Kochas, Nasriganj, Natwar, Nauhatta, Nokha, Rajpur, Rohtas, Sanjhauli, Sheosagar, Suryapura, Tilauthu, Dalimianagar, Yadunathpar, Bhanas, Sidhi, Parsathua, Baddi, Baghela, Dharmpura.
- Gram Panchayats: 226
- No. of Villages: 2072
- Municipal Corporation (Nagar Nigam): 1 (Sasaram)
- Municipal Council (Nagar parishad): 3 (Bikramganj, Dehri, Nokha)
- Nagar panchayat: 7 (Chenari, Dinara, Karakat, Koath, Kochas, Nasriganj, Rohtas)
- Lok Sabha Constituency: Sasaram
- Vidhan Sabha constituencies:
- Chenari (SC), Sasaram, Kargahar, Dinara, Nokha, Dehri, Karakat.
- Key Features:
- Famous for Sher Shah Suri’s Tomb, a fine example of Indo-Islamic architecture.
- The Rohtas Fort, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located here.
- Significance: Known for its historical sites and rich culture.
- Time Zone: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- Head Post Office: Sasaram
- PIN Code:
- Rohtas – 821311, Sasaram – 821115, Bikramganj – 802212, Dehri-on-Sone – 821307
- STD Code:
- Sasaram – 06184, Bikramganj – 06185, Dehri-on-Sone – 06184
- ISO 3166 Code: 06188
- Vehicle Registration: BR-24
- Major Highways: NH-2
- Official Website: rohtas.nic.in
Geography
- Location: South-West Bihar, bordering Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh.
- Bordering Districts:
- North: Bhojpur and Buxar
- South: Garhwa (Jharkhand)
- East: Aurangabad
- West: Kaimur
- Area: Rohtas district covers 3,851 square kilometers (1,487 sq mi), making it the 4th-largest district in Bihar.
- Height from Sea Level: 107.78 Meters
- Rivers:
- Son River – A major tributary of the Ganges.
- Karmanasa River – Important for irrigation.
- Climate:
- Summers (March-June): Hot and dry (temperatures up to 45°C).
- Monsoon (July-September): Moderate to heavy rainfall.
- Winters (December-February): Pleasant and cool (5°C – 20°C).
- The district is geographically divided into two major natural regions:
- Sasaram Plain (North and Northeast)
- A gently sloping alluvial plain with an elevation ranging from 72m in the north to 153m in the south.
- Covers Dinara, Dawath, Bikramganj, Nasriganj, Nokha, and Dehri Blocks, along with parts of Sasaram, Sheosagar, and Rohtas Blocks.
- Scattered woodlands, especially in Sasaram Block.
- Rohtas Plateau (South)
- An eastern flank of the Vindhya Plateau, with an average elevation of 300m.
- Covers parts of Nauhatta, Rohtas, Sheosagar, Sasaram, and Chenari Blocks.
- Characterized by hilly terrain and forests, with streams flowing northward, including the Durgawati, Bajari, Koel, and Sura rivers.
- Less suitable for agriculture due to rocky soil and gravelly terrain.
- Home to natural long grasses like pear grass, kus, and khas khas.
- Sasaram Plain (North and Northeast)
- Soil types include:
- ustalfs, ochrepts, orthents, fluvents, and psamments.
History
Ancient and Medieval Period:
- The region has been associated with Mauryan and Gupta dynasties.
- Rohtas was an important military and administrative center during the Mughal period.
- Sher Shah Suri (1540-1545) used Rohtas Fort as a military base.
British Colonial Era:
- Rohtas was a key region in the 1857 Revolt against British rule.
- It played an important role in the freedom struggle of India.
Post-Independence:
- Rohtas became an independent district in 1972, after being separated from Shahabad district.
Rohtas has a deep historical legacy, from ancient empires like Magadh and Maurya to Sher Shah Suri’s rule and its role in the Indian freedom struggle. Today, it stands as a region of historical and cultural significance in Bihar.
Demographics (As per the 2011 Cencus)
Population:
- Total Population: Rohtas district has a population of approximately 2,959,918 (now estimated at around 3.5 million).
- Males Population: 52.3% (15,47,856)
- Females Population: 47.7% (14,14,737)
- Urban Population: (427709) 14.45% of the total population lives in urban areas.
- Rural Population: (2,532,209) 85.55% of the total population lives in rural areas.
- Population Ranking: 127th in India (out of 640 districts) and 17th in Bihar state.
- Density: 768 persons per square kilometer (1,980/sq mi) (Ranking 34th out of 38 in Bihar).
- Population Growth (2001–2011): 20.22% reflecting significant population increase.
- Sex Ratio: 918 females per 1,000 males, which is similar to State sex ratio (Ranks 22nd out of 38 in Bihar).
Literacy Rate:
- Overall Literacy:
- 73.37% of the total population is literate, the highest among all 38 districts of Bihar and with significant efforts being made to improve education access and quality.
- Gender Disparity:
- Men: 82.88% literacy rate.
- Women: 62.97% literacy rate.
- Urban vs. Rural: Literacy is higher in urban areas compared to rural areas.
- Highest Literacy Area:
- Dehri:
- 77.70% of the district’s total population is literate.
- In the town proper, the literacy rate is 81.2%.
- Dehri:
- Lowest Literacy Area:
- Nauhatta CD Block (entirely rural): Literacy rate is 63.07%.
Religious Composition (2011 Census):
- The majority of the population follows Hinduism, with a significant Muslim community and other communities forming a significant part.
- Hinduism: 89.37%
- Scheduled Castes: 18.57% of the total population.
- Scheduled Tribes: 1.07% of the total population.
- Islam: 10.15%
- Other or not stated: 0.48%
- Hinduism: 89.37%
Languages Spoken:
- Bhojpuri: 87.67%
- Hindi: 7.47%
- Urdu: 4.38%
- Others: 0.48%
Employment Profile:
- Agriculture:
- Majority of the working population is employed in agriculture.
- Cultivators: 23.58% of the workforce (those who own or rent their own land).
- Agricultural Laborers: 43.85% of the workforce (those working on someone else’s land for wages).
- Household Industries: 5.25% of the workforce is engaged in household industries.
- Other Forms of Employment: The remaining 27.33% of the workforce is employed in all other sectors.
Administration
- The district is headed by an IAS officer of the rank of District Magistrate (DM).
- District Administrative Headquarters: Sasaram town (the largest city in the district).
- The district is divided into Sub-divisions or Tehsils, and these Tehsils are further divided into Blocks.
Subdivisions:
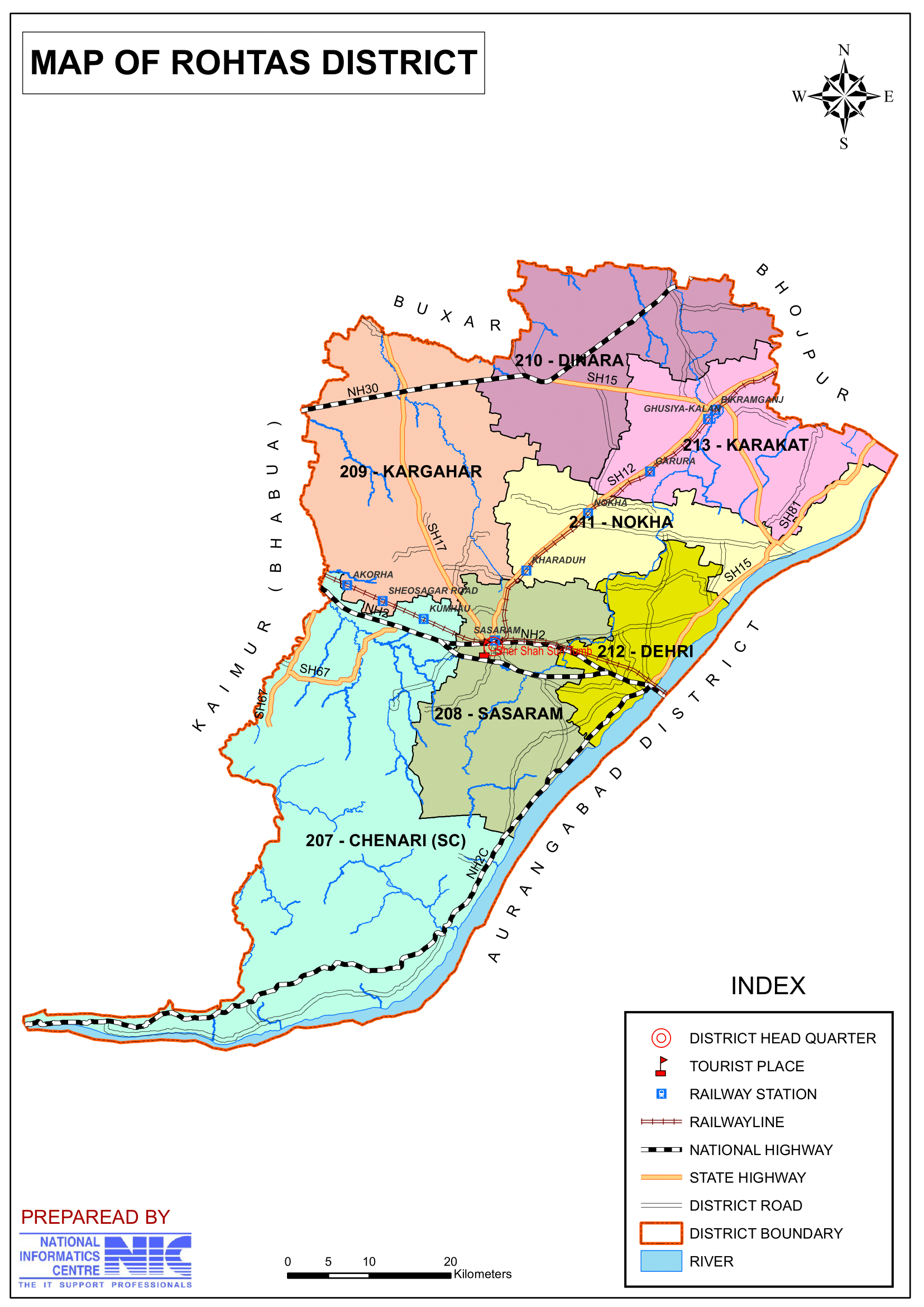
- The district has 3 revenue subdivisions or Tehsils for administrative convenience: Sasaram, Dehri-on-Sone and Bikramganj.
- Each revenue sub-division is headed by a Revenue Divisional Officer (RDO), who functions as the Sub Divisional Magistrate with jurisdiction over that division.
- Each subdivision is led by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM) who is in charge of development, revenue-related tasks, and maintaining law and order.
- Tahsildars, who are administrative officers in the appropriate cadre, assist in managing the sub-divisional offices.
- The sub-divisional offices are structured similarly to the Collectorate, serving as intermediary administrative units.
- Each sub-division consists of several Blocks, and the performance of these blocks is continuously monitored by the respective Divisional Office.
Blocks and Circles:
- Rohtas district comprises 19 administrative Blocks and Circles under 3 subdivisions are:
- Sasaram: Sasaram, Shivsagar, Chenari, Kargahar, Kochas, Nokha
- Dehri-on-Sone: Dehri, Akodhigola, Nauhatta, Rohtas, Tilouthu
- Bikramganj: Bikramganj, Karakat, Nasriganj, Dawath, Rajpur, Sanjhauli, Suryapura, Dinara
- Each block responsible for local governance and development.
- A Circle officer (CO) leads each circle, while a Block Development Officer (BDO) leads each block.
Governance:
- Lok Sabha Constituency:
- Sasaram (one of the key parliamentary constituencies in Bihar).
- Vidhan Sabha Constituencies: The district has 7 Assembly seats.
- 207-Chenari (SC), 208-Sasaram, 209-Kargahar, 210-Dinara, 211-Nokha, 212-Dehri, 213-Karakat
Organization Chart

Overall Roles and responsibilities of the Collectorate:
Plays a pivotal role in district administration and Responsible for maintaining law and order, planning, development, revenue, and disaster management within the district.
- Collector (I.A.S Cadre):
- Head of the District: Acts as the chief executive and District Magistrate.
- Law and Order: Maintains peace and enforces law and order in the district.
- Planning & Development: Oversees planning and development projects.
- Administration of Scheduled/Agency Areas: Manages areas designated as scheduled or under special agency administration.
- Election Management & Arms Licensing: Handles general elections and oversees the licensing of arms.
- Additional Collector (B.A.S Cadre):
- Revenue Administration: Runs revenue-related functions across various district departments.
- Additional District Magistrate: Shares responsibilities in maintaining law and order and administering civil functions.
- Key Responsibilities: Oversees civil supplies, land matters, management of mines and minerals, and supervises village officers.
- District Development Commissioner (B.A.S Cadre):
- Developmental Activities: Manages and coordinates various developmental initiatives across the district.
- Key Departments Overseen:
- District Medical and Health Department.
- Social Welfare Department.
- BC (Backward Classes) Welfare and BC Corporation.
- Disabled Welfare.
- Housing and other related departments.
- Additional Collector (Disaster) (B.A.S Cadre):
- Disaster Management: Focuses on planning and coordinating activities related to disaster management.
- Key Responsibilities: Oversees the disaster section and other related developmental departments during emergencies.
These roles collectively ensure that the district is well-governed, with a focus on maintaining law and order, efficient revenue collection, effective disaster management, and sustainable development across various sectors.
Economy
Agriculture:
- Primary occupation of the district.
- Major crops:
- Wheat, rice, maize, pulses, and oilseeds.
- Referred to as the “Rice Bowl of Bihar” due to its significant rice production.
- Fruits like mangoes, guavas, and litchis are also grown.
- Irrigation System: Son Canal System provides water for agriculture.
Industries & Minerals:
- Industrial History:
- Dalmianagar was once one of India’s major industrial cities until 1980.
- Historically housed factories producing sugar, vegetable oil, cement, paper, and chemicals (Rohtas Industries).
- These industries are now closed.
- Cement industry – Rohtas has one of Bihar’s largest cement manufacturing units.
- Stone mining & quarrying – The district has rich limestone deposits.
- Brick-making industry – One of the largest in Bihar.
- Small-scale industries like food processing, pottery, and handicrafts.
Government Classification and Support:
- In 2006, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj named Rohtas one of the 250 most backward districts out of 640 in India.
- It is one of the 36 districts in Bihar receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).
Education
Notable Educational Institutions:
- Shri Shankar College, Sasaram – One of the oldest institutions.
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Rohtas – A reputed CBSE school.
- Government Polytechnic College, Sasaram.
- Veer Kunwar Singh University-affiliated colleges.
- S P Jain College, Sasaram, Rohtas
- Sri Sankar College, Takia, Sasaram
Challenges:
- Need for more higher education institutions – Many students migrate to Patna and Varanasi for advanced studies.
- Limited technical and professional courses.
Culture & Festivals
Festivals:
- Chhath Puja:
- The biggest festival in Rohtas, celebrated grandly on the banks of the Sone River.
- A major Hindu festival dedicated to the Sun God (Surya), celebrated with immense faith.
- Held twice a year:
- In Chaitra (summer)
- In Kartik (beginning of winter)
- Devotees observe rigorous rituals including holy bathing, fasting, and offering water (arghya) to the setting and rising sun.
- Makar Sankranti (Tila Sankranti):
- Celebrated at the beginning of summer and marks the harvest season.
- Considered auspicious as it symbolizes the commencement of a new year in Indian culture.
- Holi:
- One of the biggest and most colorful festivals in the district.
- Celebrated with great enthusiasm, where people engage in joyous, vibrant festivities that light up the atmosphere.
- Durga Puja, Diwali, Janamashtami, Kali Pooja, Sarswati Pooja, Nag Panchemi, Shiv Ratri, Bakarid, Eid and Muharram are also widely celebrated.
- Bhojpuri Folk songs and dances are a major part of the cultural identity.
Cuisines:
- Traditional Staples:
- Daily meals typically include dishes such as sabzi (vegetable curry), roti (flatbread), dal (lentils), and bhaji (stir-fried vegetables).
- Signature Dishes:
- Litti Chokha: A popular Bihari delicacy made with roasted wheat balls (litti) served with mashed vegetables (chokha).
- Kadhi: A yogurt-based curry often spiced with traditional seasonings.
- Jhal Moori: A spicy snack mix, beloved by locals.
- Roasted gram flour, used in various dishes and beverages like Sattu Paratha, Dal Pitha and Dal Puri.
- Kachauri-Sabzi are commonly eaten.
- Sweets & Desserts:
- Renowned for its mouthwatering sweets made with pure desi ghee, which are available in local sweet shops and are commonly prepared at home during ceremonial occasions.
- Sweets like Khaja, Balushahi, Tilkut, Khurma, Thekua and Malpua are famous.
Costumes:
- Traditional Male Attire:
- Dhotis, kurtas, and pajamas are commonly worn.
- Young men may also be seen in shirts and trousers, blending traditional and modern styles.
- Traditional Female Attire:
- Women traditionally wear Ghaghara (long skirts), choli (blouses) and Saree, reflecting the rich Hindu cultural heritage.
- Attire of the Muslim Community:
- Men: Typically dress in kurta and pajama.
- Women: Often wear burkas, following traditional Muslim attire.
Religions:
- Religious Composition:
- The district is predominantly Hindu, but it also has a significant Muslim community.
- Tribal communities also reside under the district, with many adhering to their own indigenous religious practices.
- Cultural Integration:
- The region’s cultural landscape is a vibrant mix of various religious traditions, with communities having coexisted for many decades.
- Social Harmony:
- Despite the diversity, there is a strong sense of social unity and hospitality, which leaves a lasting impression on visitors.
- Heritage and Tradition:
- The rich tapestry of religious traditions contributes to a unique cultural heritage, which is evident in festivals, rituals, and everyday practices.
Tourism & Historical Places
Rohtas is one of Bihar’s top tourist destinations, known for its forts, temples, and natural beauty.
Major Attractions:
- Rohtas Fort (UNESCO-listed) – A 16th-century fort built by Sher Shah Suri, known for its massive walls, gates, and water tanks.
- Sher Shah Suri Tomb, Sasaram – The mausoleum of Sher Shah Suri, a stunning architectural wonder.
- Tara Chandi Temple – A famous Hindu pilgrimage site.
- Manjhar Kund & Dhua Kund – Waterfalls known for their scenic beauty and annual fairs.
- Gupta Dham Cave Temple – A Shiva temple inside a cave.
- Indrapuri Barrage – A large dam on the Son River, offering scenic views.
- Tutla Bhawani Waterfall & Temple – A natural and religious site.
1. Gupta Dham:
- Location:
- A natural cave situated in a valley of the Kaimur hill.
- Key Feature:
- Contains a small rock formed of lime deposits in the shape of a Shivling, known as Gupteshwar Mahadev.
- Festivals:
- A fair is held during Shivratri and Basant Panchami, attracting large crowds.
2. Bandu Shivling:
- Location:
- Approximately 0.5 km south-west of Bandu village, south of Rohtas hill.
- Key Feature:
- A Shivling is established on a platform built on a huge boulder in the stream of the Sone River.
- Legend:
- According to local legends, the Shivling was established by Lankapati Ravana and is thus named Dashshishanath.
3. Chaurasan Temple:
- Location:
- Situated near Rohtasgarh Fort.
- Accessibility:
- Approximately 2 hours from Rohtas block headquarters.
- Features:
- The temple, dedicated to Lord Shiva, is reached by climbing 84 stairs – hence the name “Chaurasan”.
4. Maa Tara Chandi Temple:
- Location:
- Situated in Sasaram in a natural cave on the Kaimur hill of the Vindhya mountain range.
- Key Features:
- Houses an idol of Maa Tara with four hands:
- Right Hand: Holds a knife and a scissor.
- Left Hand: Holds a hood and a lotus.
- The left foot is positioned forward on a dead body.
- Contains a significant inscription by Mahanayak Pratap Dhavaldev of the Kharwar dynasty (12th century), written by his son Shatrudhan.
- The temple complex includes statues of Maa Tara, Surya, and a fragmentary statue of Agni, dating from the late Gupta or later Gupta period.
- Houses an idol of Maa Tara with four hands:
- Cultural Impact:
- The inscription indicates the historical spread of Tarachandi Devi’s fame during that period.
5. Tutla Bhawani Temple:
- Location:
- Situated in a picturesque valley about 8 km south-west of Tilouthu.
- Scenic Features:
- The valley, approximately 1 mile long, is lush and green with a waterfall and the Kachhuar River.
- The valley width varies from about 300 meters (east) to 50 meters (west), where a waterfall falls from approximately 180 feet.
- Temple Details:
- A ladder leads to a platform on the south side within the waterfall where an idol of Goddess Jagaddhatri Mahismardini Durga is installed.
- A rock inscription, divided into three parts, is found near the statue, credited to Nayak Pratap Dhaval Dev and dated to 1 April 1158 A.D..
- A small temple dedicated to Tutla Bhawani has been constructed at this site.
- Eco-Tourism Development:
- Recently developed as an eco-tourism destination by the forest department.
- Tourist facilities include road access, a swing bridge, and e-rickshaw services.
6. Gurudwara Chacha Phagumal:
- Historical Significance:
- Named after the house of Uncle Fagumal, where Shri Guruteg Bahadur Ji Maharaj and his wife Mata Gujari Devi visited in 1666 AD.
- Associated with the journey of the Sikh Gurus, as the tenth Guru, Sri Guru Gobind Singh, was in the womb of Mata Gujari Devi at that time.
- Pilgrimage:
- Guru Gobind Singh’s 21-day stay at Uncle Fagumal’s house turned the site into a major pilgrimage destination for Sikhs.
- Current Status:
- A Gurudwara has been built at the site, known as Chacha Fagumal Gurudwara.
7. Gurudwara Taksal Sanghat:
- Legend:
- During the journey to Uncle Fagumal’s house, Guru Gobind Singh’s horse got stuck at a spot owned by Bhai Achal Singh and Jivo Mai.
- Guru Gobind Singh declared the spot holy, inspiring the establishment of a Gurudwara.
- Establishment:
- The site was donated by Jivo Mai in V. Samvat 1723.
- The resulting Gurudwara is famous as Taksal Sanghat.
8. Dhuwan Kund:
- Location:
- Situated on Kaimur Hill, approximately 15 km from Sasaram.
- Natural Attraction:
- Features hot water springs and a waterfall that create mesmerizing views during sunrise and sunset.
- Healing Reputation:
- Believed to have sacred healing powers, drawing Hindu devotees for ritual baths.
9. Manjhar Kund:
- Location:
- Located around 15 km from Sasaram, reachable within 30 minutes from the base of the hill.
- Tourist Appeal:
- A popular picnic spot attracting thousands of locals and tourists, especially during the monsoon season.
- Scenic Beauty:
- Known for its tranquil environment and lush surroundings.
10. Dhoop Ghadi:
- Historical Background:
- A British-made clock established on Anicut Road, Dehri in 1871.
- Unique Feature:
- The only clock in the region that shows time by the sunlight (shadow).
- Design:
- Installed on a rock platform, it features both Hindi and Roman numerals.
- Original Use:
- Primarily used by workers of the irrigation department.
11. Megalithic Tombs:
- Discovery & Significance:
- First archaeological exploration of megalithic cultural sites in the Kaimur hills of Rohtas district.
- Considered a milestone in the archaeology of Bihar and India.
- Cultural Context:
- Inhabited since ancient times by various tribes:
- Nishad-vanshi tribes: Kharwar, Munda, and Santhal.
- Dravidian-origin Oraon tribe.
- These tribes have a long-standing tradition of megalithic burial that continues even today.
- Inhabited since ancient times by various tribes:
- Key Findings:
- Sangora Tombs:
- Cairn circles (Sangora Samadhis) discovered at several sites.
- Stone Pillars (Menhir):
- Two pairs of stone pillars discovered at different sites; some with a small chuchuk (cap) on top.
- Rohtasgarh Sites:
- Five megalithic sites discovered, including numerous Sangora Samadhis.
- Hurmeta Site (Nauhatta Block):
- Features eight small and large stone pillars.
- Originally, more than 30 stone pillars stood here before many were uprooted and repurposed.
- Sangora Tombs:
- Dating:
- The megalithic tombs are estimated to date from 1500 BC to 500 BC.
12. Sher Shah Suri Tomb:
- Location & Setting:
- Located in Sasaram, Bihar, India.
- The tomb stands in the middle of a huge, nearly square artificial pond spread over 22 acres.
- Pond dimensions: approximately 1130 feet (east-west) and 865 feet (north-south).
- Access to the tomb requires passing through a small domed tomb of Sher Shah’s concierge located to the north of the pond.
- Architectural Features:
- Built using red sandstone.
- Example of Indo-Islamic architecture, designed by architect Mir Muhammad Aliwal Khan.
- Constructed between 1540 and 1545 AD.
- Height: The main mausoleum stands at 122 feet.
- Plan & Structure:
- Built on an octagonal plan.
- Topped by a large dome spanning 22 meters.
- Surrounded by ornamental domed kiosks and chhatris at each corner.
- Plinth & Surroundings:
- Set on a square stone plinth with stone banks and stepped moorings on all sides.
- Connected to the mainland by a wide stone bridge.
- Additional Detail:
- Turrets built on all three storeys enhance its grandeur.
- Often referred to as the “second Taj Mahal of India”, and considered even superior by some, such as Kanindham.
- Historical Significance:
- Built in memory of Emperor Sher Shah Suri, the Pathan ruler from Bihar who defeated the Mughal Empire and founded the Suri Empire.
- Sher Shah Suri died on 13 May 1545 AD due to an accidental gunpowder explosion in the fort of Kalinjar.
- The tomb was constructed during Sher Shah’s lifetime as well as during the reign of his son Islam Shah.
- An inscription dates its completion to 16 August 1545 AD, three months after Sher Shah’s death.
13. Rohtas Garh Fort:
- Overview & Historical Significance:
- One of the largest forts in India—and in the world—spanning a radius of 26 miles.
- Named after Rohtas, established by Rohitashva, the son of Satyuga Suryavanshi King Satyaharishchandra.
- The fort’s vast expanse and strategic design highlight its historical military importance.
- Access & Defense:
- Accessed via four ancient routes (ghats) that provided strategic defense:
- Mendara Ghat (East)
- Kathoutia Ghat (West)
- Ghoda Ghat (North)
- Raj Ghat (South)
- These ghats ensured that enemies could not easily approach the fort, as each gate was fortified.
- Accessed via four ancient routes (ghats) that provided strategic defense:
- Key Structures & Attractions Within the Fort:
- Religious and Royal Structures:
- Rohitasan or Chaurasan Stairway Temple – an ancient temple reached by climbing 84 stairs.
- Parvati Temple – a significant religious site.
- Gate Structures:
- Kathoutia Ghat – one of the key entrance points.
- Singh Darwaza, Lal Darwaza, and Ghazi Darwaza – majestic gateways.
- Palatial and Administrative Buildings:
- Raj Bhavan or Mahal Sarai
- Qiladar Mahal
- Panch Mahal
- Hathiyapol and Phool Mahal
- Baradari
- Raja’s Palace and Takhtpadshahi
- Khanbagh and Zanana Palace (Queen’s Palace)
- Additional Notable Sites:
- Nach Ghar – a traditional assembly area.
- Sher Shahi Mosque – an example of Indo-Islamic architecture within the fort.
- Habs Khan’s Tomb, Mosque, and Madrasa – historic religious structures.
- Ganesh Temple
- Shaaki Sultan’s Tomb
- Religious and Royal Structures:
- Cultural Importance:
- The fort’s layout, with its strategically placed ghats and multiple structures, reflects the rich architectural and cultural heritage of the region.
- It stands as a testament to the fortifications and urban planning of ancient times, offering visitors a glimpse into a glorious past.
14. Sher Garh Fort:
- Location & Setting:
- Situated in an area of six square miles.
- Located on a hill about 800 feet high in the Kaimur Range.
- Approximately 20 miles southwest of Sasaram.
- Historical Background:
- Originally known as Bhurkunda, home to the Kharwar kings.
- Later came under the control of the Suris when Hasan Khan Sur acquired the jagir of Sasaram.
- Eventually, the fort became associated with Sher Shah, giving it the name Sher Garh.
- Key Features & Structures:
- Singhdwara (Lion Gate):
- A huge and grand gate built on top of the impenetrable ramparts.
- Ramparts:
- Massive, impenetrable ramparts that cling to the hill, clearly visible from below.
- Surrounding Landscape:
- Another hill is visible in front.
- The Durgawati River flows sluggishly through the middle.
- The northern side offers picturesque views of valleys, hills, greenery, and the Durgawati Reservoir Project.
- Interior and Ancillary Structures:
- Rani Pokhara
- Guards Hall
- An underground circular well
- Zanana Mahal (Diwan-E-Khas)
- Several underground rooms
- Singhdwara (Lion Gate):
- Scenic & Cultural Value:
- The fort and its surroundings provide a unique, shaded valley and stunning natural vistas.
15. Karamchat Dam:
- Location & Tourism:
- Located near Chenari in Rohtas district, about 35-km from Sasaram.
- A popular tourist destination, offering mesmerizing scenic views during sunrise and sunset.
- Project Background:
- Initiated as part of the Durgavati Reservoir Project after the severe famine in 1966 to irrigate unirrigated plains of Rohtas.
- Inspected and approved by Agriculture Minister AR Kidwai and Irrigation Minister K.L.Rao.
- Foundation stone laid on 10 June 1976 by Union Agriculture Minister Babu Jagjivan Ram.
- A high-level committee led by Irrigation Minister Sachchidanand Singh cleared obstacles in 1977.
- Faced delays until December 2011 when the Supreme Court granted permission, and work resumed in early 2012.
- Approximately Rs 1064 crore was spent by 2014.
- Inaugurated on 15 October 2014 by then Chief Minister Jitan Ram Manjhi.
- Dam & Reservoir Specifications:
- Dimensions:
- Height: 46.3 meters.
- Length: 1615.40 meters.
- Water Storage:
- Total capacity: 287.7 million cubic meters.
- Useful storage: 257.5 million cubic meters.
- Submergence area at full reservoir level: 2337 hectares.
- Water Source:
- Rainwater from an area of 627 sq. km in the Kaimur hills.
- Dimensions:
- Irrigation and Canal System:
- Command Areas:
- Gross Command Area (GCA): 40,131 hectares.
- Agriculture Command Area (ACC): 33,467 hectares.
- Canals:
- Two main canals have been constructed on the east and west sides:
- One measures 34.08-km.
- The other measures 22.6-km.
- Two main canals have been constructed on the east and west sides:
- Irrigation Coverage:
- 11,695-hectares in Chenari, Sivasagar, and Sasaram blocks (Rohtas district).
- 5,572-hectares in Rampur, Bhabua, Bhagwanpur, Kudra, Mohania, and Durgavati blocks (Kaimur district).
- An additional 16,200-hectares irrigated by the Kudra Weir canal.
- Command Areas:
- Local Impact & Employment:
- Provided jobs to 184 people affected by the project.
- The project significantly boosts agricultural productivity in the region.
16. Kaimur Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Overview:
- Largest wildlife sanctuary in Bihar, spanning 1,504.96 km² (581.07 sq mi).
- Established in 1979.
- Located in the plateaued landscape of the Kaimur Range, straddling parts of Kaimur and Rohtas districts.
- Forest Types & Natural Features:
- Dominated by various forest types:
- Tropical Dry Mixed Deciduous Forests
- Dry Sal Forests
- Boswellia Forests
- Dry Bamboo Brakes
- Home to numerous seasonal streams and waterfalls; best visited during the monsoon and winter seasons.
- Notable waterfalls include:
- Karkat Waterfall
- Manjhar Kund
- Dhua Kund
- Tutla Bhawani Waterfall
- Geeta Ghat Waterfall
- Kashish Waterfall
- Telhar
- Dominated by various forest types:
- Water Bodies & Infrastructure:
- Contains several dams and lakes, such as:
- Anupam Lake
- Karamchat Dam
- Kohira Dam
- The water source is primarily rainwater from an area in the Kaimur hills.
- Contains several dams and lakes, such as:
- Flora & Fauna:
- Fauna:
- Home to Bengal tigers, Indian leopards, Indian boars, Indian pangolins, sloth bears, sambar deer, Indian muntjacs, four-horned antelopes, chitals, nilgais, and various reptiles, insects, and butterflies.
- Birdlife:
- More than 70 species of resident birds; numbers increase in winter due to migratory birds from Central Asia.
- Common species include peafowl, grey partridge, quail, Malabar pied hornbill, swallow, nightjar, drongo, paradise flycatcher, kingfisher, bulbul, mynas, pigeons, blue jay, owl, falcon, kites, and various eagles.
- Migratory birds include the lesser white-fronted goose, ferruginous duck, Baer’s pochard duck, lesser and greater adjutant storks, black-necked stork, and Asian openbill stork.
- Aquatic Life & Reptiles:
- Fishes are found in Anupam Lake and Kalidah near Rameshwar Kund.
- Common snakes include cobras and kraits; pythons are occasionally spotted.
- Fauna:
- Archaeological & Historical Significance:
- The sanctuary area also hosts historical structures like Rohtasgarh Fort and Shergarh Fort.
- Contains several megaliths, prehistoric rock paintings, and stone inscriptions, highlighting the region’s rich archaeological heritage.
- The Government of Bihar has plans to develop the sanctuary into a Tiger Reserve.
Rock paintings, petroglyphs, and inscriptions:
1. Rock Painting of Barhamsiya Maan:
- Location:
- Situated in Sasaram’s Barahmasiya rock shelter.
- Features:
- Red-colored rock paintings.
- Depicts ten large anthropomorphic figures with outstretched limbs.
- A superimposed image shows a man hunting a reindeer using arrows and bows.
- A dog is shown accompanying the hunter.
2. Rock Painting of Ghorghat Valley Maan:
- Location:
- Found in the Ghorghat valley in Sasaram.
- Features:
- Displays a group of small human figures moving forward on the wall.
- In front of these figures is a drawing of an animal, with its skeleton visible.
- Suggests a scene where people are in pursuit of the animal (likely for a hunt).
3. Rock Painting of Tarvakhal Maan:
- Location:
- Situated on the Kajhiya hill of Rohtasgarh.
- Approximately 150 meters beyond, a smaller hill named “Tarvakhal Man Hill” is found.
- Features:
- The rock shelter shows seating areas (on the northern and southern sides of a ‘dhoke’) where a band or row is formed in the rock.
4. Petroglyph of Hathiya Maan:
- Name Origin:
- Called “Hathiya Maan” due to the carved elephants.
- Location:
- Located in a rock shelter in Sasaram facing southwest.
- Features:
- Contains several carved figures from the historical period.
- Depicts five elephants.
- Features additional carvings:
- Three sets of figures (“sixteen gotias”) used for playing games.
- Two separate engravings associated with the traditional game Chaupad (Chausar).
5. Phulwariya Inscription:
- Location:
- In Phulwaria village, located on top of a hill (~1500 feet high) in the Tilothu block of Rohtas district.
- Historical Importance:
- The village is archaeologically significant due to various ancient evidences.
- Inscription by Pratap Dhaval Dev:
- A document of the Khayarwal dynasty, revealing its complete genealogy.
- Written on 27 March 1169 AD (Thursday) in the Vaishakh month of Vikram Samvat 1225 (twelfth day of Krishna Paksha).
- Language & Script:
- Written in Sanskrit using early Nagari script.
- Content:
- The lower part consists of five lines in bold Sanskrit.
- Mentions the construction of a road on the river and mountain, and the building of steps.
6. Ashokan Miniature Inscription on Chandan Shahid Hill:
- Historical Context:
- Dates back to the reign of the third Mauryan emperor Ashoka (272–232 BC).
- Part of Ashoka’s series of inscriptions intended to spread his Dhamma.
- Location:
- Found on the northern wall of a small cave on Chandan Shaheed (Aashiqpur) hill in Sasaram.
- Located about 30 feet below the hilltop.
- Features:
- Inscription is written in Brahmi script, with language very close to Pali.
- Preserved in 1917 by the Archaeological Conservation Department during British rule.
Transportation
Roadways:
- Road Connectivity:
- Sasaram is well connected via the Grand Trunk Road (NH-2).
- NH-19 and NH-119 pass through Rohtas.
- Bus Services:
- Regular public and private buses run to and from Sasaram.
- Buses connect Sasaram with major cities such as Patna, Ara, Bilaspur, Varanasi, New Delhi, Kolkata, Bokaro, and Jamshedpur.
- Bus Station: Located in the main town area.
Railways:
- Sasaram Junction – Sasaram is located on the Grand Chord Section (Howrah-Gaya-Delhi line) of Indian Railways.
- Major Railway Stations in and near Sasaram:
- Sasaram Junction (SSM)
- Dehri-on-Sone (DOS)
- Bikramganj (XBKJ)
- Regular Trains: Connect Sasaram to major cities across India.
Airways:
- Nearest Airport:
- Gaya International Airport (GAY) – Approximately 98 km from Sasaram.
- Patna Airport (PAT) – Approximately 157 km from Sasaram.
- Varanasi Airport (VNS) – Approximately 120 km from Sasaram.
- Note:
- Patna Airport offers regular flights to major cities and is a good alternative if direct flights to Sasaram are not available.
Notable personality of Rohtas District
1. Jagjivan Ram:
- Basic Information:
- Name: Jagjivan Ram (popularly known as Babuji)
- Lifespan: 5 April 1908 – 6 July 1986
- Role in Indian Independence & Early Career:
- Active independence activist and key figure in the rural labour movement.
- Founded the All India Depressed Classes League in 1935 to fight for Dalit equality.
- Elected to the Bihar Legislative Assembly in 1937.
- Contributions to Government and Policy:
- Became the youngest minister in Jawaharlal Nehru’s interim government in 1946.
- Was a member of the Constituent Assembly of India, ensuring social justice was enshrined in the Constitution.
- Served as Labour Minister in India’s first cabinet.
- Long-Standing Ministerial Roles:
- Held various ministerial portfolios in the Indian National Congress for over 30 years.
- Served as Union Agriculture Minister during two tenures, contributing to the Green Revolution and modernizing Indian agriculture, notably during the 1974 drought.
- Played a pivotal role as Defence Minister during the Indo-Pak War of 1971, which led to the creation of Bangladesh.
- Later served as Deputy Prime Minister of India from January 1979 to July 1979.
- Political Shifts:
- Supported Prime Minister Indira Gandhi during the Emergency (1975–77).
- Left the Congress in 1977, joined the Janata Party alliance (via Congress for Democracy), and later formed Congress (J) in 1981.
- Legacy:
- At the time of his death, he was the last surviving minister of the Interim Government and the last surviving original member of India’s first cabinet.
- Remembered for his dedication to social justice, national development, and the upliftment of marginalized communities.
2. Meira Kumar:
- Basic Information:
- Born: 31 March 1945.
- An Indian politician and former diplomat.
- Member of the Indian National Congress.
- Ministerial Roles:
- Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment (2004–2009).
- Briefly served as Minister of Water Resources in 2009.
- Speaker of the Lok Sabha:
- Served as the 15th Speaker of the Lok Sabha from 2009 to 2014.
- Became the first woman to hold the position.
- Parliamentary Career:
- Elected to the 8th, 11th, 12th, and 14th Lok Sabha before her tenure as Speaker.
- Presidential Candidacy:
- Nominated by the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) in 2017 as the joint presidential candidate by the opposition.
- Became the second woman to be nominated for President by a major political block.
- Lost the presidential election to NDA nominee Ram Nath Kovind.
- Her vote share is noted as the third highest for a losing candidate, following Neelam Sanjiva Reddy (1969) and K. Subba Rao (1967).
3. Chhedi Paswan:
- Personal Background:
- Born: 4-February-1956 in Sasaram, Buxar district, Bihar.
- Family: Son of Ramchandra Paswan and Laxmina Devi; married to Premkali Devi with three sons and two daughters.
- Education: Earned an M.A. in Labour and Social Welfare from Patna University.
- Political Career & Party Affiliations:
- Former Roles:
- Member of the 16th Lok Sabha.
- Former member of the Bihar Legislative Assembly.
- Party Affiliations:
- Has been associated with multiple parties over his career:
- Janata Party (and its Charan Singh faction)
- Reunited Janata Dal
- Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
- Nationalist Congress Party (NCP)
- Lalu Prasad Yadav’s RJD
- Nitish Kumar’s JD(U)
- Represented the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) from 2014 to 2024.
- Has been associated with multiple parties over his career:
- Former Roles:
- Electoral Journey:
- Early Elections:
- Lost the 1980 Bihar Vidhan-Sabha-election from Chenari as a member of the Charan Singh faction.
- Elected as an MLA from Chenari (1985–1989) representing Lok Dal; also served as Secretary General of the Yuva-Lok-Dal (1987–1989).
- Lok Sabha Elections:
- Elected to the Lok Sabha from Sasaram in 1989 and 1991 as a Janata-Dal candidate, defeating Meira Kumar on both occasions.
- Lost the 1996 Lok Sabha election to Muni Lall (BJP).
- Also lost Lok Sabha elections from Sasaram in 1998 (as NCP) and 1999 (as BSP).
- Later State Elections:
- Elected to the Bihar-Vidhan-Sabha from Chenari (2000–2005) as a member of RJD.
- Joined JD(U); lost from Mohania in February 2005 but won from Mohania in October 2005 and again in 2010.
- Defection to BJP & Recent Controversy:
- Defected to BJP in 2014 from JD(U) after alleging that party leader Nitish Kumar was acting autocratically.
- Won the Sasaram-Lok-Sabha seat in 2014, but his victory was later set aside by the Patna High Court for failing to disclose pending criminal cases in his affidavit.
- Although the Supreme Court stayed the order, his voting rights were not restored, preventing him from participating in the 2017 presidential elections.
- Early Elections:
4. Murari Prasad Gautam:
- Basic Information:
- Born: 1 March 1980.
- Profession: Teacher.
- Background & Early Career:
- Began his professional journey as a teacher, which helped shape his grassroots approach to public service.
- His background in education influences his focus on community empowerment and local development.
- Political Roles & Contributions:
- Served as Minister of Panchayati Raj in Bihar from 16 August 2022 to 28 January 2024.
- As a member of the Bihar Legislative Assembly representing the Chenari constituency, he worked to enhance rural infrastructure and strengthen local governance.
- During his tenure, he was involved in various initiatives aimed at:
- Decentralization of administrative functions.
- Enhancing transparency and accountability in panchayati institutions.
- Improving the delivery of public services at the grassroots level.
- Party Affiliation & Transition:
- Joined the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) on 28 February 2024, ahead of the general elections.
- This strategic move aligns his extensive experience in local governance with the BJP’s developmental agenda.
- Impact & Future Prospects:
- Known for his grassroots approach and focus on community-driven development.
- His transition from teaching to a key political role is seen as exemplary in the region.
- Expected to play a significant role in shaping rural and agricultural policies within the BJP framework as elections approach.
Challenges & Issues
- Illegal stone mining – Environmental degradation due to unregulated quarrying.
- Need for industrial growth – Lack of large-scale industries and employment opportunities.
- Infrastructure development – Better roads, hospitals, and education facilities needed.
- Floods and water management – Some areas face flooding and drought issues.
- Unemployment – Many youth migrate to other states for jobs.
Conclusion
Rohtas is a historically and geographically significant district of Bihar, rich in heritage, natural beauty, and cultural diversity. The Rohtas Fort and Sher Shah Suri Tomb make it one of Bihar’s top tourist attractions. With better industrial development, education, and infrastructure, Rohtas has the potential to become a major economic and tourism hub in the state.
Would you like more details about any specific Topics on Bihar? Comment Below 😊
रोहतास जिला: किलों और प्रकृति का एक साथ अस्तित्व
अवलोकन
रोहतास जिला भारत के बिहार राज्य के 38-जिलों में से सबसे ऐतिहासिक और भौगोलिक दृष्टि से महत्वपूर्ण है। यह अपनी समृद्ध ऐतिहासिक विरासत, प्राकृतिक परिदृश्य और सांस्कृतिक विविधता के लिए जाना जाता है। यह जिला प्रसिद्ध रोहतास किले का घर है, जो यूनेस्को की विश्व धरोहर स्थल है, और भारतीय इतिहास, कृषि और पर्यटन में अपने योगदान के लिए जाना जाता है।
3,847.82 वर्ग किलोमीटर (1,485.65 वर्ग मील) के क्षेत्र में फैला, रोहतास बिहार के कुल भूमि क्षेत्र का 4.3% हिस्सा है, जो इसे राज्य का चौथा सबसे बड़ा जिला बनाता है। रोहतास 24°30” से 25°20” उत्तरी अक्षांश और 83°14” से 83°20” पूर्वी देशांतर पर स्थित है और उत्तर में भोजपुर जिला और बक्सर जिला, दक्षिण में झारखंड का गढ़वा जिला, पूर्व में औरंगाबाद जिला और पश्चिम में कैमूर जिला (भभुआ) के साथ सीमा साझा करता है। जिले का प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय सासाराम शहर में स्थित है। जिला पटना डिवीजन का हिस्सा है।
2,959,918 की आबादी और 763 व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किमी की जनसंख्या घनत्व के साथ, रोहतास जिले में बिहार के सभी 38-जिलों में सबसे अधिक साक्षरता दर है, जो 2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार 73.37% है इस जिले का निर्माण 10 नवंबर, 1972 को हुआ था, जब पूर्व शाहाबाद जिले को भोजपुर और रोहतास में विभाजित किया गया था। रोहतास जिले में मूल रूप से पूर्व शाहाबाद जिले के सासाराम और भभुआ उप-विभाग शामिल थे। 1991 में, भभुआ को कैमूर जिले में विभाजित किया गया, जिसका आधिकारिक नाम 1994 में बदल दिया गया। यहाँ बोली जाने वाली प्रमुख भाषाएँ भोजपुरी, हिंदी और अंग्रेजी हैं।
समय के साथ, इस क्षेत्र को अलग-अलग नामों से जाना जाता है- सिद्धाश्रम, सहसराम, सासराँव और अंत में, सासाराम।
रोहतास का इतिहास
रोहतास का इतिहास समृद्ध और आकर्षक है, जो प्रागैतिहासिक काल से जुड़ा है, जब भर, चीर और उरांव पठारी क्षेत्र के प्राथमिक निवासी थे। किंवदंती के अनुसार, खेरवार रोहतास के पास पहाड़ी इलाकों में मूल निवासी थे, जबकि उरांव रोहतास और पटना के बीच के क्षेत्र पर शासन करने का दावा करते हैं।
यह जिला कई पौराणिक और ऐतिहासिक हस्तियों से भी जुड़ा हुआ है। स्थानीय लोककथाएँ राजा सहस्रबाहु को जिला मुख्यालय सासाराम से जोड़ती हैं। ऐसा माना जाता है कि उन्होंने महान ब्राह्मण रक्षक संत परशुराम के खिलाफ़ एक भयंकर युद्ध लड़ा था, जिसमें सहस्रबाहु मारे गए थे। कहा जाता है कि सासाराम नाम सहस्रबाहु और परशुराम से लिया गया है।
एक अन्य किंवदंती के अनुसार रोहतास का नाम राजा हरिश्चंद्र के पुत्र रोहिताश्व के नाम पर पड़ा, जो अपनी धर्मपरायणता और सत्यनिष्ठा के लिए प्रसिद्ध थे।
प्राचीन इतिहास
जिला मुख्यालय सासाराम प्राचीन काल से ही एक महत्वपूर्ण ऐतिहासिक और पुरातात्विक केंद्र रहा है। उत्खनन और खोजों से पता चलता है कि सासाराम मध्यपाषाण युग से ही विकसित संस्कृति का केंद्र रहा है। सेनुवरगढ़, शकसगढ़, कोटागढ़ और अनंत टीला जैसे स्थानों में कई नवपाषाणकालीन बस्तियाँ पाई गई हैं, जो कृषि और पशुपालन में प्रारंभिक मानव गतिविधि का संकेत देती हैं।
वाल्मीकि रामायण के बालकांड में उल्लेख है कि सिद्धाश्रम, एक प्राचीन आश्रम, कैमूर की तलहटी में सासाराम में स्थित था। ऐसा माना जाता है कि भगवान विष्णु ने यहाँ एक हज़ार वर्षों तक ध्यान किया था और उनके वामन अवतार का जन्म महर्षि कश्यप की पत्नी माता अदिति से हुआ था, जिससे यह दुनिया के सबसे पुराने जीवित शहरों में से एक बन गया।
रोहतास छठी शताब्दी ईसा पूर्व से पांचवीं शताब्दी ईस्वी तक मगध साम्राज्य का हिस्सा था। सासाराम के पास चंदन शहीद में सम्राट अशोक के छोटे शिलालेख से इस क्षेत्र में मौर्य साम्राज्य की उपस्थिति की पुष्टि होती है। 7वीं शताब्दी ई. में यह जिला कन्नौज के शासक हर्ष के शासन में आया।
मध्यकालीन इतिहास
मौर्य काल के दौरान, सम्राट अशोक ने सासाराम में अपना लघु-शिलालेख अंकित किया, जो प्राचीन भारतीय इतिहास में इसके महत्व को दर्शाता है।
यह जिला शेरशाह सूरी के जन्मस्थान के रूप में जाना जाता है, जो सूरी वंश के संस्थापक और भारत के सबसे शक्तिशाली शासकों में से एक थे, जिन्होंने रोहतास में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई थी। उनके पिता हसन खान सूरी, जो एक अफ़गान साहसी थे, को जौनपुर के गवर्नर जमाल खान की सेवा के लिए सासाराम की जागीर मिली थी। हालाँकि, इस क्षेत्र पर शासन करना मुश्किल रहा क्योंकि यहाँ के लोग अलग-अलग तरह के थे और जमींदार स्वतंत्र थे। शेरशाह के बेटे जलाल खान ने बाद में इस्लाम शाह के रूप में दिल्ली की गद्दी संभाली। सूरी वंश के अन्य शासक, जैसे फिरोज शाह और आदिल शाह भी इसी क्षेत्र से थे।
1529 में, बाबर ने बिहार पर आक्रमण किया, जहाँ उसे शेरशाह के प्रतिरोध का सामना करना पड़ा। अपने संस्मरणों में, बाबर ने कर्मनाशा नदी के बारे में हिंदुओं के अंधविश्वासों का वर्णन किया और बताया कि कैसे उसने 1528 में बक्सर में गंगा को तैरकर पार किया था।
बाबर की मृत्यु के बाद, शेरशाह एक शक्तिशाली शक्ति के रूप में फिर से उभरा। 1537 में, मुगल सम्राट हुमायूं ने उसके खिलाफ़ आगे बढ़कर चुनार और रोहतास गढ़ पर कब्ज़ा कर लिया। हालाँकि, बाद में हुमायूं को चौसा में एक विनाशकारी हार का सामना करना पड़ा, जिससे शेरशाह को दिल्ली की गद्दी पर बैठने का मौक़ा मिला। सूरी राजवंश, जिसकी उन्होंने स्थापना की थी, अल्पकालिक था, क्योंकि मुगलों ने जल्द ही नियंत्रण हासिल कर लिया था।
बाद में, अकबर ने मुगल साम्राज्य का विस्तार और समेकन किया, रोहतास को अपने प्रशासन के अधीन लाया।
यह जिला हेमू (हेमचंद्र) का भी घर था, जो एक रौनियार वैश्य व्यापारी था, जो मध्यकालीन भारत में दिल्ली का एकमात्र गैर-मुस्लिम सम्राट बन गया, जिसने विक्रमादित्य की उपाधि धारण की।
ब्रिटिश काल और स्वतंत्रता संग्राम
18वीं शताब्दी के दौरान, बनारस के राजा चैत सिंह के विद्रोह से जिला हिल गया था, जिनका शासन रोहतास और बक्सर सहित शाहाबाद के बड़े हिस्से तक फैला हुआ था। चैत सिंह ने अंग्रेजों के खिलाफ विद्रोह किया और उनकी सेना ने चुनार और गाजीपुर में ब्रिटिश सैनिकों को हराया, जिससे भारत में ब्रिटिश शासन के लिए कुछ समय के लिए खतरा पैदा हो गया। हालांकि, अंततः उन्हें हार का सामना करना पड़ा।
1857 में, जिले ने भारतीय विद्रोह (स्वतंत्रता का पहला युद्ध) में भूमिका निभाई। भोजपुर के क्रांतिकारी नेता कुंवर सिंह ने रोहतास की स्थानीय सेनाओं के समर्थन से अंग्रेजों के खिलाफ लड़ाई लड़ी। इस क्षेत्र के पहाड़ी इलाके ब्रिटिश शासन का विरोध करने वालों के लिए एक प्राकृतिक शरणस्थली प्रदान करते थे।
भारतीय स्वतंत्रता आंदोलन के दौरान, रोहतास ने महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया, जिसमें कई लोगों ने असहयोग और सविनय अवज्ञा आंदोलनों में भाग लिया।
भारत की आज़ादी के बाद, रोहतास शाहाबाद जिले का हिस्सा बना रहा, जब तक कि इसे अलग नहीं कर दिया गया और 10 नवंबर 1972 को आधिकारिक तौर पर एक जिला बना दिया गया।
रोहतास ऐतिहासिक, सांस्कृतिक और भौगोलिक महत्व का जिला है। पौराणिक कथाओं और प्रारंभिक सभ्यताओं के साथ अपने प्राचीन संबंधों से लेकर मध्यकालीन भारतीय इतिहास में अपनी भूमिका तक, यह जिला बिहार की समृद्ध विरासत का एक अभिन्न अंग बना हुआ है। अपनी उच्च साक्षरता दर, बड़े वन क्षेत्र और अद्वितीय भूगोल के साथ, रोहतास राज्य के विकास में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
रोहतास जिले के बारे में मुख्य तथ्य
- देश:
 भारत
भारत - राज्य:
 बिहार
बिहार - प्रमंडल: पटना
- स्थापना: 10 नवंबर 1972
- क्षेत्रफल: 3,847.82 km2 (1,485.65 वर्ग मील)
- जिला मुख्यालय: सासाराम
- जिला मजिस्ट्रेट: उदिता सिंह, IAS
- पुलिस अधीक्षक: रोशन कुमार, IPS
- मंडल वन अधिकारी: मनीष कुमार वर्मा, IFS
- जनसंख्या (2011):
- कुल: 2,959,918
- घनत्व: 770/km2 (2,000/वर्ग मील)
- साक्षरता: 73.37%
- लिंग अनुपात: 914/1000
- राजभाषा: हिंदी
- उप-मंडलों (तहसीलों) की संख्या: 3 (सासाराम, बिक्रमगंज, डेहरी)
- ब्लॉक/सर्कल की संख्या: 19
- अकोढ़ी गोला, बिक्रमगंज, चेनारी, दावथ, डेहरी, दिनारा, काराकाट, करगहर, कोचस, नासरीगंज, नौहट्टा, नोखा, राजपुर, रोहतास, संझौली, सासाराम, शिवसागर, सूर्यपुरा, तिलौथू
- पुलिस स्टेशनों की संख्या: 38
- डेहरी मुफस्सिल (इंद्रपुरी), डेहरी टाउन, सासाराम मुफस्सिल, सासाराम टाउन, सासाराम मॉडल थाना, एससी/एसटी थाना (डेहरी), महिला थाना (डेहरी), अगरेर, अकोढ़ीगोला, अयार कोठा, बिक्रमगंज, चेनारी, चुटिया, दरिहट, दावथ, दिनारा, कछवां, काराकाट, करगहर, कोचस, नासरीगंज, नटवार, नौहट्टा, नोखा, राजपुर, रोहतास, संझौली, श्योसागर, सूर्यपुरा, तिलौथू, डालिमियानगर, यदुनाथपर, भानस, सीधी, परसथुआ, बद्दी, बघैला, धर्मपुरा।
- ग्राम पंचायतें: 226
- नगर निगम: 1 (सासाराम)
- गांवों की संख्या: 2072
- नगर परिषद: 3 (बिक्रमगंज, डेहरी, नोखा)
- नगर पंचायत: 7 (चेनारी, दिनारा, काराकाट, कोआथ, कोचस, नासरीगंज, रोहतास)
- लोकसभा क्षेत्र: सासाराम
- विधान सभा क्षेत्र:
- चेनारी (एससी), सासाराम, करगहर, दिनारा, नोखा, डेहरी, काराकाट।
- प्रमुख विशेषताऐं:
- शेर शाह सूरी के मकबरे के लिए प्रसिद्ध, जो इंडो-इस्लामिक वास्तुकला का एक बेहतरीन उदाहरण है।
- यूनेस्को विश्व धरोहर स्थल रोहतास किला यहीं स्थित है।
- महत्व: अपने ऐतिहासिक स्थलों और समृद्ध संस्कृति के लिए जाना जाता है।
- समय क्षेत्र: UTC+05:30 (IST)
- मुख्य डाकघर: सासाराम
- पिन कोड:
- रोहतास – 821311, सासाराम – 821115, बिक्रमगंज – 802212, डेहरी-ऑन-सोन – 821307
- एसटीडी कोड:
- सासाराम – 06184, बिक्रमगंज – 06185, डेहरी-ऑन-सोन – 06184
- ISO 3166 कोड: 06188
- वाहन पंजीकरण: BR-24
- प्रमुख राजमार्ग: NH-2
- आधिकारिक वेबसाइट: rohtas.nic.in
भूगोल
- स्थान: दक्षिण-पश्चिम बिहार, झारखंड और उत्तर प्रदेश की सीमा से लगा हुआ।
- सीमावर्ती जिले:
- उत्तर: भोजपुर और बक्सर
- दक्षिण: गढ़वा (झारखंड)
- पूर्व: औरंगाबाद
- पश्चिम: कैमूर
- क्षेत्रफल: रोहतास जिला 3,851 वर्ग किलोमीटर (1,487 वर्ग मील) में फैला हुआ है, जो इसे बिहार का चौथा सबसे बड़ा जिला बनाता है।
- समुद्र तल से ऊँचाई: 107.78 मीटर
- नदियाँ:
- सोन नदी – गंगा की एक प्रमुख सहायक नदी।
- कर्मनासा नदी – सिंचाई के लिए महत्वपूर्ण।
- जलवायु:
- ग्रीष्मकाल (मार्च-जून): गर्म और शुष्क (तापमान 45 डिग्री सेल्सियस तक)।
- मानसून (जुलाई-सितंबर): मध्यम से भारी वर्षा।
- सर्दियाँ (दिसंबर-फरवरी): सुखद और ठंडी (5 डिग्री सेल्सियस – 20 डिग्री सेल्सियस)।
- भौगोलिक दृष्टि से यह जिला दो प्रमुख प्राकृतिक क्षेत्रों में विभाजित है:
- सासाराम मैदान (उत्तर और उत्तर-पूर्व)
- उत्तर में 72 मीटर से लेकर दक्षिण में 153 मीटर तक की ऊँचाई वाला एक हल्का ढलान वाला जलोढ़ मैदान।
- दिनारा, दावथ, बिक्रमगंज, नासरीगंज, नोखा और डेहरी ब्लॉक के साथ-साथ सासाराम, शिवसागर और रोहतास ब्लॉक के कुछ हिस्सों को कवर करता है।
- बिखरे हुए जंगल, खास तौर पर सासाराम ब्लॉक में।
- रोहतास पठार (दक्षिण)
- विंध्य पठार का एक पूर्वी किनारा, जिसकी औसत ऊँचाई 300 मीटर है।
- नौहट्टा, रोहतास, शिवसागर, सासाराम और चेनारी ब्लॉक के कुछ हिस्सों को कवर करता है।
- पहाड़ी इलाके और जंगलों की विशेषता, जिसमें उत्तर की ओर बहने वाली नदियाँ, जिनमें दुर्गावती, बजारी, कोयल और सुरा नदियाँ शामिल हैं।
- चट्टानी मिट्टी और बजरी वाले इलाके के कारण कृषि के लिए कम उपयुक्त।
- नाशपाती घास, कुस और खास खास जैसी प्राकृतिक लंबी घासों का घर।
- सासाराम मैदान (उत्तर और उत्तर-पूर्व)
- मिट्टी के प्रकारों में शामिल हैं:
- उस्तालफ्स, ऑक्रेप्ट्स, ऑर्थेंट्स, फ्लुवेंट्स और पसमेंट्स।
इतिहास
- प्राचीन और मध्यकालीन काल:
- यह क्षेत्र मौर्य और गुप्त राजवंशों से जुड़ा हुआ है।
- मुगल काल के दौरान रोहतास एक महत्वपूर्ण सैन्य और प्रशासनिक केंद्र था।
- शेर शाह सूरी (1540-1545) ने रोहतास किले को सैन्य अड्डे के रूप में इस्तेमाल किया।
- ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक युग:
- ब्रिटिश शासन के खिलाफ 1857 के विद्रोह में रोहतास एक महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्र था।
- इसने भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई।
- स्वतंत्रता के बाद:
- शाहाबाद जिले से अलग होने के बाद रोहतास 1972 में एक स्वतंत्र जिला बन गया।
रोहतास की एक गहरी ऐतिहासिक विरासत है, जिसमें मगध और मौर्य जैसे प्राचीन साम्राज्यों से लेकर शेरशाह सूरी के शासन और भारतीय स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में इसकी भूमिका शामिल है। आज, यह बिहार में ऐतिहासिक और सांस्कृतिक महत्व के क्षेत्र के रूप में खड़ा है।
जनसांख्यिकी (2011 की जनगणना के अनुसार)
जनसंख्या:
- कुल जनसंख्या: रोहतास जिले की जनसंख्या लगभग 2,959,918 है (अब लगभग 3.5 मिलियन होने का अनुमान है)।
- पुरुष जनसंख्या: 52.3% (15,47,856)
- महिला जनसंख्या: 47.7% (14,14,737)
- शहरी जनसंख्या: (427709) कुल जनसंख्या का 14.45% शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- ग्रामीण जनसंख्या: (2,532,209) कुल जनसंख्या का 85.55% ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में रहता है।
- जनसंख्या रैंकिंग: भारत में 127वाँ (640 जिलों में से) और बिहार राज्य में 17वाँ।
- घनत्व: 768 व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर (1,980/वर्ग मील) (बिहार में 38 में से 34वें स्थान पर)।
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि (2001-2011): 20.22%, जो महत्वपूर्ण जनसंख्या वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- लिंग अनुपात: प्रति 1,000 पुरुषों पर 918 महिलाएँ, जो राज्य लिंग अनुपात (बिहार में 38 में से 22वें स्थान पर) के समान है।
साक्षरता दर:
- समग्र साक्षरता:
- कुल जनसंख्या का 73.37% साक्षर है, जो बिहार के सभी 38-जिलों में सबसे अधिक है और शिक्षा की पहुँच और गुणवत्ता में सुधार के लिए महत्वपूर्ण प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं।
- लिंग असमानता:
- पुरुष: 82.88% साक्षरता दर।
- महिलाएँ: 62.97% साक्षरता दर।
- शहरी बनाम ग्रामीण: ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों की तुलना में शहरी क्षेत्रों में साक्षरता अधिक है।
- उच्चतम साक्षरता क्षेत्र:
- देहरी:
- जिले की कुल आबादी का 77.70% साक्षर है।
- शहर में साक्षरता दर 81.2% है।
- देहरी:
- सबसे कम साक्षरता क्षेत्र:
- नौहट्टा सीडी ब्लॉक (पूरी तरह से ग्रामीण): साक्षरता दर 63.07% है।
धार्मिक संरचना (2011 की जनगणना):
- अधिकांश आबादी हिंदू धर्म का पालन करती है, जिसमें एक महत्वपूर्ण मुस्लिम समुदाय और अन्य समुदाय महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा बनाते हैं।
- हिंदू धर्म: 89.37%
- अनुसूचित जाति: कुल आबादी का 18.57%।
- अनुसूचित जनजाति: कुल आबादी का 1.07%।
- इस्लाम: 10.15%
- अन्य या नहीं बताया गया: 0.48%
- हिंदू धर्म: 89.37%
बोली जाने वाली भाषाएँ:
- भोजपुरी: 87.67%
- हिंदी: 7.47%
- उर्दू: 4.38%
- अन्य: 0.48%
रोज़गार प्रोफ़ाइल:
- कृषि:
- कामकाजी आबादी का अधिकांश हिस्सा कृषि में कार्यरत है।
- खेती करने वाले: कार्यबल का 23.58% (वे जो अपनी ज़मीन के मालिक हैं या किराए पर लेते हैं)।
- खेती करने वाले मज़दूर: कार्यबल का 43.85% (वे जो मज़दूरी के लिए किसी और की ज़मीन पर काम करते हैं)।
- घरेलू उद्योग: कार्यबल का 5.25% घरेलू उद्योगों में लगा हुआ है।
- रोज़गार के अन्य रूप: कार्यबल का शेष 27.33% अन्य सभी क्षेत्रों में कार्यरत है।
प्रशासन
- जिले का नेतृत्व जिला मजिस्ट्रेट (डीएम) रैंक के आईएएस अधिकारी करते हैं।
- जिला प्रशासनिक मुख्यालय: सासाराम शहर (जिले का सबसे बड़ा शहर)।
- जिले को उप-विभागों या तहसीलों में विभाजित किया गया है, और इन तहसीलों को आगे ब्लॉकों में विभाजित किया गया है।
- उप-मंडल:
- जिले में प्रशासनिक सुविधा के लिए 3 राजस्व उप-मंडल या तहसील हैं: सासाराम, डेहरी-ऑन-सोन और बिक्रमगंज।
- प्रत्येक राजस्व उप-मंडल का नेतृत्व राजस्व मंडल अधिकारी (आरडीओ) करता है, जो उस प्रभाग पर अधिकार क्षेत्र के साथ उप-मंडल मजिस्ट्रेट के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- प्रत्येक उप-मंडल का नेतृत्व उप-मंडल मजिस्ट्रेट (एसडीएम) करता है, जो विकास, राजस्व-संबंधी कार्यों और कानून व्यवस्था बनाए रखने का प्रभारी होता है।
- तहसीलदार, जो उपयुक्त संवर्ग में प्रशासनिक अधिकारी होते हैं, उप-विभागीय कार्यालयों के प्रबंधन में सहायता करते हैं।
- उप-विभागीय कार्यालयों की संरचना समाहरणालय के समान ही होती है, जो मध्यवर्ती प्रशासनिक इकाइयों के रूप में कार्य करते हैं।
- प्रत्येक उप-विभाग में कई ब्लॉक होते हैं, और इन ब्लॉकों के प्रदर्शन की निगरानी संबंधित विभागीय कार्यालय द्वारा निरंतर की जाती है।
- ब्लॉक और सर्किल:
- रोहतास जिले में 19 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और सर्किल शामिल हैं, जो 3 उप-विभागों के अंतर्गत आते हैं:
- सासाराम: सासाराम, शिवसागर, चेनारी, करगहर, कोचस, नोखा
- डेहरी-ऑन-सोन: डेहरी, अकोढ़ीगोला, नौहट्टा, रोहतास, तिलौथू
- बिक्रमगंज: बिक्रमगंज, काराकाट, नासरीगंज, दावथ, राजपुर, संझौली, सूर्यपुरा, दिनारा
- प्रत्येक ब्लॉक स्थानीय शासन और विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
- प्रत्येक सर्किल का नेतृत्व एक सर्किल अधिकारी (सीओ) करता है, जबकि प्रत्येक ब्लॉक का नेतृत्व एक ब्लॉक विकास अधिकारी (बीडीओ) करता है।
- रोहतास जिले में 19 प्रशासनिक ब्लॉक और सर्किल शामिल हैं, जो 3 उप-विभागों के अंतर्गत आते हैं:
- शासन:
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र:
- सासाराम (बिहार के प्रमुख संसदीय निर्वाचन क्षेत्रों में से एक)।
- विधानसभा क्षेत्र: जिले में 7 विधानसभा सीटें हैं।
- 207-चेनारी (एससी), 208-सासाराम, 209-करगहर, 210-दिनारा, 211-नोखा, 212-डेहरी, 213-काराकाट
- लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र:
कलेक्टरेट की समग्र भूमिकाएँ और जिम्मेदारियाँ:
जिला प्रशासन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है और जिले के भीतर कानून और व्यवस्था, योजना, विकास, राजस्व और आपदा प्रबंधन को बनाए रखने के लिए जिम्मेदार होता है।
- कलेक्टर (आई.ए.एस. कैडर):
- जिले का मुखिया: मुख्य कार्यकारी और जिला मजिस्ट्रेट के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- कानून और व्यवस्था: जिले में शांति बनाए रखता है और कानून और व्यवस्था लागू करता है।
- योजना और विकास: योजना और विकास परियोजनाओं की देखरेख करता है।
- अनुसूचित/एजेंसी क्षेत्रों का प्रशासन: अनुसूचित या विशेष एजेंसी प्रशासन के तहत नामित क्षेत्रों का प्रबंधन करता है।
- चुनाव प्रबंधन और शस्त्र लाइसेंसिंग: आम चुनावों को संभालता है और शस्त्रों के लाइसेंसिंग की देखरेख करता है।
- अतिरिक्त कलेक्टर (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- राजस्व प्रशासन: विभिन्न जिला विभागों में राजस्व संबंधी कार्यों को चलाता है।
- अतिरिक्त जिला मजिस्ट्रेट: कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने और नागरिक कार्यों को संचालित करने में जिम्मेदारियों को साझा करता है।
- प्रमुख जिम्मेदारियाँ: नागरिक आपूर्ति, भूमि मामलों, खानों और खनिजों के प्रबंधन की देखरेख करना और ग्राम अधिकारियों की देखरेख करना।
- जिला विकास आयुक्त (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- विकासात्मक गतिविधियाँ: जिले भर में विभिन्न विकासात्मक पहलों का प्रबंधन और समन्वय करना।
- देखरेख करने वाले प्रमुख विभाग:
- जिला चिकित्सा और स्वास्थ्य विभाग।
- समाज कल्याण विभाग।
- बीसी (पिछड़ा वर्ग) कल्याण और बीसी निगम।
- विकलांग कल्याण।
- आवास और अन्य संबंधित विभाग।
- अतिरिक्त कलेक्टर (आपदा) (बी.ए.एस. कैडर):
- आपदा प्रबंधन: आपदा प्रबंधन से संबंधित गतिविधियों की योजना बनाने और समन्वय करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना।
- प्रमुख जिम्मेदारियाँ: आपात स्थिति के दौरान आपदा अनुभाग और अन्य संबंधित विकास विभागों की देखरेख करना।
ये भूमिकाएँ सामूहिक रूप से सुनिश्चित करती हैं कि जिला अच्छी तरह से शासित हो, जिसमें कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने, कुशल राजस्व संग्रह, प्रभावी आपदा प्रबंधन और विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में सतत विकास पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया जाता है।
अर्थव्यवस्था
- कृषि:
- जिले का प्राथमिक व्यवसाय।
- प्रमुख फसलें:
- गेहूँ, चावल, मक्का, दालें और तिलहन।
- इसके महत्वपूर्ण चावल उत्पादन के कारण इसे “बिहार का चावल का कटोरा” कहा जाता है।
- आम, अमरूद और लीची जैसे फल भी उगाए जाते हैं।
- सिंचाई प्रणाली: सोन नहर प्रणाली कृषि के लिए पानी उपलब्ध कराती है।
- उद्योग और खनिज:
- औद्योगिक इतिहास:
- डालमियानगर 1980 तक भारत के प्रमुख औद्योगिक शहरों में से एक था।
- ऐतिहासिक रूप से चीनी, वनस्पति तेल, सीमेंट, कागज और रसायन (रोहतास उद्योग) बनाने वाली फैक्ट्रियाँ थीं।
- ये उद्योग अब बंद हो चुके हैं।
- सीमेंट उद्योग – रोहतास में बिहार की सबसे बड़ी सीमेंट निर्माण इकाइयों में से एक है।
- पत्थर खनन और उत्खनन – जिले में चूना पत्थर के समृद्ध भंडार हैं।
- ईंट बनाने का उद्योग – बिहार में सबसे बड़ा उद्योग है।
- खाद्य प्रसंस्करण, मिट्टी के बर्तन और हस्तशिल्प जैसे लघु उद्योग।
- औद्योगिक इतिहास:
- सरकारी वर्गीकरण और सहायता:
- 2006 में, पंचायती राज मंत्रालय ने रोहतास को भारत के 640 में से 250 सबसे पिछड़े जिलों में से एक नामित किया।
- यह बिहार के 36 जिलों में से एक है, जो पिछड़ा क्षेत्र अनुदान निधि कार्यक्रम (BRGF) से धन प्राप्त करता है।
शिक्षा
- उल्लेखनीय शैक्षणिक संस्थान:
- श्री शंकर कॉलेज, सासाराम – सबसे पुराने संस्थानों में से एक।
- जवाहर नवोदय विद्यालय, रोहतास – एक प्रतिष्ठित सीबीएसई स्कूल।
- सरकारी पॉलिटेक्निक कॉलेज, सासाराम।
- वीर कुंवर सिंह विश्वविद्यालय से संबद्ध कॉलेज।
- एसपी जैन कॉलेज, सासाराम, रोहतास
- श्री शंकर कॉलेज, तकिया, सासाराम
- चुनौतियाँ:
- अधिक उच्च शिक्षा संस्थानों की आवश्यकता – कई छात्र उन्नत अध्ययन के लिए पटना और वाराणसी चले जाते हैं।
- सीमित तकनीकी और व्यावसायिक पाठ्यक्रम।
संस्कृति और त्यौहार
त्यौहार:
- छठ पूजा:
- ज़िला में सबसे बड़ा त्यौहार, सोन नदी के तट पर भव्य रूप से मनाया जाता है।
- सूर्य भगवान (सूर्य) को समर्पित एक प्रमुख हिंदू त्यौहार, जिसे अपार आस्था के साथ मनाया जाता है।
- वर्ष में दो बार मनाया जाता है:
- चैत्र (गर्मी) में
- कार्तिक (सर्दियों की शुरुआत) में
- भक्त पवित्र स्नान, उपवास और डूबते और उगते सूर्य को जल (अर्घ्य) चढ़ाने सहित कठोर अनुष्ठान करते हैं।
- मकर संक्रांति (तिला संक्रांति):
- गर्मियों की शुरुआत में मनाया जाता है और फसल के मौसम को चिह्नित करता है।
- इसे शुभ माना जाता है क्योंकि यह भारतीय संस्कृति में नए साल की शुरुआत का प्रतीक है।
- होली:
- जिले में सबसे बड़े और सबसे रंगीन त्योहारों में से एक।
- बहुत उत्साह के साथ मनाया जाता है, जहाँ लोग खुशी और जीवंत उत्सव मनाते हैं जो माहौल को रोशन करते हैं।
- दुर्गा पूजा, दिवाली, जन्माष्टमी, काली पूजा, सरस्वती पूजा, नाग पंचमी, शिव रात्रि, बकरीद, ईद और मुहर्रम भी व्यापक रूप से मनाए जाते हैं।
- भोजपुरी लोकगीत और नृत्य सांस्कृतिक पहचान का एक प्रमुख हिस्सा हैं।
व्यंजन:
- पारंपरिक स्टेपल:
- दैनिक भोजन में आमतौर पर सब्ज़ी (सब्जी करी), रोटी (चपटी रोटी), दाल (दाल) और भाजी (हलचल-तली हुई सब्जियाँ) जैसे व्यंजन शामिल होते हैं।
- सिग्नेचर डिश:
- लिट्टी चोखा: भुने हुए गेहूँ के गोले (लिट्टी) से बना एक लोकप्रिय बिहारी व्यंजन जिसे मसली हुई सब्ज़ियों (चोखा) के साथ परोसा जाता है।
- कढ़ी: दही से बनी करी जिसे अक्सर पारंपरिक मसालों के साथ पकाया जाता है।
- झाल मूरी: स्थानीय लोगों द्वारा पसंद किया जाने वाला एक मसालेदार स्नैक मिक्स।
- भुना हुआ बेसन, सत्तू पराठा, दाल पीठा और दाल पूरी जैसे विभिन्न व्यंजनों और पेय पदार्थों में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
- कचौरी-सब्जी आम तौर पर खाई जाती हैं।
- मिठाई और डेसर्ट:
- शुद्ध देसी घी से बनी अपनी मुंह में पानी लाने वाली मिठाइयों के लिए प्रसिद्ध, जो स्थानीय मिठाई की दुकानों में उपलब्ध हैं और आमतौर पर घर पर समारोह के अवसरों पर बनाई जाती हैं।
- खाजा, बालूशाही, तिलकुट, ठेकुआ, खुरमा और मालपुआ जैसी मिठाइयाँ प्रसिद्ध हैं।
वेशभूषा:
- पारंपरिक पुरुष पोशाक:
- धोती, कुर्ता और पायजामा आम तौर पर पहने जाते हैं।
- युवा पुरुषों को पारंपरिक और आधुनिक शैलियों के मिश्रण वाली शर्ट और पतलून में भी देखा जा सकता है।
- पारंपरिक महिला पोशाक:
- महिलाएँ पारंपरिक रूप से घाघरा (लंबी स्कर्ट), चोली (ब्लाउज) और साड़ी पहनती हैं, जो समृद्ध हिंदू सांस्कृतिक विरासत को दर्शाती हैं।
- मुस्लिम समुदाय की पोशाक:
- पुरुष: आम तौर पर कुर्ता और पायजामा पहनते हैं।
- महिलाएं: पारंपरिक मुस्लिम पोशाक का पालन करते हुए अक्सर बुर्का पहनती हैं।
धर्म:
- धार्मिक संरचना:
- जिला मुख्य रूप से हिंदू है, लेकिन इसमें एक महत्वपूर्ण मुस्लिम समुदाय भी है।
- जिले में आदिवासी समुदाय भी रहते हैं, जिनमें से कई अपनी स्वदेशी धार्मिक प्रथाओं का पालन करते हैं।
- सांस्कृतिक एकीकरण:
- क्षेत्र का सांस्कृतिक परिदृश्य विभिन्न धार्मिक परंपराओं का एक जीवंत मिश्रण है, जिसमें समुदाय कई दशकों से सह-अस्तित्व में हैं।
- सामाजिक सद्भाव:
- विविधता के बावजूद, सामाजिक एकता और आतिथ्य की एक मजबूत भावना है, जो आगंतुकों पर एक स्थायी छाप छोड़ती है।
- विरासत और परंपरा:
- धार्मिक परंपराओं की समृद्ध टेपेस्ट्री एक अनूठी सांस्कृतिक विरासत में योगदान देती है, जो त्योहारों, अनुष्ठानों और रोजमर्रा की प्रथाओं में स्पष्ट है।
पर्यटन और ऐतिहासिक स्थल
रोहतास बिहार के शीर्ष पर्यटन स्थलों में से एक है, जो अपने किलों, मंदिरों और प्राकृतिक सुंदरता के लिए जाना जाता है।
मुख्य आकर्षण:
- रोहतास किला (यूनेस्को-सूचीबद्ध) – शेर शाह सूरी द्वारा निर्मित 16वीं शताब्दी का किला, जो अपनी विशाल दीवारों, द्वारों और पानी की टंकियों के लिए जाना जाता है।
- शेर शाह सूरी का मकबरा, सासाराम – शेर शाह सूरी का मकबरा, एक आश्चर्यजनक वास्तुशिल्प आश्चर्य।
- तारा चंडी मंदिर – एक प्रसिद्ध हिंदू तीर्थ स्थल।
- मंझर कुंड और धुंआ कुंड – झरने अपनी प्राकृतिक सुंदरता और वार्षिक मेलों के लिए जाने जाते हैं।
- गुप्त धाम गुफा मंदिर – एक गुफा के अंदर एक शिव मंदिर।
- इंद्रपुरी बैराज – सोन नदी पर एक बड़ा बांध, जो सुंदर दृश्य प्रस्तुत करता है।
- तुतला भवानी झरना और मंदिर – एक प्राकृतिक और धार्मिक स्थल।
1. गुप्त धाम:
- स्थान:
- कैमूर पहाड़ी की घाटी में स्थित एक प्राकृतिक गुफा।
- मुख्य विशेषता:
- शिवलिंग के आकार में चूने के जमाव से बनी एक छोटी चट्टान है, जिसे गुप्तेश्वर महादेव के नाम से जाना जाता है।
- त्यौहार:
- शिवरात्रि और बसंत पंचमी के दौरान मेला लगता है, जिसमें बड़ी भीड़ उमड़ती है।
2. बंदू शिवलिंग:
- स्थान:
- रोहतास पहाड़ी के दक्षिण में, बंदू गांव से लगभग 0.5 किमी दक्षिण-पश्चिम में।
- मुख्य विशेषता:
- सोन नदी की धारा में एक विशाल शिलाखंड पर बने चबूतरे पर एक शिवलिंग स्थापित है।
- किंवदंती:
- स्थानीय किंवदंतियों के अनुसार, शिवलिंग की स्थापना लंकापति रावण ने की थी और इसलिए इसका नाम दशशिनाथ पड़ा।
3. चौरासन मंदिर:
- स्थान:
- रोहतासगढ़ किले के पास स्थित है।
- पहुँच:
- रोहतास ब्लॉक मुख्यालय से लगभग 2 घंटे की दूरी पर।
- विशेषताएँ:
- भगवान शिव को समर्पित इस मंदिर तक 84 सीढ़ियाँ चढ़कर पहुँचा जा सकता है – इसलिए इसका नाम “चौरासन” पड़ा।
4. माँ तारा चंडी मंदिर:
- स्थान:
- विंध्य पर्वत श्रृंखला की कैमूर पहाड़ी पर एक प्राकृतिक गुफा में सासाराम में स्थित है।
- मुख्य विशेषताएँ:
- चार हाथों वाली माँ तारा की मूर्ति है:
- दायाँ हाथ: चाकू और कैंची पकड़े हुए है।
- बायाँ हाथ: फन और कमल पकड़े हुए है।
- बायाँ पैर एक शव पर आगे की ओर रखा हुआ है।
- खरवार वंश (12वीं शताब्दी) के महानायक प्रताप धवलदेव द्वारा लिखित एक महत्वपूर्ण शिलालेख है, जिसे उनके बेटे शत्रुधन ने लिखा था।
- मंदिर परिसर में माँ तारा, सूर्य और अग्नि की एक खंडित मूर्ति शामिल है, जो गुप्त काल के अंत या बाद के गुप्त काल की है।
- चार हाथों वाली माँ तारा की मूर्ति है:
- सांस्कृतिक प्रभाव:
- शिलालेख उस अवधि के दौरान ताराचंडी देवी की प्रसिद्धि के ऐतिहासिक प्रसार को इंगित करता है।
5. तुतला भवानी मंदिर:
- स्थान:
- तिलौथू से लगभग 8 किमी दक्षिण-पश्चिम में एक सुरम्य घाटी में स्थित है।
- दर्शनीय विशेषताएँ:
- घाटी, लगभग 1 मील लंबी, एक झरने और कछुआर नदी के साथ हरी-भरी है।
- घाटी की चौड़ाई लगभग 300 मीटर (पूर्व) से 50 मीटर (पश्चिम) तक भिन्न होती है, जहाँ लगभग 180 फीट की ऊँचाई से एक झरना गिरता है।
- मंदिर का विवरण:
- एक सीढ़ी झरने के भीतर दक्षिण की ओर एक मंच की ओर जाती है जहाँ देवी जगद्धात्री महिषमर्दिनी दुर्गा की एक मूर्ति स्थापित है।
- मूर्ति के पास तीन भागों में विभाजित एक शिलालेख पाया जाता है, जिसका श्रेय नायक प्रताप धवल देव को दिया जाता है और 1 अप्रैल 1158 ई. का है।
- इस स्थल पर तुतला भवानी को समर्पित एक छोटा मंदिर बनाया गया है।
- इको-टूरिज्म विकास:
- हाल ही में वन विभाग द्वारा इको-टूरिज्म गंतव्य के रूप में विकसित किया गया है।
- पर्यटक सुविधाओं में सड़क मार्ग, झूला पुल और ई-रिक्शा सेवाएँ शामिल हैं।
6. गुरुद्वारा चाचा फगुमल:
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- चाचा फगुमल के घर के नाम पर, जहाँ श्री गुरुतेग बहादुर जी महाराज और उनकी पत्नी माता गुजरी देवी 1666 ई. में आए थे।
- सिख गुरुओं की यात्रा से जुड़ा हुआ है, क्योंकि दसवें गुरु, श्री गुरु गोबिंद सिंह उस समय माता गुजरी देवी के गर्भ में थे।
- तीर्थयात्रा:
- चाचा फगुमल के घर पर गुरु गोबिंद सिंह के 21 दिनों के प्रवास ने इस स्थल को सिखों के लिए एक प्रमुख तीर्थ स्थल बना दिया।
- वर्तमान स्थिति:
- इस स्थान पर एक गुरुद्वारा बनाया गया है, जिसे चाचा फगुमल गुरुद्वारा के नाम से जाना जाता है।
7. गुरुद्वारा टकसाल संघत:
- किंवदंती:
- चाचा फगुमल के घर की यात्रा के दौरान, गुरु गोबिंद सिंह का घोड़ा भाई अचल सिंह और जीवो माई के स्वामित्व वाले स्थान पर फंस गया।
- गुरु गोविंद सिंह ने इस स्थान को पवित्र घोषित किया, जिससे एक गुरुद्वारा की स्थापना की प्रेरणा मिली।
- स्थापना:
- यह स्थान जीवो माई द्वारा वी. संवत 1723 में दान किया गया था।
- परिणामी गुरुद्वारा टकसाल संघट के नाम से प्रसिद्ध है।
8. धुवन कुंड:
- स्थान:
- सासाराम से लगभग 15 किमी दूर कैमूर पहाड़ी पर स्थित है।
- प्राकृतिक आकर्षण:
- इसमें गर्म पानी के झरने और एक झरना है जो सूर्योदय और सूर्यास्त के दौरान मंत्रमुग्ध कर देने वाले दृश्य प्रस्तुत करता है।
- उपचार संबंधी प्रतिष्ठा:
- माना जाता है कि इसमें पवित्र उपचार शक्तियाँ हैं, जो हिंदू भक्तों को अनुष्ठान स्नान के लिए आकर्षित करती हैं।
9. मंझार कुंड:
- स्थान:
- सासाराम से लगभग 15 किमी दूर स्थित, पहाड़ी के तल से 30 मिनट के भीतर पहुँचा जा सकता है।
- पर्यटक आकर्षण:
- एक लोकप्रिय पिकनिक स्थल जो हज़ारों स्थानीय लोगों और पर्यटकों को आकर्षित करता है, खासकर मानसून के मौसम में।
- प्राकृतिक सौंदर्य:
- अपने शांत वातावरण और हरे-भरे परिवेश के लिए जाना जाता है।
10. धूप घड़ी:
- ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि:
- 1871 में डेहरी के एनीकट रोड पर स्थापित एक ब्रिटिश निर्मित घड़ी।
- अनोखी विशेषता:
- इस क्षेत्र की एकमात्र घड़ी जो सूर्य के प्रकाश (छाया) से समय दिखाती है।
- डिजाइन:
- एक चट्टानी मंच पर स्थापित, इसमें हिंदी और रोमन दोनों अंक हैं।
- मूल उपयोग:
- मुख्य रूप से सिंचाई विभाग के श्रमिकों द्वारा उपयोग किया जाता है।
11. मेगालिथिक कब्रें:
- खोज और महत्व:
- रोहतास जिले के कैमूर पहाड़ियों में मेगालिथिक सांस्कृतिक स्थलों की पहली पुरातात्विक खोज।
- बिहार और भारत के पुरातत्व में एक मील का पत्थर माना जाता है।
- सांस्कृतिक संदर्भ:
- प्राचीन काल से विभिन्न जनजातियों द्वारा बसा हुआ:
- निषाद-वंशी जनजातियाँ: खरवार, मुंडा और संथाल।
- द्रविड़ मूल के ओरांव जनजाति।
- इन जनजातियों में मेगालिथिक दफन की एक पुरानी परंपरा है जो आज भी जारी है।
- प्राचीन काल से विभिन्न जनजातियों द्वारा बसा हुआ:
- मुख्य निष्कर्ष:
- संगोरा कब्रें:
- कई स्थलों पर केयर्न सर्कल (संगोरा समाधि) की खोज की गई।
- पत्थर के खंभे (मेनहिर):
- विभिन्न स्थलों पर पत्थर के खंभों के दो जोड़े खोजे गए; कुछ के ऊपर एक छोटा चुचुक (टोपी) है।
- रोहतासगढ़ स्थल:
- अनेक संगोरा समाधियों सहित पाँच मेगालिथिक स्थल खोजे गए।
- हुरमेटा स्थल (नौहट्टा ब्लॉक):
- इसमें आठ छोटे और बड़े पत्थर के खंभे हैं।
- मूल रूप से, यहाँ 30 से अधिक पत्थर के खंभे खड़े थे, इससे पहले कि कई उखाड़ दिए गए और उनका फिर से उपयोग किया गया।
- संगोरा कब्रें:
- तिथि:
- मेगालिथिक कब्रों का अनुमान 1500 ईसा पूर्व से 500 ईसा पूर्व तक लगाया गया है।
12. शेर शाह सूरी का मकबरा:
- स्थान और सेटिंग:
- भारत के बिहार के सासाराम में स्थित है।
- मकबरा 22 एकड़ में फैले एक विशाल, लगभग चौकोर कृत्रिम तालाब के बीच में स्थित है।
- तालाब का आयाम: लगभग 1130 फीट (पूर्व-पश्चिम) और 865 फीट (उत्तर-दक्षिण)।
- मकबरे तक पहुँचने के लिए तालाब के उत्तर में स्थित शेर शाह के दरबान के एक छोटे गुंबददार मकबरे से गुजरना पड़ता है।
- वास्तुशिल्प विशेषताएँ:
- लाल बलुआ पत्थर का उपयोग करके निर्मित।
- वास्तुकार मीर मुहम्मद अलीवाल खान द्वारा डिज़ाइन किया गया इंडो-इस्लामिक वास्तुकला का उदाहरण।
- 1540 और 1545 ईस्वी के बीच निर्मित।
- ऊँचाई: मुख्य मकबरा 122 फीट ऊँचा है।
- योजना और संरचना:
- अष्टकोणीय योजना पर निर्मित।
- 22 मीटर तक फैले एक बड़े गुंबद से ऊपर।
- प्रत्येक कोने पर सजावटी गुंबददार कियोस्क और छतरियों से घिरा हुआ है।
- प्लिंथ और आस-पास:
- चारों ओर पत्थर के किनारों और सीढ़ीदार घाटों के साथ एक चौकोर पत्थर के प्लिंथ पर स्थापित।
- एक चौड़े पत्थर के पुल द्वारा मुख्य भूमि से जुड़ा हुआ है।
- अतिरिक्त विवरण:
- तीनों मंजिलों पर बने बुर्ज इसकी भव्यता को बढ़ाते हैं।
- इसे अक्सर “भारत का दूसरा ताजमहल” कहा जाता है, और कुछ लोग इसे और भी बेहतर मानते हैं, जैसे कि कनिंधम।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- बिहार के पठान शासक सम्राट शेर शाह सूरी की याद में बनाया गया, जिन्होंने मुगल साम्राज्य को हराया और सूरी साम्राज्य की स्थापना की।
- शेर शाह सूरी की मृत्यु 13 मई 1545 ई. को कालिंजर के किले में एक आकस्मिक बारूद विस्फोट के कारण हुई थी।
- मकबरे का निर्माण शेर शाह के जीवनकाल के साथ-साथ उनके बेटे इस्लाम शाह के शासनकाल के दौरान भी किया गया था।
- एक शिलालेख के अनुसार इसका निर्माण 16 अगस्त 1545 ई. में पूरा हुआ था, जो शेरशाह की मृत्यु के तीन महीने बाद हुआ था।
13. रोहतास गढ़ किला:
- अवलोकन और ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- भारत और दुनिया के सबसे बड़े किलों में से एक, जो 26 मील की परिधि में फैला हुआ है।
- रोहतास के नाम पर, सतयुग सूर्यवंशी राजा सत्यहरिश्चंद्र के पुत्र रोहिताश्व द्वारा स्थापित।
- किले का विशाल विस्तार और रणनीतिक डिजाइन इसके ऐतिहासिक सैन्य महत्व को उजागर करता है।
- पहुँच और रक्षा:
- रणनीतिक सुरक्षा प्रदान करने वाले चार प्राचीन मार्गों (घाटों) के माध्यम से पहुँचा जा सकता है:
- मेंदरा घाट (पूर्व)
- कठौतिया घाट (पश्चिम)
- घोड़ा घाट (उत्तर)
- राजघाट (दक्षिण)
- इन घाटों ने सुनिश्चित किया कि दुश्मन आसानी से किले तक नहीं पहुँच सकते, क्योंकि प्रत्येक द्वार किलेबंद था।
- रणनीतिक सुरक्षा प्रदान करने वाले चार प्राचीन मार्गों (घाटों) के माध्यम से पहुँचा जा सकता है:
- किले के भीतर प्रमुख संरचनाएँ और आकर्षण:
- धार्मिक और शाही संरचनाएँ:
- रोहितासन या चौरासन सीढ़ी मंदिर – 84 सीढ़ियाँ चढ़कर पहुँचा जाने वाला एक प्राचीन मंदिर।
- पार्वती मंदिर – एक महत्वपूर्ण धार्मिक स्थल।
- गेट संरचनाएँ:
- कठौतिया घाट – प्रमुख प्रवेश बिंदुओं में से एक।
- सिंह दरवाज़ा, लाल दरवाज़ा और गाजी दरवाज़ा – राजसी प्रवेश द्वार।
- महलीय और प्रशासनिक इमारतें:
- राजभवन या महल सराय
- किलादार महल
- पंच महल
- हथियापोल और फूल महल
- बारादरी
- राजा का महल और तख्तपादशाही
- खानबाग और जनाना महल (रानी का महल)
- अतिरिक्त उल्लेखनीय स्थल:
- नच घर – एक पारंपरिक सभा क्षेत्र।
- शेर शाही मस्जिद – किले के भीतर इंडो-इस्लामिक वास्तुकला का एक उदाहरण।
- हब्स खान का मकबरा, मस्जिद और मदरसा – ऐतिहासिक धार्मिक संरचनाएँ।
- गणेश मंदिर
- शाकी सुल्तान का मकबरा
- धार्मिक और शाही संरचनाएँ:
- सांस्कृतिक महत्व:
- किले का लेआउट, इसके रणनीतिक रूप से रखे गए घाटों और कई संरचनाओं के साथ, इस क्षेत्र की समृद्ध वास्तुकला और सांस्कृतिक विरासत को दर्शाता है।
- यह प्राचीन काल की किलेबंदी और शहरी नियोजन का एक प्रमाण है, जो आगंतुकों को एक शानदार अतीत की झलक प्रदान करता है।
14. शेर गढ़ किला:
- स्थान और सेटिंग:
- छह वर्ग मील के क्षेत्र में स्थित है।
- कैमूर रेंज में लगभग 800 फीट ऊंची पहाड़ी पर स्थित है।
- सासाराम से लगभग 20 मील दक्षिण-पश्चिम में।
- ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि:
- मूल रूप से भुरकुंडा के नाम से जाना जाता है, जो खरवार राजाओं का घर था।
- बाद में हसन खान सूर द्वारा सासाराम की जागीर हासिल करने के बाद यह सूरी के नियंत्रण में आ गया।
- आखिरकार, किला शेर शाह से जुड़ गया, जिससे इसे शेर गढ़ नाम दिया गया।
- मुख्य विशेषताएं और संरचनाएं:
- सिंहद्वार (सिंह द्वार):
- अभेद्य प्राचीर के शीर्ष पर बना एक विशाल और भव्य द्वार।
- प्राचीर:
- पहाड़ी से चिपकी विशाल, अभेद्य प्राचीर, जो नीचे से स्पष्ट रूप से दिखाई देती है।
- आसपास का परिदृश्य:
- सामने एक और पहाड़ी दिखाई देती है।
- दुर्गावती नदी बीच से धीमी गति से बहती है।
- उत्तरी भाग से घाटियों, पहाड़ियों, हरियाली और दुर्गावती जलाशय परियोजना के मनोरम दृश्य दिखाई देते हैं।
- आंतरिक और सहायक संरचनाएँ:
- रानी पोखरा
- गार्ड हॉल
- एक भूमिगत गोलाकार कुआँ
- ज़नाना महल (दीवान-ए-ख़ास)
- कई भूमिगत कमरे
- सिंहद्वार (सिंह द्वार):
- सुंदर और सांस्कृतिक मूल्य:
- किला और उसके आस-पास एक अनोखी, छायादार घाटी और आश्चर्यजनक प्राकृतिक दृश्य प्रदान करते हैं।
15. करमचट बांध:
- स्थान और पर्यटन:
- रोहतास जिले में चेनारी के पास स्थित, सासाराम से लगभग 35 किलोमीटर दूर।
- एक लोकप्रिय पर्यटन स्थल, जो सूर्योदय और सूर्यास्त के दौरान मनमोहक प्राकृतिक दृश्य प्रस्तुत करता है।
- परियोजना पृष्ठभूमि:
- 1966 में भयंकर अकाल के बाद रोहतास के असिंचित मैदानों की सिंचाई के लिए दुर्गावती जलाशय परियोजना के हिस्से के रूप में शुरू किया गया।
- कृषि मंत्री एआर किदवई और सिंचाई मंत्री केएल राव द्वारा निरीक्षण और अनुमोदन किया गया।
- 10 जून 1976 को केंद्रीय कृषि मंत्री बाबू जगजीवन राम द्वारा आधारशिला रखी गई।
- सिंचाई मंत्री सच्चिदानंद सिंह की अगुआई में एक उच्च स्तरीय समिति ने 1977 में बाधाओं को दूर किया।
- दिसंबर 2011 तक देरी का सामना करना पड़ा जब सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने अनुमति दी, और 2012 की शुरुआत में काम फिर से शुरू हुआ।
- 2014 तक लगभग 1064 करोड़ रुपये खर्च किए गए।
- 15 अक्टूबर 2014 को तत्कालीन मुख्यमंत्री जीतन राम मांझी ने इसका उद्घाटन किया।
- बांध और जलाशय की विशिष्टताएँ:
- आयाम:
- ऊँचाई: 46.3 मीटर।
- लंबाई: 1615.40 मीटर।
- जल संग्रहण:
- कुल क्षमता: 287.7 मिलियन क्यूबिक मीटर।
- उपयोगी संग्रहण: 257.5 मिलियन क्यूबिक मीटर।
- पूर्ण जलाशय स्तर पर डूब क्षेत्र: 2337 हेक्टेयर।
- जल स्रोत:
- कैमूर पहाड़ियों में 627 वर्ग किलोमीटर क्षेत्र से वर्षा जल।
- आयाम:
- सिंचाई और नहर प्रणाली:
- कमांड क्षेत्र:
- सकल कमांड क्षेत्र (जीसीए): 40,131 हेक्टेयर।
- कृषि कमांड क्षेत्र (एसीसी): 33,467 हेक्टेयर।
- नहरें:
- पूर्व और पश्चिम की ओर दो मुख्य नहरें बनाई गई हैं:
- एक 34.08 किलोमीटर लंबी है।
- दूसरी 22.6 किलोमीटर लंबी है।
- पूर्व और पश्चिम की ओर दो मुख्य नहरें बनाई गई हैं:
- सिंचाई कवरेज:
- चेनारी, शिवसागर और सासाराम ब्लॉक (रोहतास जिला) में 11,695 हेक्टेयर।
- रामपुर, भभुआ, भगवानपुर, कुदरा, मोहनिया और दुर्गावती ब्लॉक (कैमूर जिला) में 5,572 हेक्टेयर।
- कुदरा वियर नहर द्वारा अतिरिक्त 16,200 हेक्टेयर की सिंचाई की गई।
- कमांड क्षेत्र:
- स्थानीय प्रभाव और रोजगार:
- परियोजना से प्रभावित 184 लोगों को रोजगार प्रदान किया गया।
- इस परियोजना से क्षेत्र में कृषि उत्पादकता में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि हुई है।
16. कैमूर वन्यजीव अभयारण्य:
- अवलोकन:
- बिहार का सबसे बड़ा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य, 1,504.96 वर्ग किमी (581.07 वर्ग मील) में फैला हुआ है।
- 1979 में स्थापित।
- कैमूर रेंज के पठारी परिदृश्य में स्थित, कैमूर और रोहतास जिलों के कुछ हिस्सों में फैला हुआ है।
- वन प्रकार और प्राकृतिक विशेषताएँ:
- विभिन्न प्रकार के वनों का प्रभुत्व:
- उष्णकटिबंधीय शुष्क मिश्रित पर्णपाती वन
- शुष्क साल वन
- बोसवेलिया वन
- शुष्क बांस ब्रेक
- अनेक मौसमी धाराओं और झरनों का घर; मानसून और सर्दियों के मौसम के दौरान सबसे अच्छा दौरा किया जाता है।
- उल्लेखनीय झरनों में शामिल हैं:
- करकट झरना
- मंझर कुंड
- धुआ कुंड
- तुतला भवानी झरना
- गीता घाट झरना
- कशिश झरना
- तेलहर
- विभिन्न प्रकार के वनों का प्रभुत्व:
- जल निकाय और बुनियादी ढाँचा:
- इसमें कई बाँध और झीलें हैं, जैसे:
- अनुपम झील
- करमचट बाँध
- कोहिरा बाँध
- जल स्रोत मुख्य रूप से कैमूर पहाड़ियों के एक क्षेत्र से वर्षा का पानी है।
- इसमें कई बाँध और झीलें हैं, जैसे:
- वनस्पति और जीव:
- जीव:
- बंगाल के बाघ, भारतीय तेंदुए, भारतीय सूअर, भारतीय पैंगोलिन, सुस्त भालू, सांभर हिरण, भारतीय मुंटजैक, चार सींग वाले मृग, चीतल, नीलगाय और विभिन्न सरीसृप, कीड़े और तितलियों का घर।
- पक्षी जीवन:
- निवासी पक्षियों की 70 से अधिक प्रजातियाँ; मध्य एशिया से प्रवासी पक्षियों के कारण सर्दियों में संख्या बढ़ जाती है।
- आम प्रजातियों में मोर, ग्रे पार्ट्रिज, बटेर, मालाबार पाइड हॉर्नबिल, स्वैलो, नाइटजार, ड्रोंगो, पैराडाइज फ्लाईकैचर, किंगफिशर, बुलबुल, मैना, कबूतर, ब्लू जे, उल्लू, बाज़, पतंग और विभिन्न चील शामिल हैं।
- प्रवासी पक्षियों में छोटे सफेद-सामने वाले हंस, फेरुगिनस बत्तख, बेयर के पोचर्ड बत्तख, छोटे और बड़े सहायक सारस, काली गर्दन वाले सारस और एशियाई ओपनबिल सारस शामिल हैं।
- जलीय जीवन और सरीसृप:
- रामेश्वर कुंड के पास अनुपम झील और कालीदह में मछलियाँ पाई जाती हैं।
- आम साँपों में कोबरा और क्रेट शामिल हैं; कभी-कभी अजगर भी देखे जाते हैं।
- जीव:
पुरातात्विक और ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- अभयारण्य क्षेत्र में रोहतासगढ़ किला और शेरगढ़ किला जैसी ऐतिहासिक संरचनाएँ भी हैं।
- इसमें कई मेगालिथ, प्रागैतिहासिक शैल चित्र और पत्थर के शिलालेख हैं, जो इस क्षेत्र की समृद्ध पुरातात्विक विरासत को उजागर करते हैं।
- बिहार सरकार ने इस अभयारण्य को टाइगर रिजर्व के रूप में विकसित करने की योजना बनाई है।
शैल चित्र, शैलचित्र और शिलालेख:
1. बरहमसिया मान की शैल चित्रकला:
- स्थान:
- सासाराम के बरहमसिया शैलाश्रय में स्थित है।
- विशेषताएँ:
- लाल रंग की शैल चित्रकला।
- इसमें दस बड़ी मानवरूपी आकृतियाँ फैली हुई भुजाओं के साथ दिखाई गई हैं।
- एक छवि में एक व्यक्ति तीर-धनुष का उपयोग करके हिरन का शिकार करता हुआ दिखाया गया है।
- शिकारी के साथ एक कुत्ते को दिखाया गया है।
2. घोरघाट घाटी मान की शैल चित्रकला:
- स्थान:
- सासाराम में घोरघाट घाटी में पाया गया।
- विशेषताएँ:
- दीवार पर आगे बढ़ते हुए छोटे मानव आकृतियों के समूह को प्रदर्शित करता है।
- इन आकृतियों के सामने एक जानवर का चित्र है, जिसमें उसका कंकाल दिखाई दे रहा है।
- यह एक दृश्य दर्शाता है जिसमें लोग जानवर का पीछा कर रहे हैं (संभवतः शिकार के लिए)।
3. तरवाखाल मान की शैल चित्रकला:
- स्थान:
- रोहतासगढ़ की कझिया पहाड़ी पर स्थित है।
- लगभग 150 मीटर आगे, “तरवाखाल मान पहाड़ी” नामक एक छोटी पहाड़ी पाई जाती है।
- विशेषताएँ:
- चट्टान आश्रय में बैठने की जगह (‘ढोके’ के उत्तरी और दक्षिणी किनारों पर) दिखाई देती है जहाँ चट्टान में एक पट्टी या पंक्ति बनी हुई है।
4. हथिया मान की शैलचित्र:
- नाम उत्पत्ति:
- हाथियों की नक्काशी के कारण इसे “हथिया मान” कहा जाता है।
- स्थान:
- दक्षिण-पश्चिम की ओर मुख करके सासाराम में एक शैल आश्रय में स्थित है।
- विशेषताएँ:
- ऐतिहासिक काल की कई नक्काशीदार आकृतियाँ हैं।
- पाँच हाथियों को दर्शाया गया है।
- अतिरिक्त नक्काशी की विशेषताएँ:
- खेल खेलने के लिए इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली आकृतियों के तीन सेट (“सोलह गोटिया”)।
- पारंपरिक खेल चौपड़ (चौसर) से जुड़ी दो अलग-अलग नक्काशी।
5. फुलवरिया शिलालेख:
- स्थान:
- रोहतास जिले के तिलौथू प्रखंड में एक पहाड़ी (~1500 फीट ऊंची) की चोटी पर स्थित फुलवरिया गांव में।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व:
- विभिन्न प्राचीन साक्ष्यों के कारण यह गांव पुरातात्विक दृष्टि से महत्वपूर्ण है।
- प्रताप धवल देव द्वारा शिलालेख:
- खयारवाल राजवंश का एक दस्तावेज, जिसमें इसकी पूरी वंशावली का खुलासा किया गया है।
- विक्रम संवत 1225 (कृष्ण पक्ष के बारहवें दिन) के वैशाख महीने में 27 मार्च 1169 ई. (गुरुवार) को लिखा गया।
- भाषा और लिपि:
- प्रारंभिक नागरी लिपि का उपयोग करते हुए संस्कृत में लिखा गया।
- विषयवस्तु:
- निचले हिस्से में संस्कृत में पाँच पंक्तियाँ हैं।
- नदी और पहाड़ पर सड़क के निर्माण और सीढ़ियों के निर्माण का उल्लेख है।
6. चंदन शहीद पहाड़ी पर अशोक का लघु शिलालेख:
- ऐतिहासिक संदर्भ:
- तीसरे मौर्य सम्राट अशोक (272-232 ईसा पूर्व) के शासनकाल का है।
- अशोक के शिलालेखों की श्रृंखला का एक हिस्सा जिसका उद्देश्य उनके धम्म का प्रसार करना था।
- स्थान:
- सासाराम में चंदन शहीद (आशिकपुर) पहाड़ी पर एक छोटी सी गुफा की उत्तरी दीवार पर पाया गया।
- पहाड़ी की चोटी से लगभग 30 फीट नीचे स्थित है।
- विशेषताएँ:
- शिलालेख ब्राह्मी लिपि में लिखा गया है, जिसकी भाषा पाली के बहुत करीब है।
- ब्रिटिश शासन के दौरान पुरातत्व संरक्षण विभाग द्वारा 1917 में संरक्षित किया गया।
परिवहन
- सड़क मार्ग:
- सड़क संपर्क:
- सासाराम ग्रांड ट्रंक रोड (NH-2) के माध्यम से अच्छी तरह से जुड़ा हुआ है।
- NH-19 और NH-119 रोहतास से होकर गुजरते हैं।
- बस सेवाएँ:
- सासाराम से आने-जाने के लिए नियमित सार्वजनिक और निजी बसें चलती हैं।
- बसें सासाराम को पटना, आरा, बिलासपुर, वाराणसी, नई दिल्ली, कोलकाता, बोकारो और जमशेदपुर जैसे प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ती हैं।
- बस स्टेशन: मुख्य शहर क्षेत्र में स्थित है।
- सड़क संपर्क:
- रेलवे:
- सासाराम जंक्शन – सासाराम भारतीय रेलवे के ग्रांड कॉर्ड सेक्शन (हावड़ा-गया-दिल्ली लाइन) पर स्थित है।
- सासाराम में और उसके आस-पास के प्रमुख रेलवे स्टेशन:
- डेहरी-ऑन-सोन (DOS)
- सासाराम जंक्शन (SSM)
- बिक्रमगंज (XBKJ)
- नियमित ट्रेनें: सासाराम को भारत भर के प्रमुख शहरों से जोड़ती हैं।
- वायुमार्ग:
- निकटतम हवाई अड्डा:
- गया अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डा (GAY) – सासाराम से लगभग 98 किमी।
- पटना हवाई अड्डा (PAT) – सासाराम से लगभग 157 किमी।
- वाराणसी हवाई अड्डा (VNS) – सासाराम से लगभग 120 किमी।
- नोट:
- पटना हवाई अड्डा प्रमुख शहरों के लिए नियमित उड़ानें प्रदान करता है और यदि सासाराम के लिए सीधी उड़ानें उपलब्ध नहीं हैं तो यह एक अच्छा विकल्प है.
रोहतास जिले के उल्लेखनीय व्यक्तित्व
1. जगजीवन राम:
- मूलभूत जानकारी:
- नाम: जगजीवन राम (बाबूजी के नाम से लोकप्रिय)
- जीवनकाल: 5 अप्रैल 1908 – 6 जुलाई 1986
- भारतीय स्वतंत्रता में भूमिका और प्रारंभिक कैरियर:
- सक्रिय स्वतंत्रता कार्यकर्ता और ग्रामीण मजदूर आंदोलन में प्रमुख व्यक्ति.
- दलित समानता के लिए लड़ने के लिए 1935 में अखिल भारतीय दलित वर्ग लीग की स्थापना की.
- 1937 में बिहार विधान सभा के लिए चुने गए।
- सरकार और नीति में योगदान:
- 1946 में जवाहरलाल नेहरू की अंतरिम सरकार में सबसे कम उम्र के मंत्री बने।
- भारत की संविधान सभा के सदस्य थे, जिन्होंने यह सुनिश्चित किया कि संविधान में सामाजिक न्याय निहित हो।
- भारत की पहली कैबिनेट में श्रम मंत्री के रूप में कार्य किया।
- लंबे समय तक मंत्री पद पर रहे:
- 30 से अधिक वर्षों तक भारतीय राष्ट्रीय कांग्रेस में विभिन्न मंत्री पद संभाले।
- दो कार्यकालों के दौरान केंद्रीय कृषि मंत्री के रूप में कार्य किया, हरित क्रांति में योगदान दिया और भारतीय कृषि को आधुनिक बनाया, विशेष रूप से 1974 के सूखे के दौरान।
- 1971 के भारत-पाक युद्ध के दौरान रक्षा मंत्री के रूप में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई, जिसके कारण बांग्लादेश का निर्माण हुआ।
- बाद में जनवरी 1979 से जुलाई 1979 तक भारत के उप प्रधानमंत्री के रूप में कार्य किया।
- राजनीतिक बदलाव:
- आपातकाल (1975-77) के दौरान प्रधानमंत्री इंदिरा गांधी का समर्थन किया।
- 1977 में कांग्रेस छोड़ दी, जनता पार्टी गठबंधन (कांग्रेस फॉर डेमोक्रेसी के माध्यम से) में शामिल हो गए, और बाद में 1981 में कांग्रेस (जे) का गठन किया।
- विरासत:
- अपनी मृत्यु के समय, वे अंतरिम सरकार के अंतिम जीवित मंत्री और भारत के पहले मंत्रिमंडल के अंतिम जीवित मूल सदस्य थे।
- सामाजिक न्याय, राष्ट्रीय विकास और हाशिए पर पड़े समुदायों के उत्थान के प्रति उनके समर्पण के लिए याद किया जाता है।
2. मीरा कुमार:
- मूलभूत जानकारी:
- जन्म: 31 मार्च 1945.
- एक भारतीय राजनीतिज्ञ और पूर्व राजनयिक।
- भारतीय राष्ट्रीय कांग्रेस की सदस्य।
- मंत्री पद की भूमिकाएँ:
- सामाजिक न्याय और अधिकारिता मंत्री (2004-2009)।
- 2009 में कुछ समय के लिए जल संसाधन मंत्री के रूप में कार्य किया।
- लोकसभा अध्यक्ष:
- 2009 से 2014 तक लोकसभा के 15वें अध्यक्ष के रूप में कार्य किया।
- इस पद को संभालने वाली पहली महिला बनीं।
- संसदीय कैरियर:
- अध्यक्ष के रूप में अपने कार्यकाल से पहले 8वीं, 11वीं, 12वीं और 14वीं लोकसभा के लिए चुनी गईं।
- राष्ट्रपति पद की उम्मीदवारी:
- 2017 में विपक्ष द्वारा संयुक्त राष्ट्रपति पद के उम्मीदवार के रूप में संयुक्त प्रगतिशील गठबंधन (UPA) द्वारा नामित।
- किसी प्रमुख राजनीतिक समूह द्वारा राष्ट्रपति पद के लिए नामित होने वाली दूसरी महिला बनीं।
- एनडीए उम्मीदवार रामनाथ कोविंद से राष्ट्रपति चुनाव हार गईं।
- नीलम संजीव रेड्डी (1969) और के. सुब्बा राव (1967) के बाद, हारने वाले उम्मीदवारों में उनका वोट शेयर तीसरा सबसे बड़ा माना जाता है।
3. छेदी पासवान:
- व्यक्तिगत पृष्ठभूमि:
- जन्म: 4 फरवरी 1956, सासाराम, बक्सर जिला, बिहार।
- परिवार: रामचंद्र पासवान और लक्ष्मीना देवी के पुत्र; प्रेमकली देवी से विवाहित, तीन बेटे और दो बेटियाँ।
- शिक्षा: पटना विश्वविद्यालय से श्रम और समाज कल्याण में एम.ए. की उपाधि प्राप्त की।
- राजनीतिक कैरियर और पार्टी संबद्धता:
- पूर्व भूमिकाएँ:
- 16वीं लोकसभा के सदस्य।
- बिहार विधानसभा के पूर्व सदस्य।
- पार्टी संबद्धता:
- अपने करियर के दौरान कई पार्टियों से जुड़े रहे हैं:
- जनता पार्टी (और उसका चरण सिंह गुट)
- पुनः एकजुट जनता दल
- बहुजन समाज पार्टी (बसपा)
- राष्ट्रवादी कांग्रेस पार्टी (राकांपा)
- लालू प्रसाद यादव की राजद
- नीतीश कुमार की जद (यू)
- 2014 से 2024 तक भारतीय जनता पार्टी (भाजपा) का प्रतिनिधित्व किया।
- अपने करियर के दौरान कई पार्टियों से जुड़े रहे हैं:
- पूर्व भूमिकाएँ:
चुनावी यात्रा:
- शुरुआती चुनाव:
- चरण सिंह गुट के सदस्य के रूप में चेनारी से 1980 का बिहार विधानसभा चुनाव हार गए।
- लोक दल का प्रतिनिधित्व करते हुए चेनारी से विधायक चुने गए (1985-1989); युवा-लोक-दल के महासचिव (1987-1989) के रूप में भी कार्य किया।
- लोकसभा चुनाव:
- 1989 और 1991 में जनता दल के उम्मीदवार के रूप में सासाराम से लोकसभा के लिए चुने गए, दोनों मौकों पर मीरा कुमार को हराया।
- 1996 का लोकसभा चुनाव मुनि लाल (भाजपा) से हार गए।
- 1998 (राकांपा के रूप में) और 1999 (बसपा के रूप में) में सासाराम से लोकसभा चुनाव भी हार गए।
- बाद में राज्य चुनाव:
- राजद के सदस्य के रूप में चेनारी (2000-2005) से बिहार विधानसभा के लिए चुने गए।
- जद(यू) में शामिल हुए; फरवरी 2005 में मोहनिया से हार गए लेकिन अक्टूबर 2005 और फिर 2010 में मोहनिया से जीते।
- भाजपा में दलबदल और हालिया विवाद:
- पार्टी नेता नीतीश कुमार पर तानाशाही तरीके से काम करने का आरोप लगाने के बाद 2014 में जद(यू) से भाजपा में शामिल हो गए।
- 2014 में सासाराम-लोकसभा सीट जीती, लेकिन बाद में पटना उच्च न्यायालय ने अपने हलफनामे में लंबित आपराधिक मामलों का खुलासा करने में विफल रहने के कारण उनकी जीत को रद्द कर दिया।
- हालाँकि सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने आदेश पर रोक लगा दी, लेकिन उनके मतदान के अधिकार बहाल नहीं किए गए, जिससे उन्हें 2017 के राष्ट्रपति चुनावों में भाग लेने से रोक दिया गया।
4. मुरारी प्रसाद गौतम:
- मूल जानकारी:
- जन्म: 1 मार्च 1980
- पेशा: शिक्षक
- पृष्ठभूमि और प्रारंभिक कैरियर:
- एक शिक्षक के रूप में अपनी पेशेवर यात्रा शुरू की, जिसने सार्वजनिक सेवा के लिए उनके जमीनी स्तर के दृष्टिकोण को आकार देने में मदद की।
- शिक्षा में उनकी पृष्ठभूमि सामुदायिक सशक्तिकरण और स्थानीय विकास पर उनके ध्यान को प्रभावित करती है।
- राजनीतिक भूमिकाएँ और योगदान:
- 16 अगस्त 2022 से 28 जनवरी 2024 तक बिहार में पंचायती राज मंत्री के रूप में कार्य किया।
- चेनारी निर्वाचन क्षेत्र का प्रतिनिधित्व करने वाले बिहार विधानसभा के सदस्य के रूप में, उन्होंने ग्रामीण बुनियादी ढाँचे को बढ़ाने और स्थानीय शासन को मजबूत करने के लिए काम किया।
- अपने कार्यकाल के दौरान, वे विभिन्न पहलों में शामिल रहे, जिनका उद्देश्य था:
- प्रशासनिक कार्यों का विकेंद्रीकरण।
- पंचायती संस्थाओं में पारदर्शिता और जवाबदेही बढ़ाना।
- जमीनी स्तर पर सार्वजनिक सेवाओं की डिलीवरी में सुधार करना।
- पार्टी संबद्धता और परिवर्तन:
- आम चुनावों से पहले 28 फरवरी 2024 को भारतीय जनता पार्टी (भाजपा) में शामिल हुए।
- यह रणनीतिक कदम स्थानीय शासन में उनके व्यापक अनुभव को भाजपा के विकासात्मक एजेंडे के साथ जोड़ता है।
- प्रभाव और भविष्य की संभावनाएँ:
- अपने जमीनी दृष्टिकोण और समुदाय-संचालित विकास पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने के लिए जाने जाते हैं।
- शिक्षक से एक प्रमुख राजनीतिक भूमिका में उनके परिवर्तन को इस क्षेत्र में अनुकरणीय माना जाता है।
- चुनावों के करीब आने पर भाजपा के ढांचे के भीतर ग्रामीण और कृषि नीतियों को आकार देने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाने की उम्मीद है।
चुनौतियाँ और मुद्दे
- अवैध पत्थर खनन – अनियमित उत्खनन के कारण पर्यावरण का क्षरण।
- औद्योगिक विकास की आवश्यकता – बड़े पैमाने पर उद्योगों और रोजगार के अवसरों की कमी।
- बुनियादी ढांचे का विकास – बेहतर सड़कें, अस्पताल और शिक्षा सुविधाओं की आवश्यकता।
- बाढ़ और जल प्रबंधन – कुछ क्षेत्रों में बाढ़ और सूखे की समस्याएँ हैं।
- बेरोज़गारी – कई युवा नौकरी के लिए दूसरे राज्यों में पलायन करते हैं।
निष्कर्ष
रोहतास बिहार का एक ऐतिहासिक और भौगोलिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण जिला है, जो विरासत, प्राकृतिक सुंदरता और सांस्कृतिक विविधता से समृद्ध है। रोहतास किला और शेरशाह सूरी का मकबरा इसे बिहार के शीर्ष पर्यटक आकर्षणों में से एक बनाते हैं। बेहतर औद्योगिक विकास, शिक्षा और बुनियादी ढाँचे के साथ, रोहतास में राज्य में एक प्रमुख आर्थिक और पर्यटन केंद्र बनने की क्षमता है।
क्या आप बिहार के किसी विशेष विषय के बारे में अधिक जानकारी चाहते हैं? नीचे टिप्पणी करें 😊
पदानुक्रमिक संरचना: बिहार का विस्तृत रोडमैप
बिहार में प्रमंडल और उसके जिलों का विवरण
| DEPARTMENT | TOLL FREE HELPLINE NUMBER |
| Police | 100 |
| Fire Service | 101 |
| Ambulance | 102 |
| Indian Railway General Enquiry | 139 |
| Election Commission Of India | 1950 |
| Women Helpline | 1091/ 9771468012 |
| Child HelpLine | 1098 |
| Control Room | 06156-224601 |
| HIV/AIDS Helpline Number | 1097 |
| Electricity | 1912 |
Important Links
𝕋𝕙𝕒𝕟𝕜 𝕐𝕠𝕦 𝔽𝕠𝕣 𝕍𝕚𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕚𝕟𝕘 𝕆𝕦𝕣 𝕎𝕖𝕓𝕤𝕚𝕥𝕖𝕤 🙂

4 thoughts on “Rohtas District: A Special Land of Forts, Nature & Heritage”